Understanding Coulomb's Law in Electrostatic Interactions
Coulomb's Law states that charges with the same sign repel each other, while charges with opposite signs attract. The strength of the electrostatic force between two particles is directly related to the amount of charge each possesses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The law can be used to calculate forces between charges and understand interactions in the atomic level, such as between electrons and protons. Learn about polarization, induction, gravitational forces, and more in this comprehensive guide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
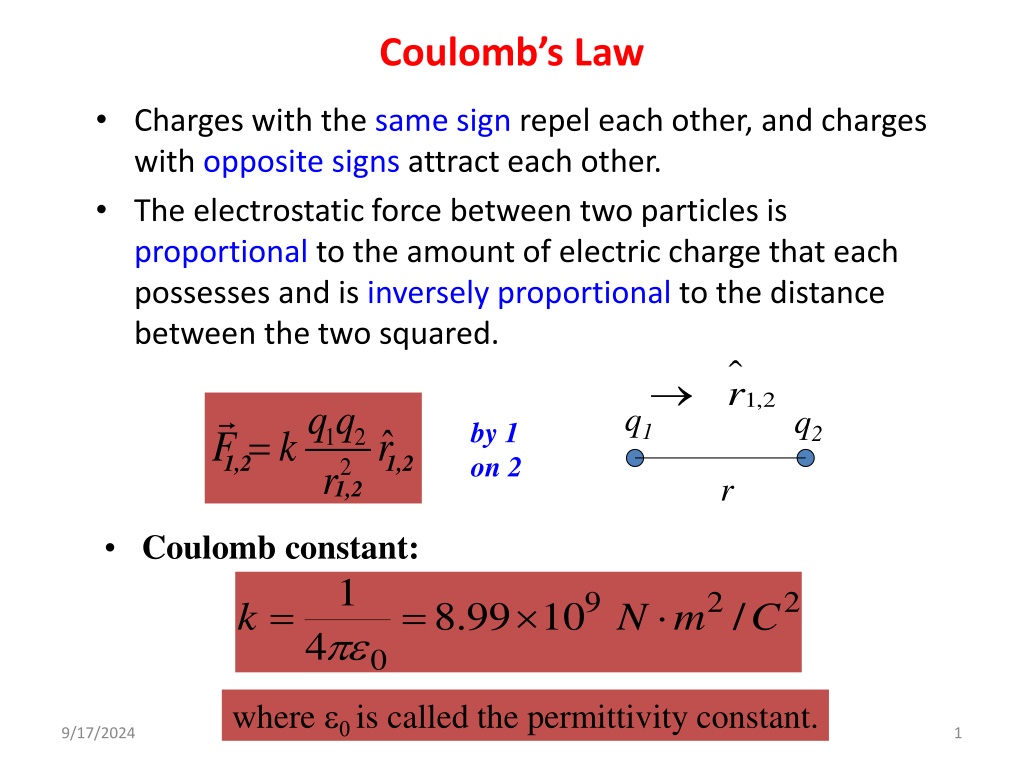
Coulombs Law Charges with the same sign repel each other, and charges with opposite signs attract each other. The electrostatic force between two particles is proportional to the amount of electric charge that each possesses and is inversely proportional to the distance between the two squared. r 1,2 qq q1 q2 by 1 on 2 = 1 2 2 r 1,2 F 1,2 k r 1,2 r Coulomb constant: 1 9 2 2 = = . 8 99 10 / k N m C 4 0 where is called the permittivity constant. 9/17/2024 1
Can We charged an object without touching it? polarization by induction grounding 9/17/2024 2
How strong are Coulomb forces? Electron and proton in a hydrogen atom 2 9 2 2 19 2 (8.99 10 / )(1.60 10 ) m N kg ) e r Nm C C = 7 (10 ) F k O N 2 1 1 2 (5.3 10 (10 ) (10 O 7 O = 23 2 / (10 ) / a F m O m s e 30 ) Compare electric and gravitational forces m m 2 e r electron and proton = = p r e F k F G e g 2 2 2 F F ke me = 9.11x10-31 kg, = 39 2.27 10 e Gm m mp =1.67x10-27 kg g p e 9/17/2024 3
quiz A Human weight 120 lb, which of the following is correct? a) A large fraction of the weight come from the attraction force between the charges on human body and earth. b) All the weight comes the attraction force between the charges on human body and earth. c) All the weight come from the gravitational forces. The electric forces are negligible. 9/17/2024 4
Quiz Two point charges are separated by distance d as shown. Where can you put a third charge of +1 C so that there is no net electric force acting on it? (Take Q > 0.) a) to the right of charge -Q b) c) between the two charges d) some other place e) nowhere to the left of charge 2Q - Q 2Q d e = 1.6 10-19 C k = 8.99 109 Nm2/C2 9/17/2024 5
Principle of Superposition of Electric Force = + + + F F F F 1 12 13 14 q1 q3 F13 Add by components or F12 Magnitude and direction separately by using trigonometry F14 q2 q4 9/17/2024 6
Two positive charges, one 2 C and the other 7 C, are separated by a distance of 20 cm. What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force that each charge exerts upon the other? 10 99 . 8 4 1 9 2 2 = = / k N m C 0 q1= 2 C q2= 7 C r = 20 cm = 0.2 m a) b) c) d) e) 0.32 N 0.63 N 0.70 N 2.02 N 3.15 N F =kq1q2 r2 9 109 N m2/C2 ( )2 10 6 C ( 0.2 m ( )7 10 6 C ( ) = ) 2 =0.126 N m2 0.04 m2 = 3.15 N 9/17/2024 7
Three positive charges are located along a line as shown. What is the net force exerted on the 0.02-C charge by the other two charges? k = 1 9 2 2 = . 8 99 10 / N m C 4 0 q1= 0.02 C q2= 0.04 C r =1 m a) b) c) d) e) 2.25 x 106 N 4.5 x 106 N 9.0 x 106 N 1.8 x 107 N 2.7 x 106 N F =kq1q2 r2 9 109 N m2/C2 ( )0.02 C ( 1 m ( ) )0.04 C ( ) = 2 = 7.2 106 N (to the left) F = F1 F2 = 7.2 106 N 4.5 106 N = 2.7 106 N (to the left) 9/17/2024 8
The Electric Field How do the charges exert forces on each other, when they are not even touching? The concept of an electric field describes how one charge affects the space around it, which then exerts a force on another charge. The electric field at a given point in space is the electric force per unit positive charge that would be exerted on a charge if it were placed at that point. E =F q 9/17/2024 9
We can then use the field to find the force on any other charge placed at that point: The direction of the electric field is the direction of the force exerted on a positive test charge. If the charge q is negative, the minus sign indicates that the direction of the force on a negative charge is opposite to the direction of the field. We can talk about the field at a point in space even if there is no charge at that point. The electric field can exist even in a vacuum. The field concept can also be used to define a gravitational field or a magnetic field, as well as others. 9/17/2024 10
Principle of Superposition for the Electric Field E E E E = + + + 1 2 3 4 q1 q3 E3 Add by components or E2 Magnitude and direction separately by using trigonometry E4 q2 q4 9/17/2024 11
Electric Field Produced by a Point Charge q kq F = 1 2 2 r kq F = = ( ) 2 E q q 2 2 r 1 kq F = = ( ) 1 E q q 1 2 r 2 9/17/2024 12
Are Q1 and Q2 positive or negative ? A. Q1 is positive, Q2 is negative B. Q1 is positive, Q2 is positive C. Q1 is negative, Q2 is negative D. Q1 is negative, Q2 is positive Q2 Q1 9/17/2024 13
An electric dipole is two charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by a small distance. Electric field lines originate on positive charges and end on negative charges. The field lines point away from the positive charge, and in toward the negative charge. 9/17/2024 14
Demos: 5A-34 Electric Field Lines 9/17/2024 15
Q20 Is it possible for an electric field to exist at some point in space at which there is no charge? Yes. Electric fields are created by charge but extend to infinity Q21 Two charges, of equal magnitude but opposite sign, lie along a line as shown in the diagram. Using arrows, indicate the directions of the electric field at points A, B, C, and D shown on the diagram. -q q C A B - + D 9/17/2024 16
quiz If we change the negative charge in the diagram for question 21 to a positive charge of the same magnitude, what are the directions of the electric field at points A, B, C, and D? (Indicate with arrows.) q q C A B + + D a) b) c) A:n/a, B:right, C:left, D:down A:n/a, B:right, C:left, D:up A:n/a, B:left, C:right, D:left 9/17/2024 17
Questions Chapter 12 Q2 Two pith balls are both charged by contact with a plastic rod that has been rubbed by cat fur, A. What sign will the charges on the pith balls have? Explain. B. Will the two pith balls attract or repel one another? Explain. A.The sign of the charge is negative. B. They will repel Q3 Two pith balls are charged by touching one to a glass rod that has been rubbed with a nylon cloth and the other to the cloth itself, A. What sign will the charge on each pith ball have? Explain. B. Will the two pith balls attract or repel one another? Explain. A. The first ball will have positive charge the second negative charge B. The two balls will attract each other 9/17/2024 18
Q13 Will bits of paper be attracted to a charged rod even if they have no net charge? Yes because the charge will attract the opposite charge in the paper Q14 Why are pith balls initially attracted to a charged rod and later repelled by the same rod, even though they have not touched any other charged object? Because once they touch the charged rod they pick up some of the charge and the ball is repelled Q19 Can both the electrostatic force and the gravitational force be either attractive or repulsive? No, the gravitational force is always attractive. 9/17/2024 19
Q23 Three equal positive charges are located at the corners of a square, as in the diagram. Using arrows, indicate the direction of the electric field at points A and B on the diagram. + q A + q B q + Q25 If we move a positive charge toward a negative charge, does the potential energy of the positive charge increase or decrease? The potential energy decreases 9/17/2024 20
Q26 If we move a negative charge toward a second negative charge, does the potential energy of the first charge increase or decrease? It increases because they repel each other it means as you get closer the force gets larger. You have to do work to bring them closer Q32 Would you be more likely to be struck by lightning if you stood on a platform made from a good electrical insulator than if you stood on the ground? Standing on an insulator is the safest which is why the safest place in inside a car because the tires are insulators. It s also the same with fallen power lines 9/17/2024 21
CH 12 E14 Charge q = -4 10-6 c placed in Electric field of E = 8.5 104 N/C Towards right. What is the electrostatic (vector) force on charge q? E 9m F = qE = (4 10-6)(8.5 104) F = 0.34 N Since positive charge moves with field lines and q is negative, q moves to the left F = 0.34 N to left 9/17/2024 22
CH 12 CP 2 2 equal charges (positive) are near one another (see diagram). a) Using small arrows indicate the direction of the electric field at labeled points on diagram. (Think about what a positive test charge would do!) b) Sketch electric field lines E F D B A C + + I G H 9/17/2024 23
Ch 12 CP2 (cont) E E F D F a) D B + + A C A C + + I G I G H H b) 9/17/2024 24