Interpretation of Batch Reactor Data for Constant-Volume Systems
This content delves into the analysis and interpretation of data from constant-volume batch reactors in constant-density reaction systems. It covers integral methods for analyzing data, considerations for irreversible reactions, and the behavior of zero-order and first-order reactions. The text also discusses the obtained linear plots and ways to fit experimental data accurately.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Interpretation of Batch Reactor Data CONSTANT-VOLUME BATCH REACTOR constant-density reaction system
V= volume of reaction mixture Conversion
Integral Method of Analysis of Data General Procedure. Irreversible Reactions. Consider the reaction Unimolecular-Type First-Order
gives a straight line through the origin for this form of rate of equation. If the experimental data seems to be better fitted by a curve than by a straight line, try another rate form because the first-order reaction does not satisfactorily fit the data.
Noting that the amounts of A and B that have reacted at any time t are equal and given by CAoXA. in terms of XA as
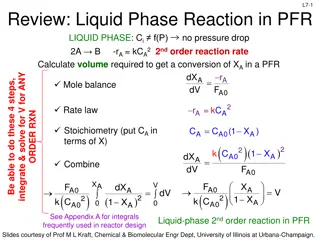
Figure below shows two equivalent ways of obtaining a linear plot between the concentration function and time for this second-order rate law.