Computation of Machine Hour Rate: Understanding MHR and Overhead Rates
Computation of Machine Hour Rate (MHR) involves determining the overhead cost of running a machine for one hour. The process includes dividing overheads into fixed and variable categories, calculating fixed overhead hourly rates, computing variable overhead rates, and summing up both for the final MHR. Types of overhead rates include actual and predetermined rates, as well as blanket and multiple rates. Actual rates are computed after the accounting period, while predetermined rates are estimated in advance. Over or under absorption of factory overheads occurs when actual rates are used.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Computation of machine hour rate(mhr) MHR refers to the overhead cost of running a machine for one hour Steps for computation: 1. The overheads concerning the machine are divided into fixed & variable overheads. Fixed are those that remain constant irrespective of the useof the machine eg. rent, lighting, supervisor salary etc. variable are those that vary with the use of the machine eg. Depreciation, repairs, poweretc.
Computation of machine hour rate(mhr) 2. The fixed or standing overheads are totaled and then divided by the machine hours to obtain fixed overhead hourly rate . 3. For each variable overhead, per hour rate is individually computed. The total of fixed & variable hourly rate are summed up to give the final MHR 4.
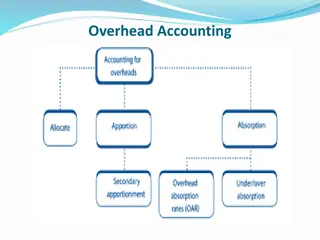
Types of overhead rates Overhead absorption rates can be : Actual & predetermined rates Blanket & multiple rates
Actual Overhead rates Actual rate: is the overhead rate arrived at after computation. actual Oh. absorption rate = actual overheads actual base The major limitation of actual rate is it cannot be computed till the end of the accounting period as a result it leads to delay in computing the cost of the product. Thereby resulting in fixing the selling price of the product.
Predetermined overhead rate Predetermined rate: is an estimated rate determined in advance and is used for computing the cost of the product and fixing the selling price. Predetermined oh. Ab. rate = Estimated amount of overheads Estimated base Facilitates cost control as the actual ohs. can be compared with the predetermined ohs. Helps to derive benefits of standard and budgetary costing
Blanket & multiple rates Blanket rate: is a single overhead rate for the entire factory. Can be used: For small firms producing single products Output is of uniform nature Blanket rate = Total ohs. For the factory Total no. of units for the factory Multiple rates: means a number of separate rates used for each deptt. or cost centre Blanket & multiple rates can be either actual or predetermined
Over & under absorption of factory overheads When the actual overheads Rates are used, the absorbed overheads will be equal to the actual overheads . Thus there are no under or over absorption of overheads. When predetermined rates are applied overheads absorbed may not be equal to the amount of the actual overheads incurred. Thus this may result in under or over absorption of overheads.
Over & under absorption of factory overheads Overabsorbtion or Over recovery of overheads: When the amount of ohs. Absorbed > amount of actual ohs Results in over stating the cost of jobs/ processes Results in over stating the cost of production Underabsorbtion or Under recovery of overheads: When the amount of ohs. Absorbed < amount of actual ohs Results in assigning lower cost to the jobs/processes Results in understating the cost of production
Causes of over & under absorption of overheads Faulty estimation of overhead cost Faulty estimation of quantity or output Faulty estimation of the base Unforeseen changes in the production capacity Unexpected changes in the methods of production Seasonal fluctuations in the amount of overheads in certain industries
Accounting treatment of under & over absorption of overheads Under or over absorption of ohs affects the COP. Under absorption understates it and over absorption inflates the COP. The methods for treating this can be : Application of supplementary rate Writing off to costing profit & loss account Carry over to the next year
Application of supplementary rate If the amount of under or over absorption is significant then supplementary oh. Absorption rate is used Supplementary oh. Rate = actual ohs. Absorbed ohs (this can be positive or negative) In case of under absorption, adjustment is done by adding this rate to the predetermined rate Actual base In case of over absorption the supplementary rate is subtracted from the pre determined rate
Writing off to costing profit & loss account This method is used: when the under or over absorbed amount is quite negligible/insignificant When it arises because of abnormal factors such as idle capacity, defective planning the under or over absorbed amount is transferred to the costing P & L A/c Major drawback is COP will either be under or over stated and will affect valuation of stocks (WIP and FG) and will get transferred to the next year
Carry over to the next year Under this method the under or over absorbed amount of overheads is transferred to overhead reserve account or suspense account and carried forward to the next year. This method is considered suitable: where normal business cycle extends to more than one year Business is of seasonal nature products The business is absolutely new
Treatment of certain items in cost accounts interest on capital Packaging expenses Bad debts Research and development depreciation
Past year questions What do you mean by absorption of ohs? Discuss different methods of absorption of factory ohs. What is the importance of machine hour as a basis for absorption of factory ohs? What are the causes of under/over absorption of factory ohs.? Explain the treatment of over & under absorption of ohs. In cost accounting? Distinguish Between allocation, apportionment & absorption of ohs.
Past year questions Discuss the treatment of the following items in the cost accounts Interest on capital Packaging expenses/ packaging material cost Distinguish between: Cost allocation & cost absorption Fixed ohs and variable ohs.