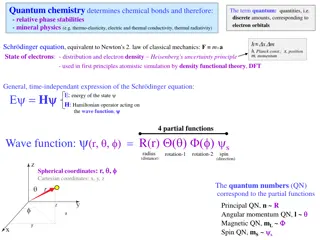
Quantum Interactions: Electrons, Phonons, and Hubbard Interaction
Exploring the complexities of electron-electron and electron-phonon interactions, nonequilibrium Green's functions, Hartree-Fock method, Coulomb's law, quantum operator forms, Hubbard interaction, and electron-phonon interactions from first principles. The interactions delve into the behavior of charges, quantum operators, and modes, highlighting key principles in quantum mechanics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Week 4 Electron-electron, electron- phonon interactions, nonequilibrium Green s functions, Hartree-Fock method
Coulombs law between charges q1, r1 q2, r2 1 1 2 q q r = = = F m 12 1 ( , ) r r , 4 1 (atomic u nits), 8.854187813 10 V 1 2 0 0 r 4 0 1 2 r ( ) = = 1 = 2 ( ) r r r r , , ( ) ( ) V q q 1 1 1 2 1 2 0 = = = = E E F E , , q V 1 0
Coulomb interaction in quantum operator form = = = j j q n , , (for electron) q c c c c q e j j j j j j 1 1 ? = = 1 2 q q , 1 2 q q 1 2 1 1 2 2 q q c c c c v ij 4 r r 0 i j N N N N ( ) = = + j j i ij i v c cc c ij i v c c c c ij i v c c ij i v c c c c i j ij j j ij j j i = = = = , 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 i j i j i j i j c c 1 2 N e ( ) 2 = + = = 1 2 N , , , , H c Hc ij i v c c c c c c c c c j j i 2 = , 1 i j c N
Hubbard interaction Onsite interaction: putting two electrons of the same spin on the same location is not possible due to Pauli exclusion principle. Putting two electrons on the same site must have opposite spins. = 0 c c j j j j Uc c c c j j = j Un n j
Electron phonon interaction, a simple consideration (SSH type) tc c + + + i i i h.c. ( ) h.c. tc c gc c u u j j j i j hopping t = + + 2 ( ) ( ) t a '( ) t a ( ) ( ) t x x M u u O u j i j i = = + , x M u x a M u i i j j distance
Electron-phonon interaction, first principles 1 2 ( ) Problem: work out the explicit relationship between real space and mode space representations of the Hamiltonian. = + + + T j 2 H c Hc p u Ku c M c u j j 1 2 k q = + + n v c c k a a q k k q q n n v v n v 1 N ( ) + + q v mn m v ( ) k g c c a a + k q k q q n v , , , , m n k q n,k ,q R ( ) R 1 M H = k ij g | | e M i j k k m,k+q
Electron Greens function of a single mode 1 i dc dt i i t = = = = , [ , c H ] , ( ) c t (0) H c c c c e i i i i t i t = = = ( ) ( ) (0) c t c (1 ) g t e cc e f 1 1 i i i t = + = = = = ( ) (0) ( ) c t , , g t c e f f c c + ( ) 1 e k T B i i t = = , ( ) 1 if = r ( ) ( ) t ( ) ( ) ( ) t e 0 and 0 if 0 g t g t g t t t t i i t = = t e a ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) g t t g t g t = = + + t g t = = + + = = + = t r r a ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) t g t ( ) ( ) ( ( ) ) t g t ( ) ( ) g g g g t g t t g t g g g g g g g g iA t r t tg
Electron Greens function of a single mode, go into E space + + E E dE i t i t = = = ( ) g E ( ) ( ) ( ) g E e , / g t e dt g t E 2 = = = = 2 ( ) E 2 ( )( 1) 1 = g i E f i ( ) E 2 ( ) ( ), ( ) A E 2 ( ) g i E f i f A E E + E 1 i i i t i t t + = ( ) t e = = * r a ( ) ( ) E 0 g E e dt g + E = = + + = = + = t r r a g g g g g g g g g g g g g g iA t r t t
Greens functions of many degrees, diagonalize H H H H H H c c 11 12 1 1 N ( ) 21 22 2 = = 1 2 N , , , H c Hc c c c H H c 1 N NN N N = = = = i c H c H H S S SS I ij j = , 1 i j 0 0 1 0 ( ) 2 = = = , , , , , S HS H S 1 2 n n n N 0 0 0 N d d 1 N 2 = = = = n , H c Hc d d d S c n n = 1 n d N
Many degree Greens function i i as N N matrix = = k ( ) t ( ) (0) or c t c ( ) ( ) (0) c t c G G t jk j = = = = m , , , (1 ) c Sd c d S S HS d d f n n nm m , , , , , a r t t , , , , , a r t t = ( or ) t ( or ) t G E S g E S , , r a t ( ) t dG ( ) 1 = + i = , ,( ) r r a t ( ) ( ) , ( ) t I G E E I H i HG t dt
Fluctuation-dissipation theorem in thermal equilibrium = = r a ( ) ( ) f E ( ) G E G G if A E Prove this important result using the Lehmann representation. 1 ( ) = = a r ( ) f E , G G + ( ) E 1 e ( ) = = ( ) E G G e G G
Greens function, complex z i = ( ) t e = / / r iHt iHt ( ) compare: ( ) (0) G t t e N ( ) 1 = = n n ( ) z (resolvent of ) G z zI H H z = 1 n n + i r Retarded Advanced ( ) is obtainef if ( ) is obtained if G E G E z E i a z E + (2 1) n + = = 0, 1, 2, M Matsubara ( ) is obtained if , , G z i n n n n
Equation of motion of (free) Green s functions , , r a t ( ) t dG = , , r a t ( ) t ( ) t I i HG Problem: Prove this from the definitions of Green s functions, with the Heisenberg equation of motion for c, ? ?? dt , ( ) t dG = , ( ) t 0 i HG dt ??= ??. t ( ) dG t dt = t ( ) ( ) t I i HG t
Contour ordered Greens function + - ( ) ( ') if c ' c i i ( , ') = ( ) ( ') c = G T c ( ') ( ) if ' c c ( , ), t = + + ++ + t G G G G G G G G ( , ') = = = ' ' ( , ') t t ( ') G G G t t + t
Equation of motion on contour ? + ? + ( , ') G ( , ') = ( , ') i HG I ( , ') ' = ( '), 1 t t ( , ) t
Handle Coulomb interaction, the simplest way, mean-field theory 1 2 = + 2 j k H c Hc e v c c c c jk k j jk j k c c c c j k j k c c k c c c c c c k j k j j + = HF 2 k j 2 j k c c k H c Hc e v c c c c e v c c c H c jk k j jk j jk jk Hartree tern Fock term
Hartree and Fock self energies m j k = F jk 2 k e v c c jk j j = + + HF H F H H = H jk 2 m m c c e v jk jm m HF H c H c
Greens function in Hartree- Fock approximation + = HF 2 k j 2 j k c c k H c Hc e v c c c c e v c c c H c jk k j jk j jk jk 1 = + i + + r 2 k ( ) ( ) G E E H e e v c c jk jk j jk jk j jk 1 1 = = = k ( ) , e v c c f E j jk k + ( ) E 1 e k T k B + i ( ) = = * iEt r jk r kj k / ( ) E (0) ( ) c t ( ) f E G ( ) ( ) E G c e dt E G jk j + dE = = = HF n k * kn ( ) E ( ) , ( ) j c c i G S f S S j jk jn jn n 2 n
A computational procedure for Hartree-Fock self-consistency 1) Compute ???matrix, set the Coulomb interaction terms (Hartree and Fock terms) to 0 in the first step. 2) Solve the eigenvalue problem ??? ?= ?? ?. Normalize ? to 1. 3) Compute ?? 4) Go back to 1). Repeat until energy and eigen functions are converged. ?? = ? ?? ?(??) ? (?).
Solve the benzene ring with PPP model using Hartree-Fock? Need spin! 1 2 6 = + + i h.c. ( 1)( 1) H t c c V n n + 1, ' i ij i j = = , , , ' i j 1, , i U = V ij + 2 r r 1 | | i j