Understanding Overhead Accounting and Allocation Process
Overhead accounting involves allocating and apportioning overhead costs to different departments or cost centers in a company. This process includes dividing cost centers into production and service departments, assigning overhead costs accurately, and distributing common overhead costs proportionately. Allocation assigns specific costs directly to a cost center, while apportionment distributes shared costs among multiple cost centers.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
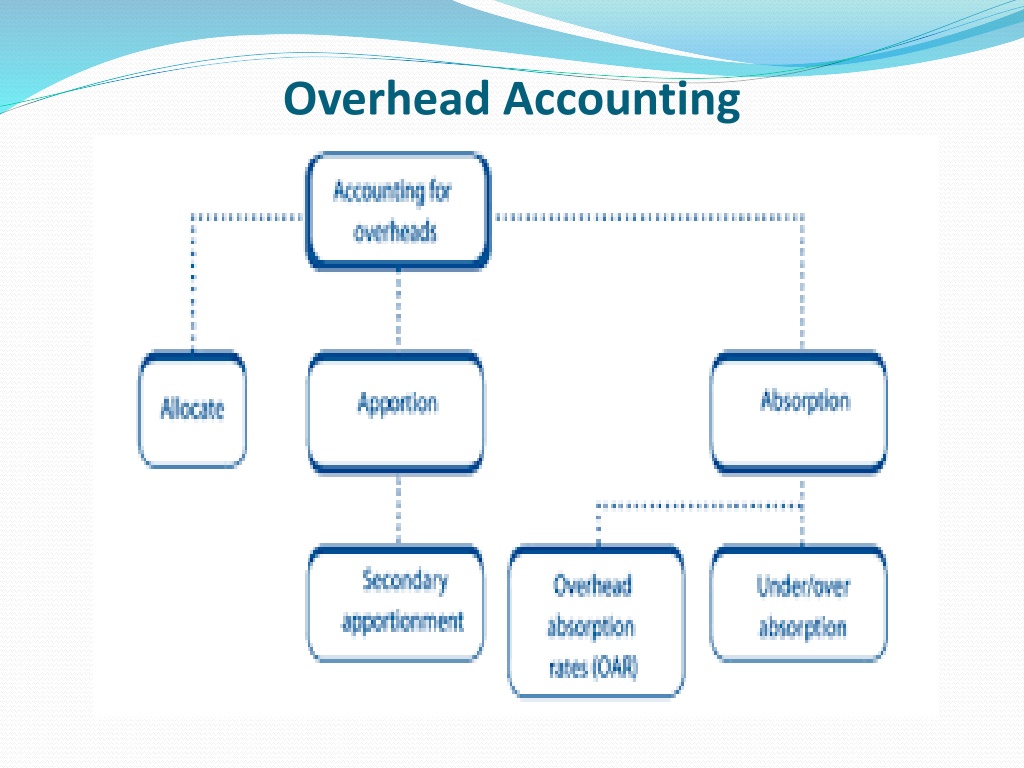
Allocation & Apportionment of Overheads After the overheads costs are collected & codified the next step is Allocation ands Apportionment. Departmentalization or Primary Distribution It is the process of allocation & apportionment of overhead cost to different departments or cost centres. Cost centres/ departments are divided into: Production deptt. Service Deptt 1. 2.
Production Department A production deptt/ cost centre: production activity by conversion of raw material into finished production. The number of such departments and their number will depend upon the nature of industry, type of work performed and the size of the factory. For example, in Steel Rolling Mill, Hot Mill, Cold Mill, Pickling Shop, Annealing Shop, Hardening, Polishing and Grinding are the producing departments. is engaged in
Service Department A Service Deptt/ costcentre : are those which are ancillary to and render service to other production and service costcentres. The number of departments in a factory and the names to be assigned to them depends upon size of the factory, nature of industry and the nature of service rendered. The service departments, common to most concerns are stores, cost office, personnel department, planning and progress department, tool room, hospital and dispensary, machine maintenance maintenance section and electrical
Allocation of overheads Allocation is the process of assigning the whole item of cost directly toa cost centre Allocation can be done only when the exact item of overhead cost in a costcentre is definitely known. For example, the whole of overtime wages paid to the workers relating to a particular department should be charged to that department or the cost of repairs and maintenance of machine should be charged to that particular department wherein the machine is located a particular
Apportionment of Overheads Apportionment refers to proportionate distribution of overheads to more than one cost centre on a suitable basis. Thus where a overhead cost is common to different cost centres, it is charged to them on a suitable basis. For eg. factory rent, insurance, factory lighting etc. may benefit a number of departments. The need to be apportioned (i.e. distribution to various departments in the factory)
Primary Distribution of Overheads Primary distribution of overheads refers to allocation and apportionment of overhead expenses among production and service departments of an organization. This process involves allocation of overheads which can be directly identified with a particular department and apportionment of common item of overheads on appropriate basis among all the departments. The entire process of allocation and apportionment is systematically presented in a perform which is known as primary distribution overhead summary or overhead distribution summary.
Primary distribution Overhead summary While preparing overheads distribution summary, it is important to note: that the direct costs of the service departments should be considered as overheads. Hence the direct material, direct labour and direct expenses of the service departments are allocated directly and recorded distribution summary since these are overheads from production point of view. in the overheads But the direct material, direct labour and direct expenses of the production departments need to be excluded from this summarysince these are not overheads.
Re-apportionment of Service Department cost (secondary distribution) Once apportioned to production & service department the next step is to reapportion the total cost of service departmenttoproductiondepartment. The ultimate objective is to charge the entire overheads to cost units as cost units are produced in the production deptt. Thus the cost of the service deptt must becharged to the productiondeptt. This is known as Secondarydistribution the overheads have been allocated or
Apportionment of service department overheads Re-apportionment of service deptt cost Re-app to prod. Deptt only Re app to prod. & service deptt Non-reciprocal basis Reciprocal basis Repeated distribution method Simultaneous equation method Trial & error method
Reapportionment to production department only This method is adopted when the various service departments render services only to the production department and there is no exchange of services among them. Do eg. 3 from S. singh pg 5.15 OR Do illustration 4.3 from MN Arora pg 4.14
Reapportionment to production as well as service deptt. This method is followed when the service department provides services not only to the production deptt but also to other service deptt. For eg. Power house service deptt provides electricity service to both production and other services department like maintenance deptt, canteen deptt., warehousing deptt etc. This type of inter-service deptt apportionment may be either reciprocal or non-reciprocal.
Reciprocal and non-reciprocal basis of apportionment Non- Reciprocal basis: is when the service deptt renders service to the production and other service deptt but does not receive services of other deptts i.e one-way flow. Service department are not inter-dependent We follow the step- ladder method: Do eg. 4 from S. singh. Pg 5.17 or ills 4.4 mn arora pg 4.16
Reciprocal and reciprocal basis of apportionment This method of apportionment is used when the service department renders service to production as well as other service departments and in turn also receives services from other service department. Service departments are inter-dependent on one another. For eg: Power house provides electricity to maintenance deptt and in turn receives maintenance from them.
Methods of reciprocal basis Repeated distribution method: refer- eg. 5 S. singh book pg 5.18 Trial and Error method: refer eg 6 S. singh book pg 5.19 Simultaneous equation method: refer eg 7 s. singh book pg 5.21