Understanding Changes of State in Matter
Changes of state in matter refer to the physical transitions that substances undergo, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, and condensation. These transitions involve the addition or removal of energy, impacting the movement of particles and their arrangement. Despite the transformations, the identity of the substance remains constant. Melting involves the shift from a solid to a liquid by adding energy, while freezing represents the opposite process. Vaporization changes a liquid to a gas, either through boiling or evaporation. Lastly, condensation converts a gas back to a liquid. Understanding these changes is essential in the study of matter and its properties.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
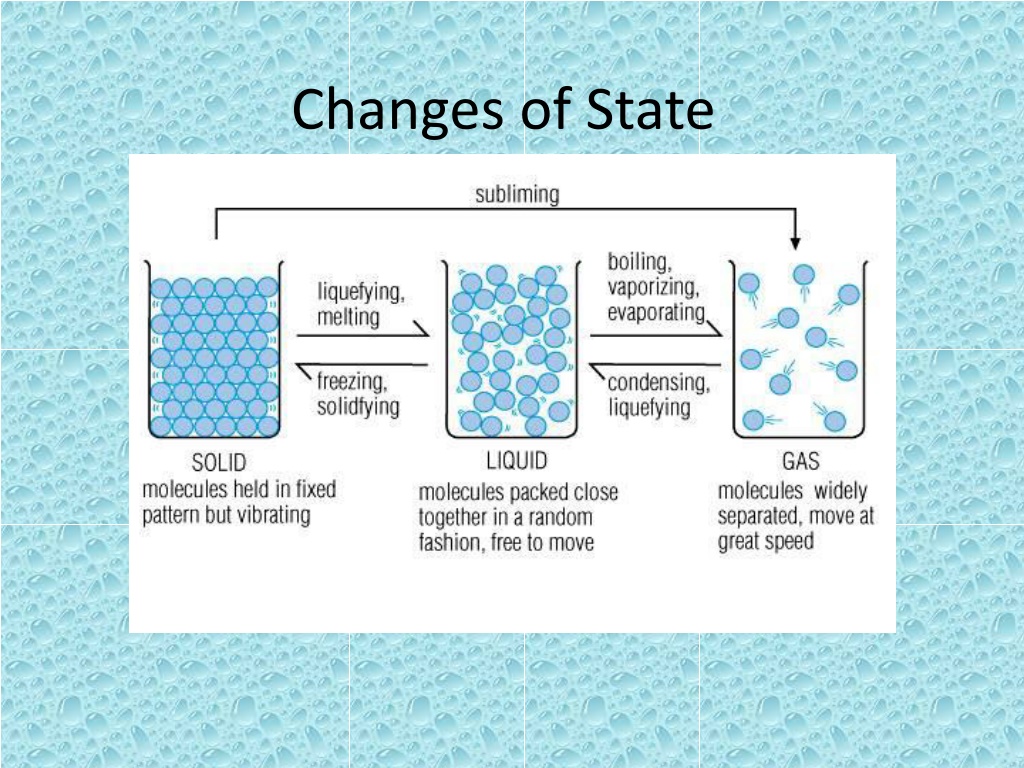
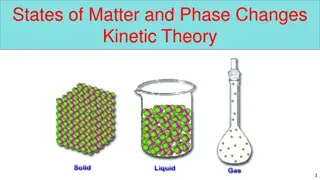
Changes of State Is the change of a substance from one physical form to the other All changes of states are physical changes, this means that the identity of a substance does not change Ex. Ice turns to water through melting. It is still made of the same thing.
Energy Particles of a substance have different amounts of energy when the substance is in different states. Ex. Particles in Liquid water have more energy than particles in ice When a change of state happens, the energy of the particles of the substance changes too. So to change state you must add or remove energy
Melting Is the change of state from a solid to a liquid. You must add energy to a solid to increase the temperature. As it heats up the particles of the solid speed up. The temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid is the Melting point. Different substances have different melting points
Melting For a solid to melt, particles must overcome their attraction to each other. Melting is endothermic change because energy is gained by the substance as it changes.
Freezing Change of state from a liquid to a solid The temperature at which a liquid changes into a solid is the freezing point Freezing and melting happen at the same temperature To turn from a liquid to a solid the particles must overcome the motion particles
Freezing Freezing is an exothermic change because energy is removed from, or taken out of the substance as it changes
Vaporization Change of state from a liquid to a gas Two types of Vaporization Takes place throughout a liquid is called boiling The temperature at which a liquid boils is called the boiling point Evaporation occurs at the surface of a liquid below boiling point.
Condensation Change of state from a gas to a liquid Condensation point is the temperature at which a substance changes from a gas to a liquid.
Sublimation Change of state from a solid directly to a gas. Ex. Dry ice is colder than ice. Unlike ice, dry ice does not melt into a puddle of liquid.