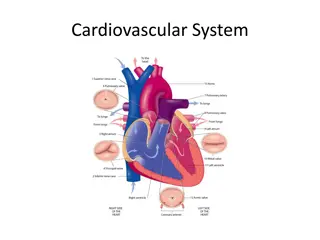
Microscopic Structure of Blood Vessels and Their Layers
The lecture covers the microscopic structure of the wall of blood vessels including large veins, elastic arteries, muscular arteries, and blood capillaries. The three concentric layers of blood vessel walls are discussed, which include the tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia. Detailed information on the composition of each layer and the differences between veins and arteries is provided.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Histology of the Histology of the Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Color index: -Main text -important -female slides -male slides -Dr.note -Extra Editing file 2 Cardiovascular Block | Histology Editing file
Objectives Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to identify and describe the microscopic structure of the wall of the blood vessels including: 01 01 04 04 Large veins. Elastic arteries. Muscular (medium-sized) arteries. 05 05 02 02 Blood capillaries. 03 03 Medium-sized veins.
Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries: Arteries: Elastic Artery/ Muscular Artery ( Distributing)( Medium-Sized)/ Arterioles. Blood Capillaries. Blood Capillaries. Veins: Veins: Large Veins/ Medium-Sized Veins/ Small Veins/ Venules.
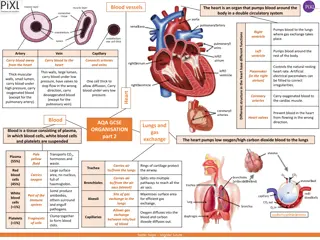
General Structure of Blood Vessels General Structure of Blood Vessels The wall of blood vessel is formed of three concentric layers: The wall of blood vessel is formed of three concentric layers: Tunica intima (Interna) Tunica intima (Interna) Tunica media Tunica media Tunica adventitia (Externa) Tunica adventitia (Externa) Innermost layer composed of: Intermediate layer composed of: Outermost layer composed of: C.T containing Vasa vasorum, which are: Endothelial cells: Simple squamous epithelium. Subendothelial layer: Loose C.T. Internal elastic lamina: fenestrated elastic sheet. Smooth muscles: Helically arranged. Elastic fibers. Type III collagen (reticular fibers). Type I collagen. Small arterioles in tunica adventitia. At the outer part of tunica media. More prevalent in the walls of veins than arteries, Because: Venous blood contains less oxygen and nutrients than arterial blood. NB: Large muscular arteries have external elastic lamina elastic lamina, separating the tunica media from the tunica adventitia. external
Muscular Arteries Muscular Arteries (Medium (Medium- -Sized Arteries) Sized Arteries) Microscopic Structure Microscopic Structure Elastic Arteries Elastic Arteries Endothelium Subendothelial C.T Internal elastic lamina: Not prominent Not prominent Indistinct Endothelium Subendothelial C.T Internal elastic lamina: Prominent Prominent Display an undulating surface T. Intema T. Intema Fenestrated Elastic Fenestrated Elastic Membranes (sheets or lamellae): (The Main component) (The Main component) Thicker than T. Adventitia or similar in thickness Smooth muscle cells (SMCs): Smooth muscle cells (SMCs): (The Main component) (The Main component) In between there are: In between there are: Elastic fibers. Elastic fibers. Type III collagen fibers Type I collagen fibers External External elastic lamina: may be identifiable. In between, there are: In between, there are: Smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells. Reticular fibers (Type III collagen) Collagen fibers (Type I collagen) Elastic fibers. T. Media (T.M): T. Media (T.M): Thinner than T.M. Composed of Loose C.T Contains Vasa Vasorum Send branches to the outer part of T.M Loose C.T T. Adventitia (T.A): T. Adventitia (T.A): Composed of Loose C.T Loose C.T Aorta Common Carotid Subclavian Common iliac Pulmonary Trunk Brachial Ulnar Renal Examples of Arteries Examples of Arteries
MEDIUM MEDIUM- -SIZED VEIN SIZED VEIN MEDIUM MEDIUM- -SIZED ARTERY SIZED ARTERY AND VEIN AND VEIN their wall is their wall is thinner artery. artery. thinner than the accompanying than the accompanying Usually forms valves No internal elastic lamina T. Intima T. Intima Thinner Thinner than T. Adventitia Consists of: - Fewer SMCs - Types I & III collagen fibers. T. Media T. Media Valves of veins Valves of veins is composed of 2 leaflets T. Adventitia T. Adventitia thicker thicker than T. Media 2 leaflets Each leaflet has a thin fold of the T. Intima. Components: Components: Endothelium Veins have more numerous vasa vasorum than Arteries Core of C.T.
Blood Capillaries Blood Capillaries - - Diameter: Diameter: usually 8-10 m. Microscopic structure: Microscopic structure: 1. Single layer 1. Single layer of squamous endothelial cells. 2. Basal lamina: 2. Basal lamina: surrounds the external surface of the endothelial cells. 3. Pericytes: 3. Pericytes: Have processes. Share the basal lamina. Act as stem cells. Types of Blood Capillaries Types of Blood Capillaries
Distribution Distribution (important) (important) Types of Blood Capillaries Types of Blood Capillaries Microscopic Structure Microscopic Structure muscles nervous T. C.T. No pores or fenestrae in their walls. Continuous Continuous The walls of their endothelial cells have pores (fenestrae). Intestine Pancreas Endocrine glands With diaphragms With diaphragms These pores are covered covered by diaphragms. Fenestrated Fenestrated The walls of their endothelial cells have pores (fenestrae). In renal glomerulus. Without diaphragms Without diaphragms These pores are NOT covered NOT covered By diaphragms. Their endothelial cells have fenestrae without diaphragms. They possess discontinuous endothelial cells. They possess discontinuous basal lamina. Macrophages may be located in or along the outside of the endothelial wall. Red bone marrow liver spleen certain endocrine glands. Sinusoidal Sinusoidal Diameter: irregular (30 Diameter: irregular (30- -40 m). 40 m).
Summary Summary Tunica intima Tunica intima (interna) (interna) Tunica adventitia Tunica adventitia (externa) (externa) Tunica media Tunica media Elastic Elastic Arteries Arteries 1) Fenestrated Elastic Membranes 1) Fenestrated Elastic Membranes Much Thinner than T.Media. Much Thinner than T.Media. 1) Endothelium 1) Endothelium 2) Subendothelial C.T. 2) Subendothelial C.T. 3) Internal elastic lamina 3) Internal elastic lamina - - (Not prominent) (Not prominent) 2) In between, there are: 2) In between, there are: Smooth muscle cells Collagen fibers (Type l) Reticular fibers (Type lll) Elastic Fibers Composed of loose Composed of loose C.T. Contains vasa vasorum C.T. Contains vasa vasorum Thicker than T.Adventitia or similar in Thicker than T.Adventitia or similar in thickness. thickness. Muscular Muscular Arteries Arteries 1) Endothelium 1) Endothelium 2) Subendothelial C.T. Layer 2) Subendothelial C.T. Layer 3) Internal Elastic Lamina 3) Internal Elastic Lamina - - (Prominent) (Prominent) 1) Smooth muscle cells 1) Smooth muscle cells 2) In between, there are: 2) In between, there are: Elastic fibers Collagen fibers (Type l) Reticular fibers (Type lll) External elastic lamina Loose C.T Loose C.T Usually forms valves Usually forms valves No internal elastic lamina Composed of 2 leaflets each leaflet has a thin fold of T. Intima which contain: Endothelium Core of C.T. Thinner Thinner than T. Adventitia Medium Medium- -sized sized veins veins Consists of: Consists of: Fewer SMCs Types I & III Collagen fibers. - - thicker thicker than T. Media 1. 2.
Test yourself: Test yourself: Q1: What is the thickest layer of blood vessel? A) Tunica intima (interna) B) Tunica media C) Tunica adventitia D) Tunica (externa) Q2: What type of collagen is found in the tunica media? A) Type 1&2 B) Type 2&4 C) Type 1&3 D) Type 1&4 Q3: In which one of the following the Internal elastic lamina become prominent ? A) Elastic artery B) Muscular artery C) Large artery D) Both A&B Q4: Where is the location of Fenestrated blood capillaries without diaphragm? A) Endocrine glands B) Red bone marrow C) Liver D) Renal glomerulus Q5: How many leaflets in the valve of a vein ? A) 2 leaflets B) 3 leaflets C) 4 leaflets D) 6 leaflets Answers: 1)B 2)C 3)B 4)D 5)A
Meet the team Meet the team Team leaders Rand Jarallah Abdulaziz Alnasser Team members Leena binabbad Shahad almarshad Noura bin hammad Layan Alburikan Saad AlAngari Saud Al Taleb Abdullah Alqarni Faisal Al Omar Cardiovascular Block | Histology 442Histology@gmail.com