Madlen Mladenova: Talented Volleyball Player Seeking College Scholarship
Meet Madlen Mladenova, a skilled female outside hitter/opposite hitter with impressive volleyball achievements. Standing at 185 cm, this Bulgarian athlete is driven to pursue a degree in Kinesiology or Exercise Science while excelling in volleyball. With a strong passion for the sport and a commitme
0 views • 10 slides
Online Consumer Complaint Filing and Response Process in India
Learn how to file a consumer complaint online and write a response as an opposite party in Consumer Forums of India through the Edaakhil portal. Understand the steps for registration, login, and filing a response for approved complaints and responses. Discover how to search for cases and access case
4 views • 15 slides
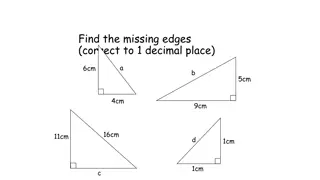
Trigonometry Essentials: Missing Edges, Angle Calculations & Triangle Identification
Explore a comprehensive guide on trigonometry covering calculating missing lengths, determining angles, labeling sides of triangles, and solving problems using trigonometry. Learn about hypotenuse, opposite side, adjacent side, and practical applications through examples and visual aids.
0 views • 40 slides
Understanding Newton's Third Law of Motion
Chapter 7 delves into Newton's Third Law, stating that every force has an equal and opposite force. The law describes the relationship between forces in an interaction - one force being the action force and the other the reaction force. These forces are equal in strength, opposite in direction, and
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Velocity vs. Speed in Physics
Velocity and speed are fundamental concepts in physics that describe how fast an object is moving and in what direction. While speed is a scalar quantity representing the rate of motion, velocity is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction. Constant velocity implies steady speed and
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Action and Reaction Forces in Physics
Explore the concept of action and reaction forces in physics through examples like a falling boulder and interactions between different masses. Understand how forces are equal and opposite, leading to accelerations based on mass and force interactions. Discover the relationship between Earth and the
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Debit and Credit in Accounting
Debit and credit are fundamental concepts in accounting that help record business transactions accurately. Debits increase assets or expenses and decrease liabilities or equity, while credits do the opposite. The rules of debit and credit ensure that accounting entries are balanced, with each transa
1 views • 8 slides
Understanding Absorption Costing and Overhead Absorption in Cost Accounting
Absorption costing is a method that includes direct costs and a fair share of production overhead costs in the cost of a product. Overhead absorption rate (OAR) is calculated using budgeted figures and can lead to over/under-absorption. Over-absorption occurs when absorbed overhead is more than actu
1 views • 23 slides
Theories of Electrolytic Dissociation and Ionization in Physical Chemistry
The theories of electrolytic dissociation by Adil Hamid and Arrhenius explain how electrolytes dissociate into ions in solution, leading to electrical conductivity. This process involves the migration of cations and anions towards opposite electrodes, affecting the conductivity of the electrolyte. T
1 views • 51 slides
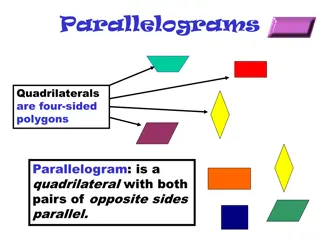
Understanding Parallelograms: Properties, Theorems, and Tests
Parallelograms are four-sided polygons with unique properties that include having both pairs of opposite sides parallel. Explore key theorems, tests, and properties of parallelograms such as opposite side and angle congruency, diagonal bisecting, and conditions for identifying a quadrilateral as a p
1 views • 19 slides
Understanding Buyback of Securities and Open Offer of Shares
Buyback of securities is a corporate action where a company repurchases its own shares from existing shareholders, opposite of a public issue. Common reasons include returning surplus cash to shareholders, improving return on equity, and enhancing earnings per share. Conditions for buy-back include
0 views • 32 slides
Understanding Decoders and Encoders in Digital Systems
Decoders and encoders are essential components in digital systems that convert input signals into specific output codes. Decoders, such as 1:2 and 2:4 decoders, translate n-bit input codewords into m-bit output codes, where m = 2^n. Encoders perform the opposite function, encoding multiple inputs in
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Acid-Base Titration in Chemistry
Acid-base titration is a quantitative technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base solution. By neutralizing the solution with the opposite component and reaching the equivalence point, students can calculate the concentration using stoichiometry principles. This method d
1 views • 24 slides
Understanding Antonyms: Types and Examples
Antonyms are words with opposite meanings, such as alive/dead, big/small, hot/cold. They are categorized as gradable or non-gradable based on their usage. Gradable antonyms can be compared, while non-gradable antonyms do not allow for comparison. The negative test helps identify non-gradable antonym
2 views • 34 slides
Understanding Newton's Third Law of Motion
Explore the concept of Newton's Third Law of Motion, which states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Discover examples illustrating this law in action and learn about inertia, unbalanced forces, and the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration according to Newto
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Circle Theorems and Equations of Circles
Explore circle theorems and equations of circles in geometry, including concepts like opposite angles in cyclic quadrilaterals, angles on a straight line, and important theorems like the perpendicular bisector of a chord passing through the center of a circle. Learn how to apply these theorems to fi
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Inflation, Deflation, and Stagflation in Economics
Inflation is the continuous increase in the general price level, leading to a loss of the money's value. This chapter explores the causes of inflation, including demand-pull and cost-push factors. Remedies such as monetary and fiscal policies are discussed to control inflation. Additionally, the con
0 views • 14 slides
Geometry Test Prep Questions
Prepare for your geometry test by reviewing essential questions on points, lines, planes, distances, and intersections. Use the provided images to practice concepts such as collinear points, intersecting lines, opposite rays, and more. Challenge yourself to solve distance problems without using form
0 views • 31 slides
Geometry Basics: Points, Lines, and Planes
Learn about the fundamental concepts in geometry such as points, lines, and planes, along with their characteristics and relationships. Explore undefined and defined terms, collinear and coplanar points, line segments, rays, and opposite rays.
3 views • 13 slides
Understanding Newton's Third Law of Motion
The Third Law of Motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This law is demonstrated through various examples in everyday life, such as pushing against a wall, jumping on a trampoline, or how rockets work. Momentum, the product of an object's mass and velocity, pla
0 views • 10 slides
A-29 Emergency Procedure - Erect Spins Revision 19
Recognize an erect spin as an oscillatory movement about the three aircraft axes with high and low speed AOA. Follow the Corrective Action Procedures (C.A.P.) of throttle idle, full opposite rudder direction, and stick neutral. When the spins stop, maintain rudder neutral, adjust throttle and stick
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding the Inverse Relationship of Addition and Subtraction
Learn about the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction through examples and visual aids. Practice writing inverse number sentences and understand how addition and subtraction are opposite operations that involve rearranging the same numbers in a different order.
3 views • 11 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's laws of motion, including the principles of inertia and dynamics, explain how objects move and interact with forces. The first law states that objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by a force, while the second law explains how a net force is required to change an object's vel
0 views • 21 slides
Exploring the Power of Adding "un" to Change Verbs and Adjectives
Discover how adding "un" to the beginning of words can change their meaning to the opposite, with examples of transforming verbs and adjectives. Practice acting out opposite words with friends and learn to give words an opposite meaning by adding "un.
0 views • 5 slides
Important Vocabulary for FCI Exam - Synonyms and Antonyms Practice
Enhance your vocabulary skills for the FCI exam with practice questions on synonyms and antonyms. Test your understanding of words like Embedded, Contemplate, and Disproportionate by finding similar or opposite meanings to improve your word knowledge.
0 views • 109 slides
Exploring Prefixes and Words with Opposite Meanings
Delve into the world of prefixes with "an-" and "anti-" meaning against or opposite. Learn about words like antonym, retrofit, retrospective, antibacterial, antidote, antacid, and more that showcase contrasting meanings or actions. Enhance your vocabulary and understanding of words through this enga
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Lexical Relations in Linguistics
Different types of lexical relations such as synonymy, antonyms, hyponymy, homophony, and homonymy play a crucial role in understanding the nuances of language. Synonyms have closely related meanings, antonyms have opposite meanings, while hyponymy and hypernymy show hierarchical relationships betwe
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Frames and Machines in Structural Analysis
Frames and machines are structural elements with multiforce members. Frames support loads while machines transmit and modify forces. To solve frame problems, isolate each member using a free-body diagram and apply equilibrium equations, considering both external and internal forces. Two-force member
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Commodity Hedging in Financial Markets
Commodity hedging involves mitigating risk associated with price fluctuations in raw materials by taking opposite positions in futures and physical markets. This strategy helps individuals and businesses safeguard against potential losses and ensure revenue certainty. An example with a wheat farmer
0 views • 10 slides
Unveiling Polarity with Polarity-Inducing Latent Semantic Analysis
Polarity-Inducing Latent Semantic Analysis (PILSA) introduces a novel vector space model that distinguishes antonyms from synonyms. By encoding polarity information, synonyms cluster closely while antonyms are positioned at opposite ends of a unit sphere. Existing models struggle with finer distinct
1 views • 29 slides
Understanding Foils in Literature and Media
A foil is a character in a story that contrasts with another character, often the protagonist, to highlight their qualities. It can be completely opposite or similar with a key difference. Foils are used to emphasize specific traits of the main character without being the antagonist. Examples of foi
0 views • 10 slides
Mathematics Bridging Course Highlights from Tseung Kwan O Catholic Primary School
In the Mathematics Bridging Course for the Secondary Curriculum at Tseung Kwan O Catholic Primary School, students are introduced to important terms related to directed numbers, such as positive and negative numbers, absolute value, and numerical comparisons. The course covers fundamental concepts l
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Lexical Relations in Language
Explore the concepts of synonymy, antonymy, hyponymy, and prototype in linguistics. Learn about words with closely related meanings (synonyms), opposite meanings (antonyms), inclusive meanings (hyponyms), and characteristic examples (prototypes) within lexical relations.
0 views • 12 slides
Lamiaceae (Labiatae) - The Fascinating Mint Family
The Lamiaceae family, commonly known as the Mint Family, comprises around 180 genera and 3500 species worldwide, with the Mediterranean region as its center of distribution. This family is characterized by bilabiate flowers, square stems, and recognition features such as opposite leaves and a minty
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Verbal Irony and Tone Through Examples
Verbal irony is the expression of words conveying the opposite of their literal meaning. It is not the same as lying and is used to emphasize a point. Tone plays a crucial role in conveying irony, as it can affect how the message is perceived. Sarcasm, though related, has a negative agenda of mockin
0 views • 7 slides
Tale of Patience and Short Temper: Ch.-san and Tanshichi
A story of patience and short temper unfolds between Ch.-san and Tanshichi, two friends with opposite personalities. Despite their differences, they share a strong bond and unique friendship. Tanshichi's impatience and Ch.-san's calm demeanor lead to amusing interactions and heartfelt moments as the
0 views • 56 slides
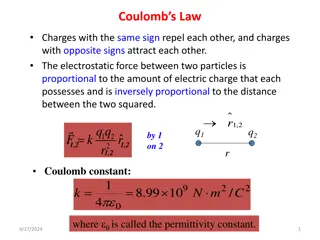
Understanding Coulomb's Law in Electrostatic Interactions
Coulomb's Law states that charges with the same sign repel each other, while charges with opposite signs attract. The strength of the electrostatic force between two particles is directly related to the amount of charge each possesses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between
0 views • 24 slides
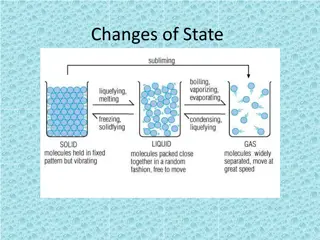
Understanding Changes of State in Matter
Changes of state in matter refer to the physical transitions that substances undergo, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, and condensation. These transitions involve the addition or removal of energy, impacting the movement of particles and their arrangement. Despite the transformations, the id
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion explain the relationship between forces and motion. The first law states that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a net force, while the second law describes how force is related to an object's mass and acceleration. The third law states that for every ac
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Real Numbers and Basic Arithmetic Operations in Algebra
Review essential concepts from the first chapter of "Intermediate Algebra" by Gustafson and Frisk. Learn about the classification of real numbers, graphical representations on the number line, intervals, arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of real number
0 views • 20 slides