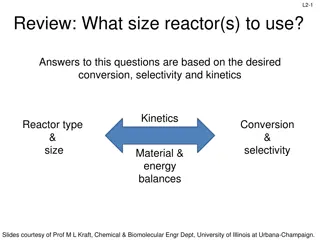
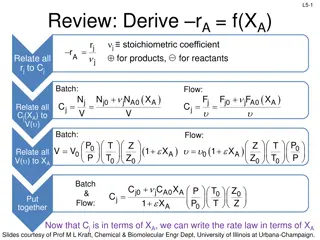
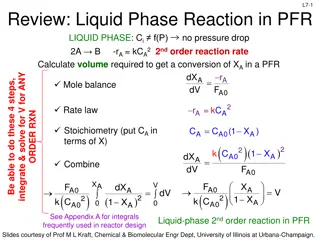
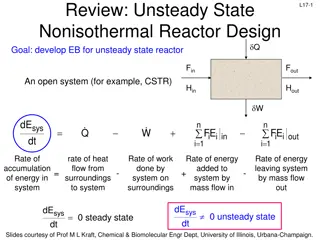
Advanced Burner Reactor Concept and Subcritical SABR Design
Discusses the rationale behind fusion-fission hybrid fast burner reactors, focusing on the SABR concept for spent nuclear fuel transmutation. The SABR design aims to address challenges in nuclear power generation, waste disposal, and fuel efficiency by utilizing a subcritical advanced burner reactor with fusion neutron source. This approach offers advantages such as increased reactivity margin, reduced fuel reprocessing steps, and optimized fuel utilization.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The SABR TRU The SABR TRU- -Zr Zr Fuel, Modular Sodium Fuel, Modular Sodium- -Pool Transmutation Reactor Concept Transmutation Reactor Concept W. M. Stacey, A. T. Bopp, J W. M. Stacey, A. T. Bopp, J- -P. Floyd, M. D. Hill, A. P. Moore, B. Petrovic, P. Floyd, M. D. Hill, A. P. Moore, B. Petrovic, C. M. Sommer, C. L. Stewart and T. M. Wilks C. M. Sommer, C. L. Stewart and T. M. Wilks Nuclear & Radiological Engineering Program Seminar Nuclear & Radiological Engineering Program Seminar Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA 30332 USA Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA 30332 USA September 22, 2016 September 22, 2016 The rationale for fusion-fission hybrid fast burner reactors is discussed. The updated Georgia Tech design concept of the SABR fusion-fission hybrid spent nuclear fuel transmutation reactor and supporting analyses are summarized. SABR is based on tokamak physics and technology that will be prototyped in ITER and fast reactor physics and technology proposed for the Integral Fast Reactor and the PRISM Reactor, which has been prototyped in EBR-II. Introduction of SABRs in a 1-to-3 power ratio with LWRs would reduce the required spent nuclear fuel HLWR capacity by a factor of 10 to 100. Pool
THE RATIONALE FOR A SUBCRITICAL ADVANCED BURNER REACTOR (SABR) THE RATIONALE FOR A SUBCRITICAL ADVANCED BURNER REACTOR (SABR) 1. Nuclear power is the only technically credible option for carbon-free electric power on the scale needed to impact climate change, at least for the first half of the present century. The major technical problem now confronting the widespread expansion of nuclear power is disposal of the extremely long half-life transuranics (TRU) in spent nuclear fuel (SNF) in high-level radioactive waste repositories (HLWRs) that can be secured for 105-106yrs . TRU can be fissioned, much more readily in a fast than a thermal neutron spectrum reactor, to yield energy and short half-life fission products (FPs), most which only need to be stored in secured HLWRs for 10-100 years. Reprocessing LWR SNF to separate TRU from the remaining U and FP for use as fuel in advanced fast burner reactors (ABRs) would reduce the required HLWR capacity for nuclear power to that needed to store the long-lived FPs and trace amounts of TRU due to inefficiencies in separation, at least by a factor of 10. (This means e.g. that the present level of nuclear power in the USA would require a new Yucca Mntn. every 300 years instead of every 30 years.) 2. 3. 4.
Rationale (cont.) 5. Subcritical operation of ABRs with a fusion neutron source (SABR) would have certain advantages: a) The reactivity margin of error to a prompt critical power excursion in a critical reactor is the delayed neutron fraction, k= , which is about 0.002 for TRU, as compared to about 0.006 for U. dictate that a critical ABR be only partially fueled with TRU (maybe 20%). In a SABR the reactivity margin of error to a prompt critical power excursion is ksub> 0.03 >> , so a SABR could be fueled 100% with TRU; and b) Since the power level (fission transmutation rate) can be maintained constant as the fuel depletes in a SABR by increasing the neutron source strength the fuel can remain in the reactor until it reaches the radiation damage limit, thereby minimizing the number of fuel reprocessing steps and the trace amount of TRU included with the FPs that go to the HLWR. On the other hand, in a critical reactor additional reactivity must be built into the fuel to offset the fuel depletion or the fuel must be removed before reaching the radiation damage limit. Prudence would probably
Rationale (cont. 2) 6. The fission physics and technology for a SABR based on: a) a pool- type Na-cooled, TRU-Zr metal fuel has been prototyped by the EBR-2 program in the USA; and the physics and technology based on b) a Na- cooled TRU-oxide fuel has been prototyped in many countries. 7. In the pyro-processing fuel cycle that would be used with the TRU-Zr fuel all the TRU (Pu, Np, Am, Te) is separated from the FPs as a single aggregate metal the Pu is never separated from the other TRU which greatly reduces any proliferation risk.
SABR Plasma Performance & Magnet System Will be Prototyped by ITER Plasma Major radius Plasma radius Elongation Toroidal magnetic field (on axis) Plasma current Inductive current startup Non-inductivecurrent drive Bootstrapcurrent fraction Heating & current-drive power Confinementfactor H98 Normalized Safety factorat 95% flux surface Max. and BOL fusion power Max. fusion neutron source Fusion gain (Qp=Pfusion/Pextheat) 4.0m 1.2m 1.5 5.6T 10 MA 6.0 MA 4.5 MA 0.55 110 MW (70 EC, 40LH) 1.2 3.2% 3.0 500 MW and 233 MW 1.8x1020n/s 4.6 N
SABR Modular Sodium-Pool Design Fuel Assembly Based on ANL IFR & GE S-PRISM Designs Using ANL 40Zr-10Am-10Np-40Pu TRU Fuel, Including a 3 mm SiC FCI to Reduce MHD Sodium Pool Number of pools Mass of fuel per pool Mass of Na per pool Power per pool Mass flow rate per pool No. of pumps per pool Pumping power / pool 10 1510.4 kg 22,067 kg 300 MW 1669 kg/s 2 20 MW
REFUELING REFUELING Rotate Pool Modules to Locations 1 and 6, Extract in Transport Cask and Remove to Hot Cell
SABR 4 SABR 4- -Batch Fuel Cycle Batch Fuel Cycle Max. Max. keff keff =0.973 at BOL. =0.973 at BOL. Pfus Pfus=233MWth BOL < 500 =233MWth BOL < 500 MWth MWthMax. Max. A SABR (@ 75% Availability & 200 dpa fuel residence) Can Burn All the TRU (Pu+MA) Produced Annually in 3, 1000MWe LWRs or All the MA Produced Annually in 25, 1000MWe LWRs , and Can Reduce the Needed HLWR Capacity by a Factor of 10 to 100.
Sodium Sodium Pool Parameters Pool Parameters Sodium Pool Number of modular pools Mass of fuel per pool Mass of Na per pool Power per pool Power Peaking Mass flow rate per pool Number of EM pumps per pool Pumping power per pool Core Inlet/Outlet temperatures Fuel Max Temp/Max Allowable Temp Clab Max Temp/Max Allowable Temp Coolant Max Temp/Max Allowable Temp 10 1510.4 kg 22,067 kg 300 MW 1.27 1669 kg/s 2 20 MW 628 K/769 K 1014 K/1200 K 814 K/973 K 787 K/1156K
TRITIUM (SABR IS MARGINALLY TRITIUM SELF-SUFFICIENT) SABR will burn 10-15 kg T annually. 8 Modular Li4SiO4 Blankets, Na-cooled. Blanket temperature window 325<T<925 C readily achieved. TBR = 1.12 200 dpa rad damage limit on cladding limits fuel residence to 700 days. Time-dependent simulation of plasma-blankets-processing-storage systems T inventories indicates T self-sufficiency for annual refueling, allowing for decay during 90 days down-time for refueling.
SHIELDING (SABR MEETS 30FPY DESIGN OBJECTIVE) Radiation Limit Value Units 1 x 109 Insulation Dosage rads Nuclear Heating Rate 1.0 5.0 mW/cc 1.0 x 1019 n/cm2 Neutron fluence (>0.1MeV) Copper Stabilizer 1.2 n m Resistivity
DYNAMIC 1. A dynamic global plasma model (particle & energy balance edge physics--boundary region/divertor--wall recycling 2D neutral transport) is being developed to study edge phenomena that would increase plasma energy loss in response to a temperature increase in order to investigate passive burn 2. A 10-node neutron dynamics and heat removal dynamics model is being developed to investigate the coupled dynamics of the 10 sodium pool reactors. Doppler, Na-voiding, fuel expansion and bowing, and core expansion effects are being modeled. SAFETY ANALYSES (in progress) control of plasma power excursions. Top view
ECONOMIC ANALYSIS ECONOMIC ANALYSIS (in progress) There are significant challenges in assessing the economic viability of a potential SABR implementation. To reduce these complex considerations to a single number, the Levelized Cost of Electricity-LCOE-(current price of electricity per kilowatt-hour, adjusted for inflation, which would offset all costs and provide a reasonable return to investors). It is not feasible at this time to estimate the cost of a SABR and its prorated share of the associated fuel processing and re-fabrication facilities a SABR+ cost . Instead, we are determining a break-even SABR+ cost as the true LCOE of nuclear power with direct burial of SNF in HLWRs. We will then determine the break-even SABR+ construction cost foreach SABR and its prorated share of the associated reprocessing and fuel fabrication facilities. ISSUE: If Pu is separated during reprocessing and used as fuel in critical fast reactors to produce additional electricity, the LCOE for the SABR scenario can be reduced; however this would mitigate the non-proliferation aspect of the reference SABR fuel cycle in which the TRU and the Pu are processed as an aggregate metal.
SUMMARY SUMMARY SABR FISSION PHYSICS & TECHNOLOGY HAS BEEN PROTOTYPED BY EBR-2. SABR FUSION PHYSICS & TECHNOLOGY WILL BE PROTOTYPED BY ITER. SABR USES THE ITER MAGNET SYSTEM AND THE ITER FIRST-WALL AND DIVERTOR SYSTEMS MODIFIED FOR NA-COOLANT. MODULAR REACTOR DESIGN ALLOWS REFUELING OF FISSION REACTOR LOCATED WITHIN MAGNET SYSTEM. SiC INSERTS IN FUEL ASSEMBLIES REDUCE MHD EFFECTS OF NA FLOWING IN MAGNETIC FIELDS. SABR IS TRITIUM SELF-SUFFICIENT. SABR IS ADEQUATELY SHIELDED TO ACHIEVE 30 FPY. SABRS CAN REDUCE THE HLWR CAPACITY NEEDED FOR NUCLEAR POWER BY A FACTOR OF 10-100. 1 SABR CAN BURN i) THE ANNUAL TRU PRODUCTION OF 3, 1000MWE LWRS OR ii) THE ANNUAL MINOR ACTINIDE PRODUCTION OF 25, 1000MWE LWRS. THE POSSIBILITY OF THE PASSIVE SAFETY OF SABR FISSION & FUSION SYSTEMS IS BEING INVESTIGATED. THE BREAK-EVEN COST OF SABR + FUEL REPROCESSING/RE-FABRICATION FACILITIES IS BEING EVALUATED BY EQUATING THE LCOEs FOR NUCLEAR POWER WITH THE SABR BURN OPTION AND WITH THE DIRECT BURIAL OF SNF IN HLWRs.