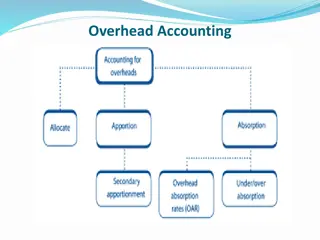
Understanding Overhead Costs in Accounting
Overheads in accounting consist of indirect materials, labor, and expenses not directly attributable to a specific cost object. They play a vital role in budgeting and pricing strategies for businesses. Overheads can be classified based on elements and functions, such as factory overhead, office and administration overhead, and selling and distribution overhead. Each category encompasses various expenses essential for business operations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Overheads- it comprise of indirect materials, indirect labor and indirect expenses which are not directly identifiable or allocable to a cost object in an economically feasible way. -Overhead refers to the ongoing business expenses not directly attributed to creating a product or service. It is important for budgeting purposes but also for determining how much a company must charge for its products or services to make a profit
Classification of overheads- overheads may be classified on different basis some of them are as follow- 1) According to element- there are three elements of cost Material , labor and expenses. On this basis overhead may be classified as indirect material , indirect labor and indirect expenses 2) According to function- on this basis overhead are of three type. a) Factory overhead- it is also called works overhead and production overhead . Under this basically three expenses are included - indirect material, indirect labor and all those indirect factory expenses that are incurred in factory. In general terms the following expenses are included in factory overhead-
1) Rent of factory building 2) Municipal tax on factory building 3) Insurance of factory machine , building etc.. 4) Depreciation on factory assets 5) Production planning, salary to staff of factory 6) Factory administration 7) Loose tools related to factory 8) Normal loss of idle time 9) Factory lighting and power 10) lubrication grease etc. 11) paid holidays 12) Haulage of machinery 13) Expenses of clerical work 14) any R&D expenses if they are not direct by nature 15) expenses on the maintenance of store 16) Normal loss or wastage of material 17) Drawing office salary if this is not considered direct
2) Office and administration overhead- this includes expenses that is related to operation policy implementation, and administration of office. This includes the following expenses- 1) Administrative and account staff 2) Depreciation repair of office machinery, building etc.. 3) Office lighting 4) Repair of office furniture 5) Postal exp, telephone fax stationary etc.. 6) Legal exp, financial exp, bank charges, sundry exp. 7) Computing office exp.
3) selling and distribution overhead- these are two expenses selling expenses are those expenses that incurred to create demand for the product while distribution expenses are those that are incurred to carry goods from business godown to customer. Collectively , they are called marketing overhead. a) Selling overhead- the followings are the selling overhead- 1) Advertisement 2) Sampling sending expenses 3) Warranty claim, after sale service 4) Packaging , marketing research, showroom exp 5) Royalty on sale, special discount , etc..
B) Distribution overhead- 1) Transportation exp., carriage outward 2) Expenses on delivery van, depreciation on it 3) Godown exp like rent depreciation repair, salary to employees, insurance of goods 4) Loss of finished goods in godown 5) Any other expenses that smoothens the process of distribution
3) According to behavior or nature- on this basis overheads may be classified in three categories 1) Fixed overhead- these do not get effected by the quantity produced they are related to a particular period that is why they are called period cost . 2) Variable overhead- the overhead that changes with the change in the quantity produced. Such overhead increases if the quantity produced is increase and decreases with the decrease in the production. Example- material , labor expenses lighting and heating etc..
3) semi variable or semi fixed- the expenditure which have both fixed and variable nature are called semi variable overheads. Semi-variable costs consist of both fixed and variable costs. Part of the cost stays consistent (often a base cost) and part fluctuates with business activity. Examples include commission payments and overage charges. Commissions are a semi- variable labor costs
4) according to controllability- A) controllable overheads B) un controllable overhead Treatment of different type of overhead Interest on capital- there are many disagreement among the scholar regarding its treatment but this can be recorded in following way 1) Interest paid on capital is included in the cost but outstanding interest is not included 2) Both Paid and unpaid interest on capital are included in the cost. 3) Both paid or outstanding interest on capital is included in cost.
Depreciation- it is diminution in the value of assets due to lapse of time, wear or tear or obsoletion. This is also included in the overhead. The main question here arises that if machine remains working even after the completion of its life span and even after the value of machine become equal to its residual value then what should be done? The answer is that the assets should be revalued again and then depreciation should be charged. Rent of factory- if any factory has been taken on rent then rent paid on it itself becomes part of overhead but if the factory building belongs to owner himself then what should be done? the answer is that a notional rent should be charged as overhead. Because it gives actual picture of organization's financial health. But if depreciation on the building is more than the rent then, of course, depreciation should be charged to overhead in place of rent .
Material carriage handling and storage- if carriage has been paid for the purchases of a particular material then it becomes the part the material but if carriage inward is for various material then it is considered as overhead. Raw material handling, loading or unloading of material etc. should be considered as overhead. Storage expenses includes salary of employees, depreciation and loss of store material. These all are considered as overhead] Material waste and losses- organization may face loss in three place say in transit loss , during storage, during manufacturing If the loss is of natural then it is charged to overhead and if it is abnormal loss then it is transferred to profit and loss account.
Drawing office expenses- these are directly charged as overhead Expenses of erection and dismantling of plant and machinery- if new machinery Is bought or erected then expenses on it is considered as capital expenditure but if there is dismantling of machinery or plant to shift from one place to another then it is considered as overhead. Dismantling of an obsolete machinery is also considered as overhead Compensatory payment to workers- this is considered a loss for the company so being an abnormal loss it is transferred to profit and loss account but where compensation is paid regularly then a provision should be made for it and it, then, should be considered as overhead
Dearness allowance- this is considered a part of the salary so it should be transferred to respective overhead as per the nature. Maintenance or repair cost- it is of two type say preventive and second corrective. The first one is for to maintain the machine in good condition and the second one is to correct the defect in the machine if any. This is considered as overhead of its respective cost centre. royalty and patent - if royalty is paid to use special right in the assets then it Is treated as factory overhead while when royalty is paid to use selling right of the assets then it is called selling overhead
Research and experimental expenses- this is treated as overhead but if R&D has been done for a particular product then it should be charged to that product as direct expenses. If a huge amount has been spent on the R&D activity then it should be treated as deferred expenditure If the R&D activity has been proven useless there arises no any benefit from then it should be transferred to profit and loss.
Cost of defective or spoiled work- defective work means quality of product below the standard level. A proper investigation should be done to find out reason of defect. A separated account named cost of defective work should be opened. If the defective is due to bad quality of raw material then discount given by the supplier should be credited to cost of defective work a/c If defect Is due to carelessness of employees and any penalty has been charged on them then this amount should be credited to above mentioned account.
If defective work is due to R&D activity then it should be treated in already mentioned way If defective work can not be corrected then it should be sold out and loss on it should be consider as overhead If defective work can be corrected then any expenses on it should be charged to rest of product produced. If defective work is due to abnormal reason then it should be charged to profit and loss a/c
Advertisement it is part of overhead. If huge amount is spent for the advertisement then it should be treated as deferred expenses and every year it should be transferred to selling overhead Bad debt when it is of normal nature or within a particular limit then it should be considered as overhead but if it is abnormally large amount then it should be transferred to cost profit and loss account. Carriage outward and carriage on return- if there is any expenses regarding carriage outward then it should be included in the bill and should be collected from the customer
In case of carriage on return if goods has been returned by the customer due to defect then if should be included in factory overhead If the return of goods is due to poor packing then carriage on return should be charged to distribution overhead. If goods had been sold on return or sale basis then on return , carriage on return should be charged to selling overhead After sale service- this expenses is charged to production overhead but under some circumstances it is considered as selling overhead.
Labor welfare expenses- it is part of production overhead. Bonus and Gratuity- bonus is varied as per the salary earned but there is concept of minimum bonus that is paid irrespective to profit of the organization. The minimum bonus is considered as direct labor cost and the bonus above the minimum bonus should be adjusted from profit. Bonus related to productivity is a part of production overhead As far as Gratuity is concerned it is part of wages so it should be considered a part of cost.
Store overhead.- these are those overhead that can not be allocated to a particular cost centre but they are incurred by store department on the work like store, purchases and issue etc.. These expenditure are considered as factory overhead .
Thank you Keep learning Don t forget to subscribe my channel Commerce yuga & The fair truth