Understanding Amines: Structure, Properties, and Uses
Amines are derivatives of ammonia with alkyl or aryl groups replacing hydrogen atoms, making them more basic due to the presence of an unshared electron pair on the nitrogen atom. This summary covers the order of basicity, key compounds like Ethylene Diamine and Amphetamine, as well as their structures, properties, and uses in various applications such as pharmaceuticals and chemical intermediates.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
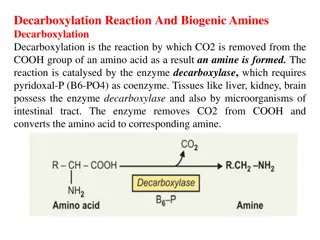
AMINES: Amines are derivative of ammonia, in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by a alkyl or aryl substituents. Amines are more basic than ammonia due to the presence of unshared electron pair on nitrogen atom THE ORDER OF BASICITY Tertiary amines- Secondary- Primary amine H H RRRN: RRN: RN: H Trimethyl amine Dimethyl amine; Methyl amine Structure and uses of Official compounds 1. Ethylene Diamine 2. Ethanolamine 3. Amphetamine
1. ETHYLENE DIAMINE (hydrate) MF:C2H8N2 H2O.; MM: 78.12; BP:117 0C H2N-CH2CH2-NH2.H2O IUPAC: Ethylene-1,2-diamine mono hydrate It is prepared from ethylene dichloride + ammonia PROPERTIES: Colorless to yellow liquid with ammonical odour, alkaline corrosive and very irritating membrane , it is miscible with water and alcohol, soluble in chloroform USES: Pharmaceutical aid Ingredient in aminophylline injection and tablet IP (Used in brancho- dilator in asthma) to skin and mucous
2. ETHANOLAMINE (ETA, MEA: Mono Ethanol Amine) MF: C2 H7 NO MM:61.084 g/m BP:170 0C Structure: HO-CH2 CH2-NH2 Nomenclature: 2-Amino 1-ethanol properties: functional compound (OH&NH2) and It is a primary amine; Colorless, viscous liquid with odour similar to ammonia. Miscible with water Uses: preparation of detergent, emulsifier, polishes, Chemical intermediates, corrosion inhibitors; Also precursor for the preparation of ETHYLENE-DI-AMINE: HO-CH2 CH2-NH2+NH3-------2HN-CHE2 CH2-NH2+H2O
3. AMPHETAMINE(Adderall ) MF: C9 H13 N; MM: 135.21 g/m ; MP:11.3 0C;BP: 203 0C IUPAC: 1-phenylpropane-2-amine ; alpha-methylphenylethylamine Uses:. Amphetamine is a central nervous system stimulant. It is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder ADHD, narcolepsy, and obesity. Also to suppress appetite (anorexia). This drug produces addiction Dose: Initial oral dose, 5mg and up to 30mg daily in divided doses. Preparations: Tablet 10mg