Managing Water Resources Data with HEC-DSSVue
Learn about managing gridded data in HEC-DSSVue, including how grids represent spatial data, storing data in DSS, naming conventions, tools for manipulation, and more. Explore the importance of grids in hydrologic modeling and the application of spatial data in HEC-HMS and HEC-RAS.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Water Resources Data Management with HEC-DSSVue Managing HEC-DSS Gridded Data
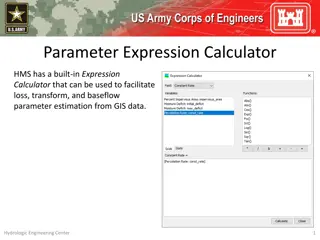
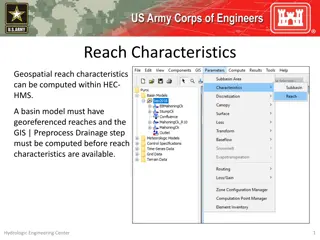
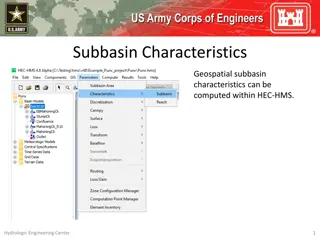
ObjectivesThis lecture should teach you How grids represent spatially distributed data Sources of gridded data How DSS stores data in grids Organization of grid data in DSS records Naming conventions for grids What tools are available for loading, viewing, and manipulating DSS grid data
Topics Why are there grids in DSS? NEXRAD radar and the modClark rainfall-runoff method The SHG grid indexing systems Storing grids in DSS Gory Details Naming Conventions The Grid Data toolkit Loading Grids Displaying grids Grouping grids into time series Calculating with grids
Gridded Meteorological Products 1990 2015 2020 1995 2005 2010 2000
Why are there grids in DSS? Reliable precipitation estimates are crucial to flood hydrograph analysis NEXRAD radar offers a potential for improvement over basin-average precipitation estimates from rain gages Use of grid methods for hydrologic modeling DSS should support data types used for hydrologic analysis and forecasting
Application of Spatial Data The inclusion of spatially distributed modeling methods in HEC-HMS and HEC-RAS require spatially distributed boundary conditions.
The Standard Hydrologic Grid (SHG) Based on USGS National Atlas Spatial Reference System (EPSG:5070) https://www.spatialreference.org/ref/sr-org/epsg-5070/html/ Albers Equal-Area Projection (handy for calculating volumes from depths) More commonly used for natural resource data than HRAP s polar stereographic Supports variable resolution (10, 20, 50 10km) Has a fixed size and positions of cells Still limited to 48-state applications Very little time-varying data natively in SHG
Standard Hydrologic Grid (SHG) SHG locations identified by cell indices For a given cell size, an index pair always refers to the same location Cell row and column numbers start at the origin of the coordinate system, so it s easy to convert cell numbers to northing and easting
Features for Grids in HEC-DSS Internally, DSS grid records contain Full coordinate system definition Position of row, column origin Interfaces to support SHG- like Grids based on UTM coordinates UTM Discretization in HEC- HMS Load UTM grids from various formats Interpolate UTM grids with HEC-HMS and HEC-MetVue UTM 39S Madagascar
Gridded Precipitation and Temperature Data Sources RFC River Forecast Center http://water.weather.gov/ahps/rfc/rfc.php https://www.hec.usace.army.mil/confluence/hmsdocs/hmsguides/en semble-analysis-simulations-in-hec-hms/applying-the-ensemble- compute-to-flood-forecasting Cumulus - https://cumulus.corps.cloud/ NCEP National Center for Environmental Predictions http://nomads.ncep.noaa.gov/
Example SNODAS grids from NOHRSC NOAA National Operational Hydrologic Remote Sensing Center (NOHRSC) SNOw Data Assimilation System (SNODAS) SWE Dept h Melt Cold Content
Gridded Data Sources https://www.hec.usace.army.mil/confluence/hmsdocs/hmsguides/working-with- gridded-boundary-condition-data/gridded-data-sources
Time Series Data Organization in DSS Header Units Data type Time offset (for Regular Time Series) Data Array Values Values & times (For Irregular Time Series) Array 90 3 3 3 40 120 140 190 Time Series
Grid Data Organization in DSS Header Units Data type Time (start & end) Location Data Array Values Like a regular time series, but at regular intervals in space Array 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Equivalent grid, array by rows from lower left cell 7 8 9 4 5 6 1 2 3
DSS Grid Header Contents (Highlights) Cell Size (in meters) Origin cell indices Number of columns Number of rows Coordinate system Position of origin cell Start time End time Data units Data type Data Statistics Data Compression method
Identifying a Grid by Pathname Parts A Part: Grid System (HRAP, SHG, UTM32S) B Part: Location C Part: Parameter (Precip, Temp) D Part: Start time E Part: End time F Part: Version (ABRFC, White River) (17JAN1996:0300) (17JAN1996:0400) (StageIII, model) Reference for C Part pathname for HEC-HMS - https://www.hec.usace.army.mil/confluence/hmsdocs /hmsum/4.11/shared-component-data/grid-data
Precipitation Grids in DSS Parameter (C part): PRECIPITATION Units: mm Data Type: PER-CUM (Period Cumulative) Time Reference: UTC (Not local time)
Examples Daily precipitation and temperature products from PRISM Hourly MRMS Forecast results NBM NAM
Grid Tools in DSS CWMS/HEC-RTS CAVI displays grids in sequence HEC-MetVue for Grid Display/Editing/Analysis, and Automated Processing. HEC-HMS for importing, processing, and creating HEC-DSSVue displays grids and metadata Methods available for scripting in DSSVue Extract sub-regions Mosaic grids together Simple math
DSS Grids in HEC Software A gridset is a sequence of grids Specified by Source file name or wildcard Pathname parts (A, B, C, F) Time step (difference between D & E parts) Allows many grid records to be managed as a single entity
CAVI Time Window and Animation Controls User-selected time window Sequence play (pseudo-animation) VCR-like controls
HEC-HMS Gridded Data Importer Purpose Streamline the process of converting various gridded dataset formats to HEC-DSS format for use within HEC-HMS. Supported Dataset Formats netCDF, HDF, GRIB, ASC, TIF, BIL, SNODAS, DSS Additional Features Project gridded data to SHG or UTM projections Clip to watershed boundary Set correct data units and type Examples provided - https://www.hec.usace.army.mil/confluence/hmsdocs /hmsguides/working-with-gridded-boundary- condition-data
HEC-HMS Gridded Data Importer Clip data to project extent Set projection Set target cell size Specify resampling method
HEC-HMS Gridded Data Importer Specify destination file and file path
HEC-HMS Gridded Data Tools Manipulate gridsets o Calculator (scale or convert data units) o Clipper (clip to watershed to reduce file size) o Grid to Point (compute subbasin time- series) o Normalizer (adjust one gridset to totals from another) o Sanitizer (remove unwanted data values) o Shifter (shift in time)
HEC-HMS Grid Interpolation Interpolation option creates gridded datasets using gage data and discretization defined in the basin model Interpolation methods: o Inverse distance o Inverse distance squared o Nearest neighbor o Bilinear Adjustment options: o Bias o Lapse rate