Assessment Framework for Mitigation Actions: A Tool for NAMA Development
This proposed tool supports the development and management of Nationally Appropriate Mitigation Actions (NAMAs) by providing a structured approach to assess and prioritize different mitigation programs. The tool is designed to assist developing countries, donor countries, and private investors in evaluating and selecting the most effective and valuable programs for international investment. Through a systematic assessment process, countries and investors can enhance transparency, prioritize initiatives, and align with international standards for mitigation actions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Assessment Framework for Mitigation Actions: A proposed tool to support development and management of NAMAs Marcos Castro Climate Change Group, World Bank UNFCCC Regional Workshop on CDM and NAMAs for Latin America and the Caribbean 31 August 2 September, Bogota, Colombia
Table of Contents 1. Introduction: why an assessment framework? 2. Objectives, goals and structure of the Assessment Framework 3. Mitigation Action Assessment Modules, Areas and Key Indicators 4. Consultation Process and Next Steps 5. Conclusions This presentation builds on presentations prepared by DNV, as part of work commissioned by World Bank.. 2
Case 1: Developing Country It has implemented different mitigation programs for which the country aims at securing international finance. The programs are different in nature and scope. It is challenging to prioritize the programs to start first in the absence of an uniform system Challenge Different new carbon regimes have different standards/regulations The country (CE) can scan the different programs based on a set of preselected assessment criteria. It can analyse how the rating changes for different programs as the weight for different rating criteria changes. Assessment approach The rating is applicable to a broad number of programs which will obtain different rating during the assessment. Self assessment tool of different alternatives to prioritize implementation based on a country level accepted evaluation/rating criteria. Value Show international investors prioritization process and value of each program (e.g., based on an agreed weight system for the assessment criteria) Self assessment of programs allows for improvement and a 'race to the top' which permits wider market access and higher value Broad range of programs are assessed. It is no longer a yes/no process. 3
Case 2: Donor Country It is presented with multiple investment opportunities. There is a broad range of cases, from projects to multisectoral policy implementation programs. Challenge Some of these ER could be used for country pledges accounting. It is required to find an equivalence system among those ER from the different NAMAs/programs to make sure there is an standardized equivalence among them. Evaluates programs at the design stage, implementation stage and execution stage providing an assessment output based on preselected criteria. Weight for assessment criteria can be changed based on cooperation/investment approach. Assessment approach Prioritize diverse interventions based on pre set range of criteria Self selection of acceptable rating output instead of a yes/no output Value The rating allows for having an equivalence system among different regimes. 4
Case 3: Private Investor It is presented with multiple investment opportunities. There is a broad range of cases, from projects to multisectoral policy implementation programs. Challenge Each opportunity is in a country with different criteria for ER accounting and it is difficult to compare among them. Evaluates programs at the design stage, implementation stage and execution stage providing a rating output based on preselected criteria. Assessment approach Weight for rating criteria can be changed based on investment approach. Value Prioritization of investment opportunities. Comparability among different program types. 5
Objectives of the Assessment Framework The main objectives of the design of this assessment system are: Establish a common framework to screen, evaluate and compare different mitigation programs Develop a mechanism for comprehensive assessment of GHG mitigation actions Provide confidence to donors/investors on viability and level of risk of different mitigation programs Facilitate benchmarking and identify areas for continuous improvement 6
Goals and Assessment Structure Establish framework to enable: Program-level assessment of environmental integrity (GHG management) and development benefits Common set of key indicators to promote comparability of mitigation programs (depending on user needs); Use a probabilistic approach to the rating of variables leading to aggregate risk numbers for each of the (risk) modules Allow the user of the assessment framework (jurisdictions, investors, donors, etc) to make overall rating based on their weighting of the risk variables; As applicable, market participants to assign a value to carbon assets generated by mitigation programs, based on performance against key indicators 7
Goals and Assessment Structure Key Considerations In order to ensure broad acceptance and use: Be independent, transparent, and accountable, with engagement by key players; Provide as much certainty and predictability around evaluation/ratings, as is practicable; Review and apply existing rating methodologies, in order to facilitate implementation and learn from previous experiences (credit, ESG and carbon ratings and their relative merits and limitations); Clearly define functions and framework for assigning responsibilities (gathering of information, operation of the rating system, etc.); Address legal and regulatory components; Address operating components. Title of Presentation 8
Mitigation Actions Assessment Protocol Assessment modules The assessment protocol for Mitigation Actions / NAMAs is formed by six independent modules. Four modules are applicable to the mitigation action program itself (program-level assessment), while two other cover the level of ambition of the executing jurisdiction, and are only relevant if carbon assets are intended to be eventually traded internationally. 9
Mitigation Actions Assessment Protocol Modules and module areas Environmental Integrity Ambition Index (jurisdiction level) Mitigation Action Program Mitigation Action Management Entity Investment Environment Development Benefits Definition & Scope Sustainable Development Objectives & Targets Management Framework Objectives & Targets Economic and political environment Level of ambition Planning Roles, Financial and Investment Capacity Framework Responsibilities & Authorities Planning & Participation Barriers Emissions reduction from Intervention Climate Change Capacity Alignment and focus Monitoring of Sustainable Development Climate Change Programs Management Monitoring and Reporting 10 Mitigation Value
Assessment Structure Module > Module Areas > Key Indicators Module s rating Module area weighting Relative importance of each risk area within a module Key indicators weighting average Higher weight will assign a larger impact Key Indicators score Score range for each level of development - Default - Override score Level of confidence 11
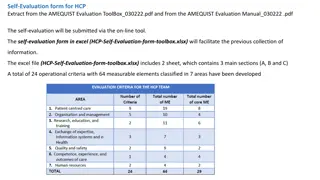
Mitigation Actions Assessment Protocol Example: Weighting of Rating Areas # Key Indicators 5 4 7 5 1 7 3 Module Rating Area Weight Definition & Scope Objectives & Targets Planning Roles, Responsibilities & Authorities Barriers Emissions Reductions from Interventions Monitoring & Reporting 14% 20% 22% 7% 7% 20% 10% 1. Mitigation Action Program Management Framework 30% 2 2. Mitigation Action Management Entity 33% 37% 45% 55% 35% 45% 20% 3 3 4 4 7 8 6 Financial & Investment Capacity Framework Climate Change Program Management Internationally Recognized Country Ratings Climate change infrastructure: program level Sustainable Dev. Objectives & Targets Planning and Participation Monitoring of Sustainable Development 3. Investment Environment 4. Development Benefits 12
Mitigation Actions Assessment Protocol Example: Module Area Key indicators Over- ride Score Area KI KI Score Range Level of Confidence Module Module Area Weighting Key Indicator Weighting Score Range Over-ride Justification KI Score The scope of the NAMA is clearly defined and documented. 60-100 Scope of the NAMA and its contributions to Sustainable Development. The scope of the NAMA is defined but it is not consistent along the documentation of the program. 40-60 20% 40-60 high 10.00 The scope of the NAMA is neither clearly defined nor documented. 0-40 The scope of the NAMA is aligned itself with the country climate change mitigation priorities as defined by the Government The NAMA contributes to climate change mitigation but does not outline how it aligns itself with the National priorities on climate change mitigation as defined by the Government The NAMA does not demonstrate how the scope is aligned with the country climate change mitigation priorities as defined by the Government The NAMAs have been developed and implemented with the approval of the relevant national authorities. (Approver in the UNFCCC NAMA Registry) The approval of the relevant national authorities has been requested but is still pending There is no evidence of the approval of the relevant national authorities. The starting date of the NAMA is clearly defined and justified in terms of when the emissions reduction can be attributed to the NAMA. Milestones are included to allow progress and effectiveness to be reviewed. even when the NAMA addresses cc mitigation and other benefits, it is taking place in a sector that is not a focus sector for the country as outlined in the National Climate Change Program 60-100 Alignment with National priorities. 20% 0-40 30 low 6.00 40-60 0-40 Program Design 60-100 NAMA approval by relevant authorities 10% 60-100 high 8.00 Definition and scope of the NAMA 40-60 0-40 20% 60-100 Starting date, milestones and length duration of the Program The starting date is defined but it is not possible to conclude that the starting date is linked to the accounting of ER due to the NAMA implementation. 20% 0-40 high 4.00 40-60 The starting date is not clearly defined, is unjustified or is inconsistent across the NAMA documentation. 0-40 The geographical boundary of the Program is defined in accordance to the jurisdiction authority of the NAMA Implementation Entity (NIE). The boundaries analysis includes the evaluation of possible double counting risk with other ongoing programs and jurisdictions. The geographical boundary of the Program is defined but there is no justification of how it can interact with the jurisdiction authority of the NAMA Implementation Entity (NIE) and do not take into account possible double counting risk with other ongoing programs and jurisdictions. the geographical boundaries are defined. For the proposed interventions, the NAMA identifies other possible jurisdiction that can be impacted. Nevertheless, the NAMA does not adress how those cross effects in ER can be quantified. 60-100 Boundaries for the Program in terms of a geographical area of implementation 30% 40-60 40.00 high 12.00 40-60 13 The geographical boundary of the Program is not clearly defined. 0-40
Mitigation Actions Assessment Protocol Example: Module Evaluation Areas 14
Mitigation Actions Assessment Protocol Example: Module Evaluation Areas Mitigation Action Program Module Definition & Scope 25 20 Monitoring and Reporting Objectives and Targets 15 10 5 max score 0 score Emissions Reductions from Interventions Planning Roles, Barriers Responsibilities and Authorities 15
Mitigation Actions Assessment Protocol Example: Evaluation Area Key Indicators 16
Development of framework: Consultation Process Stakeholder consultations Peer review Working Group - Globally Networked Carbon Markets Carbon Expo May 2013 Latin America Carbon Forum (Rio de Janeiro), FICCI (New Delhi), Asian Carbon Forum (Bangkok) Fall 2013 Comments invited from the Working Group, selected individuals and organizations 3 technical peer reviewers WB Internal Meeting June 2013 Paris Working Group meeting 1 Sept. 2013 Webinar Update Dec. 2013 Paris Working Group meeting 2-February 2014 17
Development of framework: Next Steps Road-testing of draft assessment framework: Individual NAMA proposals Portfolios of Mitigation Actions/NAMA proposals Development of online assessment tool, allowing for customization by users for, e.g.,: scanning and priorization of portfolios; ex ante evaluation of NAMA proposals. Excel-based draft version readily available, can be shared with interested stakeholders. 18
Evolution of the system Exchangeability of NAMA carbon assets in carbon markets Comparability of NAMAs (nationally, regionally, best in class) Prioritization of a NAMA portfolio 19
Thank you! Marcos Castro R. Climate Change Specialist mcastrorodriguez@worldbank.org Climate Change Group, World Bank 20