Understanding the Concept of Population and Unit Stock
The concept of population revolves around all organisms of the same species living in a specific area capable of interbreeding. It is essential to differentiate between sample populations and real populations to accurately study their attributes such as birth rates, death rates, and spatial dimensions. Factors like natality, mortality, dispersion, and ecological influences play crucial roles in determining the size and growth of populations. Various terms like meta-population, absolute population, and population density further enhance our understanding of this fundamental ecological concept.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Concept of Population & unit stock
Concept of Population: Population: Population is all the organisms of the same group or species who live in a particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. Sometimes, due to unavoidable bias it may be necessary to differentiate between a sample population population, where the sample population consists of the objects that have an equal probability of being selected. and the real
Cont.. o Population is the breeding unit of species having common spawning grounds. o A population is a group of individuals of the same species that live together in the same place, and that posses an average set of properties, such as birth rates and death rates.
Cont The simplest and least restrictive definition of population is that a population is a group of individuals of the same species that live together in a particular area (e.g., Roughgarden, 1989). However, even though this definition is widely used by ecologists, it gives rise to serious difficulties and misinterpretations.
Cont A more rigorous definition should define the spatial dimension more precisely; for example, a group of individuals of the same species that live together in an area of sufficient requirements for reproduction, migration can be met (e.g., Huffaker et al. 1984). size that survival all the and Local population is a group of organisms of the same species that live together in an area where there is a high probability of interbreeding.
Cont Meta-population is a group of populations that share occasional migrants. Absolute population is an estimate of the total number of organisms in an area. Population density is an estimate of the number of organisms per unit area (e.g., hectare) or unit of habitat.
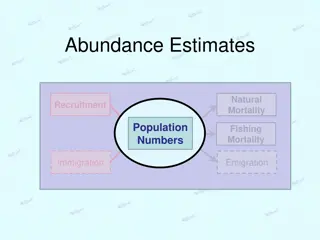
Cont Size of population is determined by growth which is influenced by natality ( + influence) mortality ( - influence) and dispersion ( + & - influence). There are various ecological density dependent and density independent factors that are the factors that controls the growth. For the purpose of fitting yield models, males and females of the populations are treated as separate units, if differences exist in all morphological and biological characters.
Cont.. For modelling purposes, population of different species coexisting in a particular area having similar characters can sometimes be treated as a single stock. Assessment could be made on stock of a species, only when biology of species is clearly understood which includes its feeding, growth, spawning and migration habits.
Malthusian theory of Population Malthusianism is the idea population growth is exponential the growth of the food supply other resources linear. that potentially while or is
Concept of a unit stock: A stock is a sub set of a species . The basic purpose of fish stock assessment is to provide suggestions exploitation of aquatic living resource such as fish and shrimp. A stock is sub set of a species which is generally considered as basic taxonomic unit. on the optimum
Cont.. Stock is a subset of one species having the same growth and mortality parameter, and inhibiting in a particular geographical area. A stock as an intraspecific group of randomly mating individuals with temporal or spatial integrity . (Ihssen at al.,1981)
Shared stock: Several countries may exploit the same stock. This is the case for many migratory stock, e.g. tunas National stock: o Fish stock exploited by a particular country.
Why does the stock unit often fail..? 1. The full distribution area of the stock is not covered by the data collected, so that only part of the stock is considered. This is a typical example where several independent fisheries are exploiting the same stock. 2. Several together, for example, because their areas of distribution overlap. independent stocks are lumped
3. Continuous immigration and emigration of the components of one or more stocks from the fishing ground. Taking into account that most of the exploited marine resources undertake migration, an essential element to perform stock assessment is an understanding and knowledge of migration routes.