Understanding Atoms and Isotopes in Chemistry
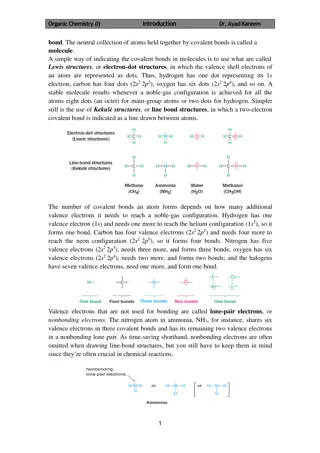
Understanding atoms and isotopes is essential in chemistry. Atoms consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons that determine their properties. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different atomic masses due to varying numbers of neutrons. Learning how to determine subatomic particles and atomic numbers helps identify elements accurately. Naming isotopes through hyphen notation or nuclide symbols aids in distinguishing between different isotopes. Practice problems further reinforce comprehension of these fundamental concepts in chemistry.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
HOW ATOMS DIFFER/ ISOTOPES HOW ATOMS DIFFER/ ISOTOPES Notes #5
I. Parts of an atom Protons positive charge Neutrons no charge Electrons negative charge 1. in constant motion around nucleus of atom; travel in orbitals, or shells A. B. C. atom
II. Determining # of each subatomic particle Atomic number - # of protons in the nucleus of an atom Atomic mass - # of protons and neutrons in the nucleus Example for Scandium atom 21 Sc 45.0 atomic # = # of p+ # p+= # e- atomic mass atomic # = n0 = ___ = ___ = ___
II. Determining # of sub. Part. Atomic number - # of protons in the nucleus of an atom Atomic mass - # of protons and neutrons in the nucleus Example for Sc atom atomic # = # of p+ # p+ = # e- atomic mass atomic # = n0 = 24 21 Sc 45.0 = 21 = 21
III. Atomic Number Identity of each element is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons. Practice problems pg. 99
IV. Isotopes A. Atoms of the same element having different atomic masses. B. Atoms of the same element having different numbers of neutrons. Hydrogen has three isotopes: Protium 0 neutrons Deuterium 1 neutron Tritium 2 neutrons
IV. Isotopes C. Naming It is often important to identify one isotope from another. This is done in two ways. 1. Hyphen notation. This gives the element name (which you can use to determine the atomic number) followed by the atomic mass which you can use to determine the number of neutrons. Hydrogen 2
2. Nuclide or nuclear symbol notation Atomic mass 4 2He Atomic number
Practice problems find p+, e-, n0 1. Symbol notation 107Ag 2. Hyphen notation Potassium 39 Potassium 40 Potassium 41 Solve practice problems pg. 99,101 # s11- 14. For #14 add on hyphen notation and symbol notation
V. Average Atomic Mass 3.An average sample of hydrogen in nature contains 99.985% protium, 0.015% deuterium and a miniscule amount of tritium. Protium has an atomic mass of 1.007825 amu. Deuterium has an atomic mass of 2.014102 amu.
Average Atomic Mass Multiply the masses of each isotope by its percentage. These are weighted values. Add all of these values together. (Do NOT divide by the number of isotopes. This is unnecessary.)
Average Atomic Mass 1.007825 * .99985 = 1.0076738 amu protium .00015 * 2.014102 = 0.0003021 amu deuterium 1.0076738 + 0.0003021 = 1.00798 amu 1.00798 amu is a weighted average because most of the hydrogen is protium.
Average Atomic Mass 1.00798 amu is a weighted average because most of the hydrogen is protium. Multiply the masses of each isotope by its percentage. These are weighted values. Add all of these values together. (Do NOT divide by the number of isotopes. This is unnecessary.)
Average Atomic Mass The normal way to determine the average mass of something would be to add the two masses and simply divide by two.
Average Atomic Mass The normal way to determine the average mass of something would be to add the two masses and simply divide by two. 1.007825 + 2.014102 = 3.021927 3.071927 / 2 = 1.5109635 amu
Sample Problem 4. What is the atomic mass of silicon if 92.21% of its atoms have mass 27.977u, 4.70% have mass 28.976 u and 3.09% have mass 29.974? 28.1 u .9221 x 27.997 = 25.82 u .0470 x 28.976 = 1.36 u .0309 x 29.974 = 0.926 u
Sample #2 5. Neon has two isotopes. Neon-20 has a mass of 19.992 u and neon-22 has a mass of 21.991 u. In any sample of 100 neon atoms, 90 will be neon-20 and 10 will be neon-22. Calculate the average atomic mass of neon. 20.192 u (.90 x 19.992) + (.10 x 21.991) 17.9928 + 2.1991