Understanding Amines in Organic Chemistry
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia, with different classifications based on the number of attached organic groups. They play vital roles in various biological processes, such as metabolism and structure formation. Biogenic amines are essential for life processes in living organisms. Explore the chemistry and importance of amines in this informative content.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
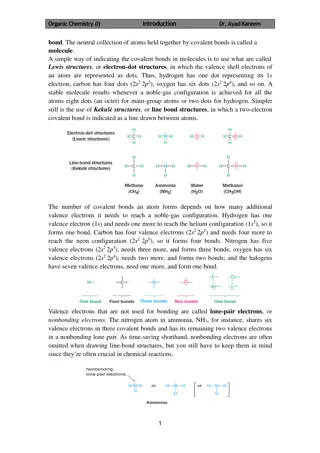
Organic Chemistry of Amines. Amines: Amines are a group of organic compounds that are derived from ammonia (NH ), compounds that has a nitrogen atom connected with two hydrogen atoms (-NH ), and a single group of some other atoms for example(R), are amines. Ammonia. NH3
Ammonia production occurs in all tissues of the body during the metabolism of a variety of compounds. Its produced by the metabolism of amino acids and other compounds which contain nitrogen.
Ammonia exists as ammonium ion (NH4+) is produced in our body mainly by the process of transamination biogenic amines. followed, by deamination, from Ammonium ion (NH4+)
Classification of Amines: Amines are classified by the number of organic compounds attached with the central nitrogen atom: 1-Primary amines compounds (RNH2) are water soluble, have one carbon atom attach to NH group & R" is an alkyl group. Primary amine RNH2
2-Secondary amines compounds (R2NH) have NH group, and two alkyl group R have been replaced in an ammonia molecule. Secondary amine R2NH
3-Tertiary amines compounds (RN) haven't NH group (water insoluble). Tertiary amine R N
4-Quaternary amines compounds (NR4+) polyatomic ions of the structure NR4+with R being alkyl . are positively charged Quaternary amine NR4+
The Biogenic Amines: Biogenic Amines are chemical compounds have at least one amine functional group in its molecular structure. Produced by living organisms or biological processes essential for maintaining the fundamental life processes.
They play an important role as source of nitrogen and precursor for the synthesis of hormones, alkaloids, nucleic acids, proteins, and amines.
Biogenic amine neurotransmitters. There are five established biogenic amine neurotransmitters: 1- Dopamine. 2- Noradrenaline. 3- Epinephrine. 4- Histamine. 5- Serotonin.
Dopamine: is an important chemical messenger involved in reward, motivation, memory, attention and even regulating body movements. Noradrenaline: is the main neurotransmitter of the sympathetic nervous system, is responsible for tonic and reflexive changes in cardiovascular tone.
Epinephrine : enters the bloodstream, then carried around the body to cells in various locations, to initiates several responses.And epinephrine s effects have a collective purpose to provide energy for muscles of the body.
Histamine: has been shown to have a key physiological role in the control of gastric acid secretion and a pathophysiological role in a range of allergic disorders. Histamine is an amine that is produced as part of a local immune response to cause inflammation.
Serotonin: is an important amine, that functions as one of the primary neurotransmitters, for the brain. It controls the feelings, of happiness, hunger, and helps in regulating the sleeping, and waking-up Cycle, of the brain. FOR SEEN ONLY
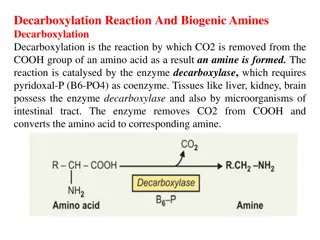
Transamination & Deamination Process: Transamination: Transamination is the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to a keto acid (amino acid without an amine group), thus creating a new amino acid and keto acid as shown below.The first step transamination in catabolizing, or breaking down, an amino acid is the removal of its amine group (-NH3). amino acid keto acid Transamination Deamination keto acid amino acid FOR SEEN ONLY
Deamination: Deamination is the removal of the amine group as ammonia (NH3), Keto acids and carbon skeletons are what remains after removed nitrogen group by deamination or transamination are used to synthesize nonessential amino acids.This transamination & deamination process are done in response to biological activity for cell need for a specific type of amino acid. amino acid keto acid Transamination Deamination keto acid amino acid
The fate of Biogenic amines : Biogenic amines (BAs) are formed by the breakdown of proteins (in foods), by metabolism process with the help of enzymes. They are formed and degraded as part of the normal metabolism of microorganisms, plants and animals, in which they have important physiological functions.
In humans, BAs are involved in brain activity, the regulation of body temperature and stomach PH. The fate of Biogenic amines: after food degradation they appear to be absorbed by intestinal microvilli's then converted directly into Amine (RNH )2, Hydrogen Peroxide H O , & Aldehyde RCHO, under normal conditions, but the toxic amine condition appear in blood can affect blood pressure, and body temperature due to high levels of the toxic Amine RCH NH in blood. intestinal microvilli's
Physiological role of amines: Biogenic amines BAs play a number of crucial roles in the physiology, and development of eukaryotic Cells. The most active example of Biogenic amines (BAs) is Histamine. It is a low molecular weight amine synthesized from L- Histidine, by L- Histidine decarboxylase enzyme only. Histamine
Histamine is present in many living tissues as a normal constituent of the body, and has multiple effects in different mammalian, and invertebrate organs. In humans, different concentrations are found in the brain, lung, stomach, small, large intestine, & uterus. Physiological role of Histamine in human body Toxicological effect of Histamine Act as neurotransmitter in central nervous system. Important for: Secretion of Pituitary Hormones. regulation of body Temperature Headache, swelling, diarrhea, blood pressure disorders.
Receptors Receptor is a cell present in the sense organs that is sensitive to specific stimuli. Example: The eyes have light receptors which can detect light and the ears have sound receptors which can detect sound. Receptor
Receptors are proteins or glycoprotein that bind signaling molecules hormones, antigens, drugs, or neurotransmitters, known as first messengers, or ligands,to transduct signal into the cell and finally cause a cellular response to initiate a signaling, or chemical response, to induces cell growth, division, and death or opens membrane channels. Receptor
There are three general categories of cell-surface receptors: 1- Ion channel-linked receptors. 2-G-protein-linked receptors. 3- Enzyme-linked receptors.
Hyperammonemia Amines are present in amino acids the building blocks of proteins, hemoglobin of the blood, & enzymes in living beings. Amino compounds reach the intestine, and by intestinal bacterial flora through the action of urease enzyme (helping in converting Amino groups to urea, Liver transform ammonia into urea. Any excess of ammonia in the blood cause Hyperammonemia.
Hyperammonemia produces non-specific symptoms such as: Decreased appetite. Lethargy. Rapid or heavy breathing. Irritability. Altered mental state.
You may be able to lower your risk of Hyperammonemia by: - Avoiding use of drugs, alcohol and tobacco. - Controlling your blood pressure. - Eating a low protein diet if you have a history of liver disease.
Application of Amine Compounds as Drugs: Ammonia production occurs in all body tissues during the metabolism of a variety of nitrogen compounds, so amines are extremely important functional groups in medicine, and are present, in many drugs (Medicines). There are many drugs can contain amines also, including over the counter cold tablets, nasal drops or sprays, and some pain relievers.
Amine compounds as Medicines. Their Function are: Demerol Commonly used as analgesics for relieving pain. Plays role in the production of some neurotransmitters in the human body that make the brain work properly. Choline Use: Emergency disinfection of drinking water. Required dosage: 8 ppm of iodine. Tetra methyl ammonium Iodide.