Understanding Aerobic Respiration and Cell Structures
Explore the process of aerobic respiration, why we need oxygen for energy production, and the importance of cell structures in this metabolic pathway. Discover the role of key organelles like mitochondria and the cell membrane, as well as the differences between animal and plant cells in respiration. Engage in activities and self-assessments to solidify your knowledge on cellular respiration.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Aerobic Respiration Progress Indicators: State the word equation for aerobic respiration Describe the process of aerobic respiration Do Now Activity: What is respiration?
Your body uses energy all the time, without energy your cells quickly die. Energy Released You obtain energy from your food, your cells break down food molecules glucose to release the energy Oxygen is needed for aerobic respiration, this is transported to your body cells in your blood Why do you breathe faster Why do you breathe faster when you exercise? when you exercise? Write you ideas down Write you ideas down from your lungs.
Task: Watch the video, we will play the video twice but try to complete the questions whilst watching it. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZkqEno1r2jk Growth and repair of cells Protein synthesis Muscle contraction Sending nerve impulses Aerobic respiration means with air and so needs oxygen to occur, anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen to occur. Energy released during respiration is used to make ATP Animals get the oxygen they need for respiration via lungs. Plants take in oxygen from their surroundings via tiny pores on the underside of the leaf Animals and plants both respire through the day and night. Plants will only photosynthesise in the day when there is light available.
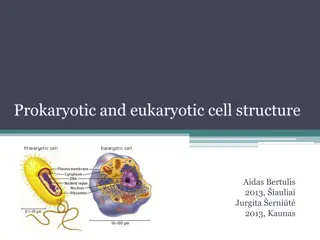
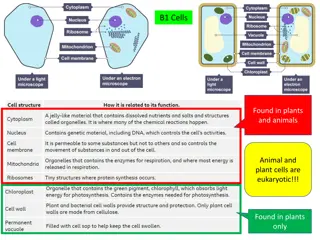
Recap: Cell Structure Plant Cell Animal Cell Task: Complete labels to correctly identify the structures found in animal and plant cells.
Self-assessment: Plant Cell Cell Wall Nucleus Mitochondria Cytoplasm Chloroplast Vacuole Cell Membrane Animal Cell
Cell structures needed for aerobic respiration Where enzymes are made. The site of reactions in anaerobic respiration Allows gases and water to pass freely into and out of the cell. Controls the passage of other molecules Task: Match the description of the part of the cell to the correct structure. Holds the genetic code for enzymes involved in respiration Contains the enzymes for aerobic respiration
Allows gases and water to pass freely into and out of the cell. Controls the passage of other molecules cell membrane Contains the enzymes for aerobic respiration - mitochondrion Holds the genetic code for enzymes involved in respiration - nucleus Self-assessment Where enzymes are made. The site of reactions in anaerobic respiration - cytoplasm
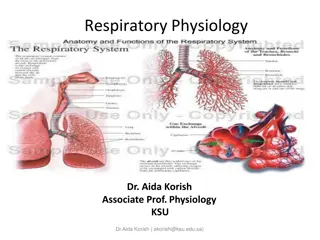
How does glucose and oxygen get into cells? Task: Read the information sheet and answer the following questions in your books: a) Describe the journey of a glucose molecule from your food to a cell, to be used in aerobic respiration. b) Why can t a starch molecule be absorbed into your blood stream? c) Describe the journey of an oxygen molecule from the air to a cell, to be used in aerobic respiration.
How does glucose and oxygen get into cells? How does glucose and oxygen get into cells? Glucose is a carbohydrate found in food. As your food is being digested, larger molecules (e.g. starch) get broken down into smaller molecules of glucose. Glucose is a carbohydrate found in food. As your food is being digested, larger molecules (e.g. starch) get broken down into smaller molecules of glucose. These molecules eventually pass through the wall of the small intestine and into the blood stream, it is carried to your cells in the plasma (liquid part) of your blood. These molecules eventually pass through the wall of the small intestine and into the blood stream, it is carried to your cells in the plasma of your blood. When you breathe in, oxygen passes into your lungs, moves across the wall of your lungs and into your bloodstream. When you breathe in, oxygen passes into your lungs, moves across the wall of your lungs and into your bloodstream. Oxygen is carried around your body by red blood cells, it binds to a special chemical called haemoglobin. When it reaches a cell requiring oxygen, the oxygen diffuses into the cell. Oxygen is carried around your body by red blood cells, it binds to a special chemical called haemoglobin. When it reaches a cell requiring oxygen, the oxygen diffuses into the cell.
Plenary ~ Take a minute! Spend a minute talking to the person next to you about what you have learnt today!