Overview of Chemical Reactor Design and Operation
Chemical reactor design involves studying the rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions, as well as the design of reactors for these reactions on a commercial scale. This field combines principles from thermodynamics, chemical kinetics, fluid mechanics, mass transfer, heat transfer, and economics to ensure the efficient operation of chemical reactors. Performance equations are crucial in predicting reactor behavior, considering factors like input materials, kinetics, and contacting patterns. Reactor design also involves developing appropriate performance equations based on reaction types and understanding reaction rates.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chemical Reactor Design- CHE 222 The field that studies the rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions and the design of the reactors in which they take place Prof. Dr. Asma abd el- sattar Professor of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering - Minia University
Contact Information Professor asma abdelsattar asmaabdelsattar11@yahoo.com Assistant Lecturer Eng. Rasha Hussien engchemical799@gmail.com 3
Text Book Chemical Reaction Engineering Third Edition Octave Levenspiel Department of Chemical Engineering Minia University 4
Overview of Chemical Reactor Design Typical chemical process Chemical reaction engineering (or reactor design) is the engineering practice concerned with the exploitation of chemical reactions on a commercial scale. Its goal is the successful design and operation of chemical reactors. Thermodynamics Chemicalkinetics Fluidmechanics Masstransfer Heattransfer Economics 4
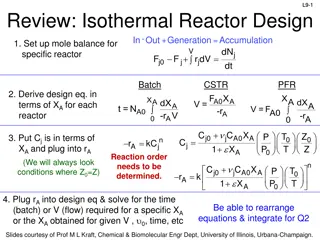
Overview of Chemical Reactor Design Performance equation relates input to output Input Output Contacting pattern or how materials flow through and contact each other in the reactor, how early or late they mix, their clumpiness or state of aggregation. By their very nature some materials are very clumpy, for instance, solids and noncoalescing liquiddroplets. Kinetics or how fast things happen. If very fast, then equilibrium tells what will leave the reactor. If not so fast, then the rate of chemical reaction, andmaybe heat and mass transfer too, will determine what willhappen. Information needed to predict what a reactor cando Output = f [input, kinetics, contacting] (1) 5
Overview of Chemical Reactor Design Develop appropriate performance equations by reactiontypes Classification of chemical reactions useful in reactor design It depends on how we choose to treat them, and this in turn depends on which description we think is more useful. 6
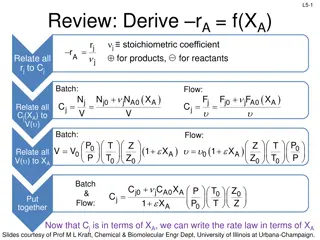
Overview of Chemical Reactor Design Reaction rate is the keyissue If the rate of change in number of moles of component i due to reaction is dNi/dt, the rate of reaction is defined as follows. Based on unit volume of reacting fluid, (2) 1 ??? ???? ? ?????? (???????? ?????)(????) ? = = ? ?? Based on unit mass of solid in fluid-solid systems, 1 ??? ???? ? ?????? (???? ?? ?????)(????) (3) ? = = ? ?? 7
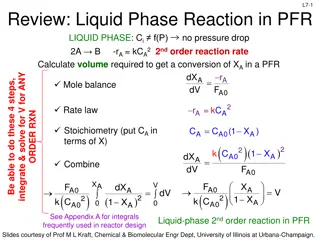
Overview of Chemical Reactor Design Reaction rate is the keyissue Based on unit interfacial surface in two-fluid systems or based on unit surface of solid in gas-solid systems, 1??? =? ??=(???????)(????) ???? ? ?????? (4) ? Based on unit volume of solid in gas-solid systems, ???? ? ?????? = (???????? ?????)(????) =1 ?? ???? (5) ? Based on unit volume of reactor, if different from the rate based on unit volume of fluid, ???? ? ?????? =1 ?? ???? = (6) ?? (???????? ???????)(????) 8
Overview of Chemical Reactor Design Relationship between thesedefinitions: Variables Affecting the Rate ofReaction In homogeneous systems the temperature, pressure, and composition are obvious variables. Heat and mass transfer may play important roles in determining the rates of heterogeneous reactions. 9
Overview of Chemical Reactor Design Broad classification of reactortypes (a) The batch reactor. (b) The steady-state flow reactor. (c), (d), and (e) Various forms of the semibatch reactor 10
Overview of Chemical Reactor Design Broad classification of reactortypes Ideal for small-scale experimental studies on reaction kinetics or small amounts of material are to be treated industrially. Batch Ideal for industrial purposes when large quantity of materials is to be processed and when the rate of reaction is fairly high to extremely high. Good product quality control can be obtai- ned (oil industry). Steady-state flow It offers good control of reaction speed because the reaction proceeds as reactants are added. It was used from the calor- imetric titrations in the laboratory to the large open hearth furnaces for steel production. Semibatch 11
Overview of Chemical Reactor Design Batch Reactor FlowReactor 12