EDF 3-Loop RPV Life Management Beyond 40 Years of Operation
Ageing management process is crucial for EDF's Long Term Operation policy, focusing on safety-related components like mechanical, electrical, and civil works. The process involves selecting structures/components prone to ageing mechanisms, identifying relevant ageing mechanisms, and implementing actions for proper management. This approach is applied to EDF's 3-loop RPV, particularly emphasizing thermal ageing of RPV outlet nozzles and irradiation ageing of RPV beltline region. The presentation at the 4th PLiM conference in Lyon also covers the application to 3-loop RPV of 900MWE fleet and emphasizes the materials, dimensions, and manufacturing features of the components.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
EDF 3-LOOP RPV LIFE MANAGEMENT BEYOND 40 YEARS OF OPERATION S. VIDARD (EDF / SEPTEN) - N. JARDIN (EDF / UNIE) - A.M. DONORE (EDF / R&D) 4thPLiM conference Lyon, october 2017
SUMMARY 1. MANAGEMENT OF NUCLEAR COMPONENTS AGEING 2. APPLICATION TO 3-LOOP RPV (900 MWE FLEET) 3. FOCUS ON TWO AGEING MECHANISMS THERMAL AGEING OF RPV OUTLET NOZZLES IRRADIATION AGEING OF RPV BELTLINE REGION 4. CONCLUSION | 2 EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017
MANAGEMENT OF NUCLEAR COMPONENTS AGEING Ageing management process is part of EDF Long Term Operation (LTO) policy The process applies to safety-related components (mechanical, electrical, civil works, ) whose failure would affect the plant safety summary : Selection of safety-related structures / components concerned by ageing mechanisms For each area of component / structure : identification of potentially relevant ageing mechanisms (depending on material, operating conditions, OPEX feedback, ) Actions demonstrating that each ageing mechanism is properly managed : in-service inspection / surveillance, repair / replacement programmes, supporting R&D ageing programmes Periodic reviews to include new OPEX feedback, additional results on ageing mechanisms, etc Process is of course applied to RPVs EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 3
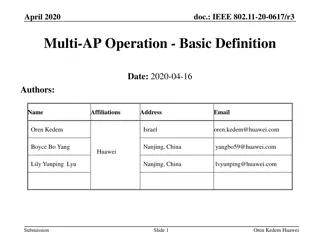
APPLICATION TO 3-LOOP RPV (900MWE FLEET) General presentation of component Main material = low alloy Cr-Ni-Mo steel (A508 cl.3 type) inner surface cladded with austenitic steel Other materials = base-nickel alloy (radial guides, CRDM adaptors, bottom-mounted instrumentation penetrations) Main dimensions : total weight = 350t / inner diameter = 4m / thickness in active core region = 200mm Main manufacturing features : Flanges, cylindrical shells, transition ring, nozzles : forged from solid ingots Circumferential welds Set-in nozzle welds Spherical shells : laminated plates or forged from solid ingots SS-DWM welds Welds of main body : all circumferential (or set-in for nozzles) + austenitic stainless steel DWMs Base-nickel alloy 600 Base-nickel alloy 690 EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 4
APPLICATION TO 3-LOOP RPV (900MWE FLEET) Identification of main relevant ageing / degradation mechanisms ? Component subject to cyclic loading conditions evaluation of fatigue risk Different types of materials and specific environmental conditions evaluation of corrosion risk : stress corrosion cracking, intergranular corrosion cracking, atmospheric corrosion, acid boric corrosion, Component operating at high temperature evaluation of thermal ageing Component partially affected by irradiation from reactor core evaluation of irradiation ageing (neutron flux) 29 [ageing mechanism / area] couples selected for analysis (covering 7 different mechanisms and 18 areas) EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 5
APPLICATION TO 3-LOOP RPV (900MWE FLEET) Conclusions on the identified couples ageing mechanisms / areas In most cases : Either the ageing mechanism on the area is not confirmed by experience, in-service inspection or R&D programmes Or the area can be repaired or replaced with reasonable difficulty The ageing mechanism is controlled For two specific cases (thermal ageing of outlet nozzles and irradiation ageing of beltline region) : The mechanism on the area is confirmed And the area cannot be repaired or replaced (or with excessive difficulty) The ageing mechanism requires specific attention EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 6
FOCUS ON TWO AGEING MECHANISMS Most significant damageing mode for outlet nozzles / beltline region : fast fracture Requirement for fast fracture analysis : loading of potential crack remains lower than material resistance at all times illustration Crack loading : depending on crack dimensions, thermohydraulic transient, (not affected by the considered ageing mechanisms) Resistance of un-aged material Crack loading / fracture toughness (MPA.m0.5) Resistance of aged material Effect of ageing mechanism shift of material resistance Material resistance : depending on metal temperature and a specific material property (RTNDT) Crack loading For both mechanisms, effect of ageing = RTNDT shift (embrittlement) 0 50 100 150 200 250 operating temperature domain EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 7
FOCUS ON TWO AGEING MECHANISMS THERMAL AGEING OF RPV OUTLET NOZZLES Why only the outlet nozzles ? of RPV (320 C instead of 285 C) operating temperature higher than the other areas Evaluation of embrittlement due to thermal ageing (RTNDT shift) : predictive model depending on material phosphorus content, operating temperature and time ( McLean model ) Embrittlement initially evaluated for 40 years of operation Demonstration of the model validity for 60 years of operation supporting R&D experimental programme (see paper # 094) Results : confirmation of the model s conservatism for 60 years operation update of mechanical properties uses as input data for mechanical calculation (fast fracture analyses) EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 8
FOCUS ON TWO AGEING MECHANISMS THERMAL AGEING OF RPV OUTLET NOZZLES Illustration of embrittlement predictions : 40 years vs. 60 years Effects of thermal ageing on RPV outlet nozzles (40years vs. 60 years) RTNDT shift for 60 years of operation (500000h eq. full power) Two concerned types of materials 45 Base metal 40 Heat affected zone 35 Base metal : limited additional RTNDT shift between 40y and 60y ( 3 C) 30 25 20 HAZ : additional shift between 40y and 60y 10 C 15 10 the impact of +20 years remains limited, limited phosphorus content Note : a minimum shift of 15 C is always considered in the mechanical analyses to account for possible strain ageing effects 5 thanks to 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 RTNDT shift for 40 years of operation (325000h eq. full power) EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 9
FOCUS ON TWO AGEING MECHANISMS THERMAL AGEING OF RPV OUTLET NOZZLES Other supporting actions for integrity demonstration of outlet nozzles Update of design analyses (RCC-M) Update of fast fracture analyses (RSE-M), with material properties at end of life (60 years) Fatigue evaluation (usage factor, crack growth) with 60 year cyclic loadings In-service inspection programme (based on previous inspection results and manufacturing conditions) during 10-year outages EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 10
FOCUS ON TWO AGEING MECHANISMS IRRADIATION AGEING OF RPV BELTLINE REGION Concerned area = beltline region Shells and weld(s) facing the core Fluence at end of life > 1018 neutron/cm Unirradiated Effect of irradiation = embrittlement (RTNDT shift) depending on : Chemical content of material (copper, phosphorus, nickel) Irradiated : Active core region ( 4,5m) Irradiation level (fluence, in neutron/cm ) Unirradiated Particular ageing mechanism, subject to mandatory requirements (including material properties) specific monitoring of EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 11
FOCUS ON TWO AGEING MECHANISMS IRRADIATION AGEING OF RPV BELTLINE REGION Key factor of irradiation ageing = neutron fluence Fluence = [neutron flux] x [time] the lower, the better R P N M L K J H G F E D C B A Limitation of fluence limitation of embrittlement 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 [time] parameter : the longer, the better need to reduce the neutron flux Two steps of improvement : 1st step in the 90s : modification of fuel assemblies pattern 40% reduction of maximum neutron flux R P N M L K J H G F E D C B A 2nd step at 4th 10-year outage : insertion of hafnium rods (neutron absorbers) in specific fuel assemblies up to 45% additional reduction expected Fuel assemblies equipped with Hafnium rods (4 x 3) Insertion of hafnium rods forecasted in all 900MWe RPVs EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 12
FOCUS ON TWO AGEING MECHANISMS IRRADIATION AGEING OF RPV BELTLINE REGION Illustration of efforts on neutron flux reduction Impact of neutron flux reduction Azimuthal neutron flux vs. core configuration (8-fold core symetry --> presentation of 45 azimuth) 10,0 10,0 8,0 Fluence - Initial design scenario 0 Fluence - 1st step : optimized pattern only 7,0 R P N M L K J H G F E D C B A 45 Fluence - 2nd step : optimized pattern + Hf rods Neutron flux (neutrons / cm /s) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 8,0 8,0 Neutron flux (1010n/cm /s , E > 1MeV) Fluence (neutrons / cm ) Neutron flux 6,0 Fuel pattern optimization (15y) 5,0 6,0 6,0 4,0 Hafnium rods insertion (40y) R P N M L K J H G F E D C B A 4,0 4,0 3,0 2,0 2,0 2,0 1,0 Standard pattern Optimized pattern Optimized pattern + Hf rods 0,0 0,0 0,0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 Time (years) Azimuth (degrees) Impact of optimizations on fluence reduction up to 40% compared to design scenario Impact of optimizations on neutron flux shape maximum effect around azimuth 0 EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 13
FOCUS ON TWO AGEING MECHANISMS IRRADIATION AGEING OF RPV BELTLINE REGION Monitoring of RPV material properties : Irradiation Surveillance Programme (ISP) Content / objectives of ISP for each RPV : capsule n 5 capsule n 2 Material specimens machined from acceptance rings / test coupons usually 6 capsules / RPV capsule n 1 Capsules periodically withdrawn to test materials measurement of irradiation effect on material properties (RTNDT shift) capsule n 6 capsule n 3 Capsules irradiated faster than RPV anticipated knowledge of materiel properties capsule n 4 Requirement : each capsule at least equivalent to RPV irradiation reached at 10-year outages (1st to 6th) EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 14
FOCUS ON TWO AGEING MECHANISMS IRRADIATION AGEING OF RPV BELTLINE REGION Results acquired so far : Range of fluence per capsule (CPY fleet) 14 Capsules 1 to 4 extracted, irradiation beyond 60 years already reached for several capsules In vessel capsules Extracted capsules 12 Fluence (1019n/cm , E > 1MeV) 10 Expected range of RPV fluence for 900MWe fleet (60 years of operation + Hf rods) 8 Incoming results for capsules 5 and 6 irradiation significantly greater than RPVs after 60 years of operation 6 4 Base metal (extracted) Base metal (in vessel) Weld (extracted) Weld (in vessel) 2 0 n 1 n 2 n 3 Capsule number n 4 n 5 n 6 EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 15
FOCUS ON TWO AGEING MECHANISMS IRRADIATION AGEING OF RPV BELTLINE REGION Use of ISP results : RTNDT shift measurements vs. fluence - ISP individual results (base metal) 100 Improvement of embrittlement model by fitting formula on ISP results (capsules 1 to 4) and experimental data Expected range of fluence for 900MWe fleet (60 years of operation + Hf rods) predictive 80 Embrittlement (RTNDTshift ( C)) Model scattering 60 Comparison of new capsules results with predictive model to check the material behaviour 40 20 Confirmation / improvement of embrittlement model at higher fluences with incoming results 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Fluence (1019neutrons / cm ) EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 16
FOCUS ON TWO AGEING MECHANISMS IRRADIATION AGEING OF RPV BELTLINE REGION Other supporting actions for integrity demonstration of nozzles Update of fast fracture analyses, with material properties at end of life (60 years) Fatigue evaluation (crack growth) with 60 year cyclic loadings Implementation of new methodologies (Warm Pre-Stressing, thermohydraulical models, ) supported by R&D programmes Complete in-service inspection of beltline region during 10-year outages with automated machine ( MIS ), with qualified NDT EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 17
CONCLUSION The ageing management process implemented by EDF as part of LTO policy, is applied to RPV and periodically reviewed Analysis of relevant ageing mechanisms for RPV shows that most of them are controlled through usual maintenance inspections policy, including adequate in-service Two mechanisms require particular attention, and are supported by specific actions : Thermal ageing (RPV nozzles), supported by R&D programme to provide adequate predictions of ageing mechanism on material properties for 60 years of operation Irradiation ageing (beltline region), supported by RPV-specific monitoring of material properties, and controlled by inserting hafnium rods to reduce neutron flux (starting from 4th10-year outages) The performed analyses and implemented actions provide good confidence for 3- loop RPV operation beyond 40 years EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 18
Thank you for your attention
APPENDICES 900MWe fleet = 34 plants RPV in French NPP Main Coolant System (MCS) Typical layout of MCS in French NPPs : Originally Westinghouse license 3 primary loops / Steam Generators / Main Coolant Pumps 1 pressurizer connected to Loop 1 through a surge line RPV located a the center of the MCS and containment building EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 20
APPENDICES EXAMPLES OF IDENTIFIED AGEING MECHANISMS Illustration on significant ageing mechanisms + preventive / corrective actions Fatigue of studs / nuts / flanges evaluation of usage factor and adequate in-service inspection SCC of CRDM adapters risk eliminated with RPV head replacement on all plants (use of alloy 690) Atmospheric stainless steel DWMs specific in-service inspection on repaired areas + risk modification of insulation corrosion of Thermal ageing of low-alloy steel relevant only on outlet nozzles (higher temperature), adequate inspection, supporting programme for ageing prediction, ageing effects included in integrity analyses in-service experimental eliminated by Irradiation ageing of low-alloy steel (shells and welds) in- service inspection of beltline region, surveillance programme of material properties, ageing effects included in integrity analyses SCC of bottom mounted penetrations (alloy 600) adequate inspection and development of repair process in-service EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 21
APPENDICES RPV MECHANICAL ANALYSES Design analyses : according to RCC-M volume B ( ASME class 1) + updated every 10 year (mandatory) Damageing modes : excessive deformation, plastic instability, progressive deformation, fatigue crack initiation and fast fracture Fast fracture (usually limiting damage for LTO) : In active core region (= fluence > 1018 n/cm at EOL) Out of active core region : all welds (including DWM), base metal of thick areas (flanges, nozzle shell, bottom transition ring), studs Applied requirements during operation : RSE-M + French Order 10th november 1999 Fast fracture analyses outside core region Typical extension of core region EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 22
APPENDICES RPV IN-SERVICE INSPECTION Inspection : during 10-year outages, mostly with an automated machine ( MIS ) Systematically inspected areas : UT : all welds of main body (+ RT / PT on DWMs) UT : base metal / weld in active core region Other inspected areas : UT : nozzles corners and inner surface, RPV head weld UT : nozzle shell (sampling) UT + eddy currents : bottom mounted instrumentation penetrations Eddy currents : studs and nuts, CRDM adapters (sampling) Inspected welds Inspected area of active core region Other inspected areas EDF 3-loop RPV life management beyond 40 years of operation | PLIM Lyon - October 2017 | 23