Overview of Urinary System Anatomy and General Terminology
This content provides detailed information on the anatomy of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It explains anatomical terms, Greek term elements related to the system, and general terms for urine and urination. Additionally, it covers urinary dysfunctions such as enuresis, ischuria, urostasis, and more.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Systema urogenitale 1. Systema urinarium M.Petrova
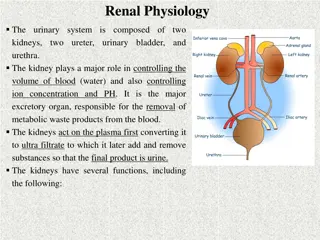
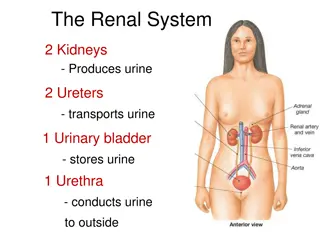
REN. Anatomic terms 1. 2. 3. ren, renis, m kidney ren dexter / sinister calix renalis m pl. calices renales - a cup-like structure/s in kidneys pyramis renalis f pl. pyramides renales -renal pyramid/s pelvis renalis f -basinlike, funnel- shaped structure medulla renalis f -the inner part of the kidney, distributed into renal pyramids cortex renalis m -the outer layer of the kidney hilum renale n -the entrance for nerves and vessels of the kidney 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
General anatomic terms ureter dexter / sinister m -tube, 41 to 46 cm long, through which the urine passes from the kidney to the bladder vesica urinaria f -urinary bladder Fundus vesicae urinariae Corpus vesicae urinariae Cervix vesicae urinariae urethra, ae, f the tubular passage through which urine is discharged from the bladder to the exterior of the body. urethra feminina f about 4 cm long urethra masculina f about 20 cm long
Greek termelements. Anatomic structures 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. -NEPHR- -CALIC- -PYEL- -URETER- -CYST- 1. ren, renis, m 2. calyx renalis m 3. pelvis renalis f 4. ureter, eris, m 5. vesica urinaria f 6. urethra, ae, f * cyst- gr. bladder, vesicle is termelement used for any structure/organ resembling a bladder; if used alone means urinary bladder; if used with application of other word element chole-cyst- (gall-bladder); dacry-cyst- (lacrimal sac) etc. ; it could also mean a cyst - patholog. sac formation (Cysta ovariidextri) 1. -URETHR-
General terms for urine, urination lat. urina, ae, f = gr. -UR-/ UR (o)-.... / .-UR-ia diuresis, is, f (gr. from dia "through" + ourein "urinate") -in bg med. terminology used for the urine 24-hour volume Urinary dysfunctions: enuresis, is, f (gr. en-in + ur-esis) -involuntary discharge of urine (enuresis nocturna -discharge during sleep,bed-wetting) syn. lat. incontinentia urinae -unintentional loss of urine (example: incontinentia stressogenes - stress urinary incontinence(SUI) click) ischuria (gr. isch-keep back, hold + ur-ia) -urinary retention; an inability to completely empty the bladder urostasis,is,f-stopping of urine (usuallyinside an organ) urosepsis,is, f -sepsis caused by a urogenitaltract infection (UTI)click
Urinary dysfunctions dys-uria -painful or difficult urination stranguria -(gr. stranx -a drop squeezed out) painful, frequent urination of small volumes an-uria-absence of urine formation; less than 100 milliliters of urine in 24 h olig-uria -(gr. olig-small= lat. parvus, a, um) low output of urine specifically more than 80 ml/24h but less than 400ml/24 h poly-uria -abnormally large production or passage of urine (greater than 2.5 L, or 3 L/24 nyct-uria -(gr. nyct-night= lat. nox, noctis. f) urination at night chromat-uria (gr. chromat-color) abnormal coloration of the urine Terms for presence of substances in the urine: haemat-uria -presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine glycos-uria -excretion of glucose into the urine ketonuria -keton bodies in the urine protein-uria -presence of excess proteins in the urine bacteriuria -presence of bacteria in urine NB! substances in the urine URIA; components of urine in... UR(o)... uro-sepsis, ur-aemia -high levels of urea in the blood click
Nephrologia - renal pathological conditions hydr-o-nephr-osis -(gr.= hydr-water+nephr-) swelling of the kidneys when urine flow is obstructed (urostasis) in any part of the urinary tract py-o-nephr-osis (gr. py-= lat. pus, puris, n) suppurative destruction of the renal parenchyma, often with kidney failure nephr-o-lithi-asis -(gr. lithus -stone; as in lithographia = lat. calculus ) presence of renal calculi, formation of kidney stone/s * -LITHIASIS (lat. syn. calculus/i) applied as termelement for all calculous diseases click nephr-o-scler-osis hardening of the kidney, usually associated with hypertension and disease of the renal arterioles nephr-o-ptosis (gr. ptosis -falling, droppping; med. a sagging or prolapse of an organ or part) downward displacementof the kidney = Lat. syn. Ren mobilis - floating, wandering kidney Insufficientia renalis acuta click/ Insufficientia renalis chronica click Necrosis corticalis (renis) click Polycystosis renalis -Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited disorder in which clusters of cysts develop primarily within kidneys, causing them to enlarge and lose function over time click
Conditions of the urinary tracts, bladder ureter-o-lithiasis, is, f -formation or presence of calculi=stones in the ureter ureter-ectasia -dilation of the ureter mega-ureter -congenital dilatation of the ureter hydr-o-ureter -acquired dilation, swelling of the ureter, which always accompanies hydronephrosis click cyst-o-lithiasis, is, f -formation or presence of calculi=stones in the urinary bladder cyst-itis, itidis, f -inflammation of urinary bladder (especially female) urethr-itis, itidis, f -inflammation of urethra (especially male) urethr-a-tres-ia -(gr. a-, not + tresis, a perforation) occlusion or imperforation of the urethra * atresia, ae, f