Cellular Processes and Functions Explained
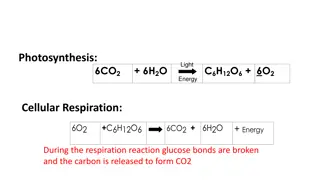
The cytoplasm is essential for cell function, housing organelles like chloroplasts and vacuoles unique to plants. Mitochondria facilitate cellular respiration, while amino acids form proteins. Enzymes are proteins, and carbohydrates consist of simple sugars. Basic pH numbers range from 8 to 14. Starch breaks down into glucose. The cell membrane regulates cell transport. Explore diffusion, osmosis, and passive transport for a deeper understanding of cellular movement.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DO NOW- quick answers! What is the function of the cytoplasm? Name 2 organelles found only in plants: What process happens in the mitochondria? Amino acids are the building blocks of . What type of biological molecule are all enzymes? What are the building blocks of carbohydrates? What numbers on the pH scale are basic? What can starch be broken down into? What is the job of the cell membrane?
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport Science Practice- Day 3 Coach Taylor & Coach Feil
Passive Transport Movement across the membrane that does NOT require energy
Diffusion The movement of substances from a high concentration to a low concentration
Diffusion The movement of substances from a high concentration to a low concentration Moving from where there is more of something to where there is less of something
Diffusion The movement of substances from a high concentration to a low concentration Moving from where there is more of something to where there is less of something Molecules will move across the membrane until the concentration is equal on both sides of the membrane Molecules will diffuse until they are in equilibrium
I I I I I I I I
Osmosis The diffusion of water Water flowing from a high concentration to a low concentration
Osmosis The diffusion of water Water flowing from a high concentration to a low concentration NO ENERGY REQUIRED
Onion (plant) Cells: When an onion cell is placed in a salt water solution, water will leave the cell. The cell membrane will shrink as water leaves the cytoplasm THE CELL WALL WILL STAY THE SAME
CELL WALL CELL MEMBRANE CYTOPLASM
CELL WALL CYTOPLASM CELL MEMBRANE
DISTILLED WATER (100% H2O, Fresh Water, Pure Water)
Active Transport Movement from a LOW concentration to a HIGH concentration From where there is LESS to where there is MORE ATP is required!!!! Against the concentration gradient
Cell Membrane The cell membrane is the organelle that controls what enters and leaves the cell Selectively Permeable Permeable- Able to pass through
Permeable- small molecules, C6H12O6, H2O, O2, CO2 NOT permeable- big molecules, STARCH