Comparative Analysis of Positive Charge's Charging Stations Evolution
This PowerPoint template example created by Romy Bailey for Positive Charge showcases a comparative study of high-speed charging stations versus traditional charging stations, along with a comparison of past year versus current year data, and a year-over-year analysis of Positive Charge's growth. It
1 views • 6 slides
Tracing Carbon Atoms in Ecosystems: Understanding the Organic Matter Pyramid
Explore the journey of 500 carbon atoms through producers, herbivores, and carnivores in an ecosystem. Discover how carbon atoms move through photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and biosynthesis, ultimately contributing to the organic matter pyramid. Follow the pathways of carbon atoms as they cyc
0 views • 7 slides
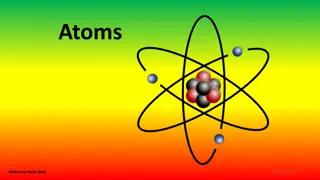
Understanding Atoms: The Building Blocks of Life
Atoms are the fundamental units of matter, composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. This article explores the structure of atoms, the atomic theory, and how atoms make up elements. Discover how changing the number of protons can create different elements, and learn about the periodic table and
5 views • 26 slides
Positive Charge Brand Audit Presentation
Conducting a brand audit is crucial to evaluate the effectiveness of Positive Charge, an EV-charging provider striving to reduce the environmental impact of fossil-fuel cars. The audit covers aspects such as brand identity, customer perception, values, competition analysis, and goals alignment to de
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Temperature Effects on Donor and Acceptor Ionization in Semiconductors
Temperature plays a crucial role in the ionization of donor and acceptor atoms in semiconductors. In N-type semiconductors, the Fermi level lies below the conduction band, while in P-type semiconductors it lies above the valence band, with the position depending on temperature and impurity atoms. Do
1 views • 13 slides
Understanding Current, Resistance, and Charge Motion
Explore the fundamentals of current flow, resistance, and charge motion in this chapter. Learn about the factors influencing current, the behavior of free electrons in metals, and the impact of potential difference on charge motion. Discover Kirchhoff's laws and how current density is calculated.
0 views • 40 slides
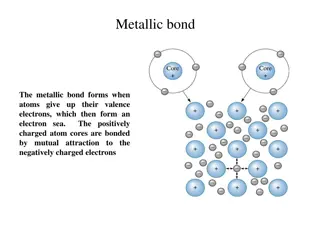
Understanding Different Types of Chemical Bonds
Metallic bonds involve atoms giving up valence electrons to form an electron sea, covalent bonds entail electron sharing to fill outer orbitals, ionic bonds form when atoms with different electronegativities attract, Van der Waals bonds include London forces between atoms, and hydrogen bonds occur i
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes in Chemistry
Atoms are neutral with equal protons and electrons. Ions are charged atoms resulting from gaining or losing electrons, while isotopes are atoms with varying numbers of neutrons. The atomic number always signifies the number of protons in an atom, unaffected by electron or neutron changes. Explore th
2 views • 5 slides
Understanding Valence Electrons in Atoms and the Periodic Table
Explore the concept of valence electrons in atoms, crucial for chemical bonding. Learn to define valence electrons, understand their role, and draw electron-dot structures for atoms. Practice identifying valence electrons in various elements and creating electron-dot structures in this educational c
1 views • 12 slides
Understanding Chemical Bonding and Stability in Atoms
Explore the significance of chemical bonds in providing stability to atoms through ionic and covalent bonding mechanisms. Learn about valence electrons, types of bonds, and why atoms form bonds for enhanced stability.
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Aldehydes and Ketones in Organic Chemistry
Aldehydes and ketones are compounds that contain carbonyl groups (>C=O). Aldehydes have the CO group linked to either two hydrogen atoms or one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group, while ketones have the CO group linked to two alkyl or aryl groups. The structure of the carbonyl group is charac
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Atoms and Molecules: Basics and Models
Explore the world of atoms and molecules with a focus on distinguishing between them, understanding atomic structures through historic models like Bohr and Rutherford, and the modern atomic model. Discover how atoms form the basis of all matter and how they are organized within molecules.
0 views • 20 slides
The Journey of Atoms: From the Big Bang to Earth
The narrative explores the intriguing evolution of atoms from the Big Bang, where protons, neutrons, and electrons were born, to the formation of hydrogen and helium atoms. Over time, denser regions condensed to form stars, triggering nuclear fusion and creating heavier elements. This led to the exi
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Atoms and the Periodic Table
Explore the fundamentals of atoms and matter, including the conservation of matter, mixtures, pure substances, and the properties of metals, metalloids, and nonmetals. Discover the significance of valence electrons, the neutral state of atoms, and the classification of elements on the periodic table
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Electric Charges and Conductors in Physics
Explore the fundamentals of electrostatics, electric charges, conductors, and insulators in physics. Learn about the Law of Electric Charges, types of charge, conductors vs. insulators, and methods of charging objects through friction, conduction, and induction. Dive into the world of atoms, electro
1 views • 14 slides
Understanding Organic Chemistry: Carbon Atoms and Molecular Diversity
In organic chemistry, carbon atoms can form diverse molecules by bonding to four other atoms, leading to molecular complexity and diversity. The versatile nature of carbon allows for the formation of various carbon skeletons, contributing to the vast array of organic compounds. Hydrocarbons, consist
0 views • 12 slides
Exploring Atom Structure and Properties Questions
This series of questions delves into the intriguing world of atoms, covering topics such as atom size comparison, proton count identification, location of metals on the Periodic Table, nucleus charge explanation, atomic number significance, various arrangements of the Periodic Table, subatomic parti
0 views • 12 slides
Kaonic Atoms Research Workshop at Istituto Nazionale Fisica Nucleare
Dive into the world of kaonic atoms physics and the latest advancements in Silicon Drift Detectors technology for precision measurements at the Istituto Nazionale Fisica Nucleare workshops held in Frascati, Italy. Explore the research conducted on strange matter and strangeness studies in Italy and
0 views • 31 slides
Exploring the World of Atoms and Molecules
Dive into the realm of atoms, molecules, and ions as we uncover the key concepts behind Dalton's Atomic Theory, the discoveries of John Dalton and J.J. Thompson, and fundamental chemical laws. From the indivisibility of atoms to the Plum Pudding Model, this journey through chemistry's building block
0 views • 54 slides
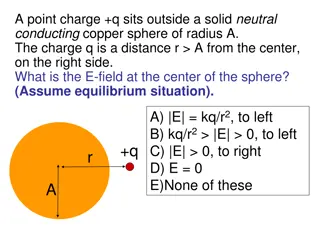
Understanding Electric Fields and Charges in Different Scenarios
Explore various scenarios involving electric fields and charges such as the E-field at the center of a conducting sphere, the effect of total charge on E-field, E-field above a charged conductor, charge distribution on the surface of a copper sphere with a hollow, field inside a charged non-conducti
0 views • 9 slides
Charge Transport Model for Swept Charge Devices (SCD) in Astrophysics Research
Exploring the charge transport model for Swept Charge Devices (SCD) in collaboration with various institutions like ISRO Satellite Centre and e2V technologies Ltd. The research aims to enhance spectral response, reduce uncertainties, and improve global lunar elemental mapping using advanced X-ray sp
0 views • 30 slides
Understanding Matter, Elements, and Molecules
Matter is anything with mass and volume, consisting of atoms. Elements are pure substances with one type of atom. Molecules are groups of bonded atoms. The content explains mass, volume, different forms of elements, allotropes, and compound properties like sodium chloride. It covers chemical symbols
0 views • 37 slides
Photoproduction of Pionic Atoms at the Gamma Factory: Research Overview
Research conducted by V. V. Flambaum, J. Jin, and D. Budker at the Gamma Factory (GF) on photoproduction of pionic atoms is detailed in this content. It explores the formation of pionic atoms with negative pions orbiting the nucleus in a hydrogen-like system, emphasizing strong interaction effects a
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Neutralization of Proton Beam Using Charge Exchange Cell in COMSOL
In various applications, collisions of neutral particle beams with target materials play a crucial role. This process involves neutralizing high-velocity proton beams by passing them through a charge exchange cell filled with neutral gas, such as argon. The cell allows protons to capture electrons f
0 views • 17 slides
Neutralization of Proton Beam Through Charge Exchange Cell
Collisions between neutral particle beams and target materials at varying projectile energies play a crucial role in numerous applications. Charge exchange cells facilitate the generation of high-velocity neutral particles by neutralizing fast ions within a high-density gas region. By capturing elec
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Ions and Their Importance in Your Body
Neutral atoms have the same number of protons and electrons, with the charge of the nucleus always positive. The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons. The number of neutrons can be calculated by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number. Ions are atoms with a positive or negative
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Atoms: From Structure to Models
Explore the fundamental building blocks of matter - atoms. Discover what materials are made of, delve into atomic theories, examine Bohr models, and learn about the intricate components such as protons, neutrons, and electrons. Engage in a journey through the microscopic world of atoms and their sig
0 views • 34 slides
Understanding Matter: Solids, Liquids, Gases, and Fluids
Matter exists in various states - solid, liquid, gas, and fluid. Solids have atoms closely packed, liquids have more freedom but still cohesion, gases have atoms spread out, and fluids flow like liquids or gases. Mass density characterizes matter based on atom proximity. Gas pressure results from mo
0 views • 22 slides
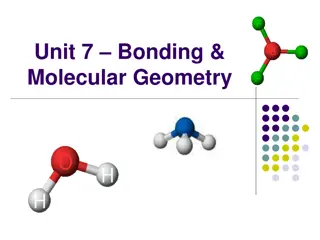
Understanding Chemical Bonds and Molecular Geometry
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together, with valence electrons playing a crucial role. Ionic bonds involve complete electron transfer between metals and nonmetals, while covalent bonds see electrons being shared. Lewis dot diagrams help in visualizing the valence electrons of atoms,
0 views • 68 slides
Explore the Atoms Family in Matterville - A Digital Notebook Adventure
Discover the quirky Atoms Family in Matterville through a fun and educational digital notebook. Meet Perky Patty Proton, Nerdy Nelda Neutron, and Enraged Elliott Electron as they hang out at the Nucleus Arcade. Learn about their personalities, favorite activities, and how the balance of electrons an
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Chemical Bonds: Covalent, Ionic, and Metallic
Explore the fascinating world of chemical bonds, including covalent bonds where atoms share electron pairs (e.g., water), ionic bonds where oppositely charged ions attract (e.g., sodium chloride), and metallic bonds formed between positively charged atoms sharing free electrons (e.g., copper wire).
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Electrostatics: Charges, Objects, and Conservation Law
Electrostatics is the study of stationary electrical charges, where objects can be neutral, positively or negatively charged based on the balance of electrons. The charge of electrons and protons, elementary charge, examples of charge calculation, and the law of conservation of charge are key concep
0 views • 25 slides
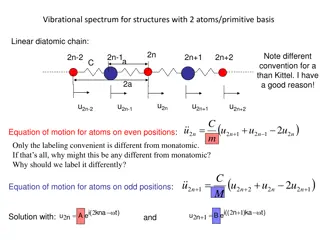
Vibrational Spectrum in Diatomic Chain Structures: Analysis and Eigenmodes
The vibrational spectrum of structures with two atoms in a linear diatomic chain is examined, focusing on the equation of motion for atoms at even and odd positions, phonon dispersion, transverse acoustic and optical modes, longitudinal eigenmodes in 1D, and extending the 1D model to 3D for phonon d
0 views • 20 slides
Factors Affecting Acid Strength: Atoms, Size, Hybridization, and Electronegativity
The strength of acids is influenced by various factors such as the atom on which the negative charge of the acid's conjugate base rests, atom size, hybridization, and electronegativity. The stability of negative charges on atoms, atom size allowing charge delocalization, preferred orbital types for
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy in Analytical Chemistry
Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) is a valuable technique for determining metal concentrations in samples. This method involves the absorption of light to measure gas-phase atoms, requiring steps like desolvation, vaporization, and volatilization to convert samples into atomic gas. The process ut
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Atoms and Isotopes in Chemistry
Understanding atoms and isotopes is essential in chemistry. Atoms consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons that determine their properties. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different atomic masses due to varying numbers of neutrons. Learning how to determine subatomic particles and ato
0 views • 17 slides
Energy Level Formation in Semiconductor Materials
Energy levels in isolated atomic structures form discrete levels which expand to bands in insulators, semiconductors, and conductors. Extrinsic materials like n-type and p-type are created by doping semiconductors with impurity atoms to alter conductivity. The n-type material involves adding pentava
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Moles in Chemistry
Matter is composed of various particles, and chemists use the concept of moles as a unit of measure to quantify the number of particles in a substance. One mole is equal to 6.02 x 10^23 representative particles of a substance, known as Avogadro's number. Moles are versatile and applicable to differe
0 views • 25 slides
Three-Body Recombination in Ultracold Atoms: Studies and Observations
Investigating three-body recombination in ultracold atoms, this study explores the Efimov scenario, experimental setups with ultracold 7Li atoms, and the implications of three-body inelastic collisions. The research delves into universality windows, real molecule comparisons, and the loss rate from
0 views • 35 slides
Understanding Static Electricity and Electrostatics
Static electricity is a result of electric charge buildup on insulating materials due to friction, causing electrons to transfer and create a charge difference. This can lead to phenomena like a balloon sticking to a wall. The origin of static charge lies in the electrons and protons within atoms, w
0 views • 9 slides