Understanding Furan and Thiophene: Structures, Properties, and Uses
Furan and Thiophene are important heterocyclic organic compounds with distinct structures and properties. Furan, a five-membered aromatic ring, is used in specialty chemical production and has unique physical properties. Thiophene, a sulfur-containing compound, finds applications in agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals due to its reactivity and versatility. Both compounds have specific preparation methods and exhibit different behaviors in various solvents. Understanding their structures, properties, and uses is essential in the field of chemistry.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Furan By Dr.S.V. Lamture Asso. Prof. &Head Dept of chemistry
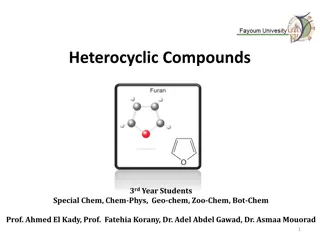
Furan (C4H4O) Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen. The class of compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans. Structurer Fig. Of Furan
Preparation of Furan Industrially, furan is manufactured by the palladium- catalyzed decarboxylation of furfural, or by the copper- catalyzed oxidation of 1,3-butadiene. In the laboratory, furan can be obtained from furfural by oxidation to furan-2-carboxylic acid, followed by decarboxylation. It can also be prepared directly by thermal decomposition of pentose-containing materials, cellulosic solids especially pine-wood.
Properties of Furan 1. Furan is a colourless volatile liquid. 2. It s boiling point is 31.4 C and melting point 85.6 C. 3. Furan having odor of chloroform. 4. It is insoluble in ether but soluble in most organic solvents. USESOF FURAN Furan is used as a starting point to other specialty chemicals.
3. Thiophene (C4H4S) Thiophene, also commonly called thiofuran, is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a flat five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. Structurer fig. of Thiophene Thiophene
Properties Of Thiophene At room temperature, thiophene is a colorless liquid with a mildly pleasant odor reminiscent of benzene. It s boiling point is 84 C and melting point -38 C. It is insoluble in water but freely soluble in ethanol, ether and acetone. The high reactivity of thiophene toward sulfonation is the basis for the separation of thiophene from benzene. Thiophene is much more reactive than benzene , thus thiophene undergoes the electrophilic substitution reactions like benzene , under moderate condition.
Uses of Thiophene Thiophenes are important heterocyclic compounds that are widely used as building blocks in many agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals. The benzene ring of a biologically active compound may often be replaced by a thiophene without loss of activity. This is seen in examples such as the NSAID lornoxicam, the thiophene analog of piroxicam.