Understanding Cell Organelles and Their Functions
Cell organelles play vital roles in the functioning of both animal and plant cells. From the cell membrane that controls the exchange of materials to the nucleus that governs cell activities, each organelle contributes uniquely. The cytoplasm provides a supportive environment for organelles, while the endoplasmic reticulum facilitates material movement. Ribosomes aid in protein synthesis, and the Golgi body modifies and packages proteins. Mitochondria generate energy, and lysosomes help in cellular waste breakdown. This detailed overview sheds light on the intricate world of cell biology.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
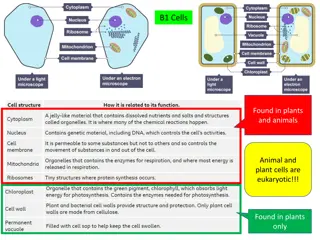
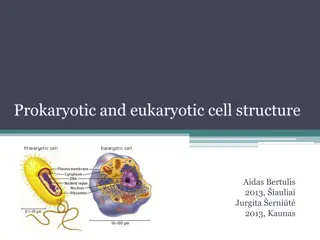
Organelles Jobs: transport proteins, releasing E, Control enter and out , balance of water Animal and planet cell Membrane of organelles : found in Eukaryote. But not in Prokaryote. Cell Membrane: Outer boundary, surrounds cytoplasm, separate cell from environment Description : double phospholipid layer , with some pores Function : Control in and out of materials , food, oxygen, wastes, and cell product, flexible and can change shape under pressure
Nucleus : Eukaryote have but Prokaryote not Location : found within cytoplasm, separated by cytoplasm by nuclear membrane Discription : largest organelle in cell , made up 3 part 1 nuclear membrane 2 chromosomes 3 nucleolus Function : controls all of the cell activities Cytoplasm : found inside a cell but outside of nucleus , Desctiption : clear, thick, jellylike, contain large amount of water (70%) , sometimes appear grainy organelles Function : contain all the organelles outside of nuclei, its moving constantly streaming
Cytoskeleton: find in cytoplasm containing long tubes and fibers made of protein Function : support cell shape, help cell moving EndoplasmicReticulum (ER) Extends from nuclei to the cell membrane , found within cytoplasm, usually near nucleus, Description : folded, tube like membrane, has ribosome on it , smooth, Function : move materials (specially proteins) , acts as a transportation system
Ribosoms : most attached to ES some are free Description: small grain like , utilize in protein synthesis from DNA GolgiBody: found in cytoplasm, Description : flat, membrane covered, look like a smooth ES. Function: sort and modify proteins from ES to different job, package cell products into vesicles for transport and this vesicles are stack to cell membrane for export outside
Mitochondria: found in cytoplasm Decription: rod shape , folded inner membrane Function : release E in food using glycolysis pathway in presence of oxygen ( ATP) Called the powerhouse of the cells , More active cells have more mitochondria Lysosome: commonly in animal cell and rare in planet, found in cytoplasm Description : small, round structure, filled with digestive enzyme . Function : break down large food molecules into small ones , the can inter mitochondria and digests waste , dead and injured cells ( cell material can be reused) act like self destruction
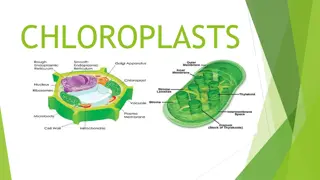
Vacuole : found in cytoplasm, large, round, fluid filled sac, Planet have one very large vacuole animal have a few one Function: storage area for food, water, wastes and other material Full filled of planet vacuoles with water Cellwall : only in planet, found outside of membrane , strong and stiff, made of boundless of non-living cellulose fiber, often remain after cell dies. Chloroplasts : only in planet, found in cytoplasm , Description : large oval-shaped , contain green pigment (chlorophyll ) , Function : food making in planet cells, use sun s energy and combine CO2 to make sugar , and this process called photosynthesis , these are a reason that planet green