ECMC: Open Source Motion Control with EtherCAT Overview
ECMC is an open-source motion control module designed for EPICS environments, integrating EtherLab's EtherCAT master. It offers advanced features like synchronized motion, distributed clocks, and PLC functionalities, making it ideal for various automation applications. The system architecture and ha
0 views • 42 slides
How To Use Wired Motion Sensor Closet Light
Motion sensor lights provide the convenience of constant, powerful illumination without the need to manually turn them on or off. Additionally, it saves time while looking for switches in places with low lighting that you could miss at first. Compared to traditional lighting solutions, motion sensor
1 views • 1 slides
Understanding Projectile Motion: Characteristics, Examples, and Formulas
Projectile motion involves the motion of objects under the influence of gravity, with both vertical and horizontal components. This type of motion is seen in activities such as throwing a ball, kicking a football, or dropping objects. The motion is described by specific formulas, including calculati
1 views • 19 slides
Understanding Projectile Motion: Components and Trajectories
Projectile motion involves the horizontal and vertical components of motion, where objects follow parabolic trajectories under the influence of gravity. The horizontal and vertical motions are independent of each other, leading to a variety of curved paths. This phenomenon is illustrated through exa
1 views • 13 slides
Demonstration of Soft Parts of Lower Limb - Part 3 by Dr. Amber Rana at King George's Medical University
This presentation outlines the structures of the lateral compartment of the leg, posterior compartment of the leg, and dorsum of the foot. It includes information on boundaries, muscles, nerves, and vessels in each region, along with detailed descriptions of specific structures such as the peroneus
0 views • 15 slides
Animal Muscle Identification and Anatomy Diagrams
This collection includes detailed diagrams showcasing the identification and anatomy of muscles in animals, specifically focusing on pig muscle anatomy. From head and neck muscles to arm and shoulder muscles, pelvis and thigh muscles, and trunk muscles, these visual aids help understand the structur
3 views • 26 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Inertia
Newton's first law of inertia states that objects remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. This law, also known as the law of inertia, explains how objects tend to maintain their current state of motion unless influenced by an external force. Objects at rest stay a
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Motion: Frames of Reference and Relative Motion
Motion is defined as a change in position over time. To describe motion accurately, one needs to understand frames of reference and relative motion. Frames of reference are systems of objects used to determine if something is in motion, while relative motion involves movement in relation to a refere
3 views • 14 slides
Demonstration of Lower Limb Soft Tissues - Part 3
This detailed demonstration by Dr. Amber Rana from King George's Medical University focuses on identifying and describing the structures of the lateral compartment of the leg, posterior compartment of the leg, and dorsum of the foot. It covers boundaries, muscles, nerves, and vessels present in each
0 views • 15 slides
Anatomy of Paravertebral Region and Root of Neck
This informative content presents the paravertebral region and the muscles of the neck, including the scalene muscles (posterior, medius, and anterior). It covers the origin, insertion, nerve supply, and actions of these muscles, providing a clear understanding of their functions. Additionally, it d
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding the Intrinsic Muscles of the Tongue - Anatomy and Physiology Overview
In this detailed presentation by Dr. Sushma Tomar, Associate Professor of Anatomy, the intrinsic muscles of the tongue are explored, along with their functions, arterial and venous supply, lymphatic drainage, and nerve supply. The lecture covers the four intrinsic muscles in each half of the tongue,
1 views • 15 slides
Understanding the Function of Muscles - Our Amazing Muscular System
Our muscles play a vital role in our bodies by helping us move, pump blood, digest food, and breathe. They are made up of muscle fibers and connected to bones by tendons. The muscles work by contracting and relaxing when we move. To keep our muscles healthy, it's important to engage in physical acti
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Motion: Concepts and Definitions in Physics
Motion in physics is defined as the change in position of an object over time. It involves concepts like rest, motion, distance, displacement, rate of motion, and types of motion. Rest and motion are relative to a reference point, while distance and displacement differ in their scalar and vector nat
2 views • 25 slides
Overview of Muscles of Mastication in Anatomy
This presentation by Dr. Sushma Tomar provides detailed information on the principal and accessory muscles of mastication, focusing on the Masseter and Temporalis muscles. It covers their origins, insertions, nerve supplies, actions, and applied aspects like trismus. The content is accompanied by im
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding the Biological Basis of Human Motion and Motor Learning
In the biological basis of human motion, a series of electro-chemical-physical reactions occur at the neuromuscular junction, enabling nerve stimulation for muscle contraction. Nerve impulses for movement originate in the central nervous system or muscles, with acetylcholine transmitting impulses be
0 views • 13 slides
Identifying Tender, Intermediate, and Tough Muscles in Various Steaks
Explore the classification of muscles into tender, intermediate, and tough categories in different cuts of meat. Specific muscles such as Psoas major, Longissimus dorsi, Gluteus medius, Multifidus dorsi, Biceps femoris, and more are highlighted in different steaks, revealing the varying textures and
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Linear and Rotational Motion in Physics
Explore the concepts of linear momentum, center of mass, rotational motion, and angular displacement in physics. Learn how to determine the center of mass of objects, analyze motion of particle groups, and understand the conservation of momentum in systems under external forces. Delve into the funda
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Circular Motion in Physics
Circular motion involves objects moving in a circular path at a constant speed, experiencing acceleration and centripetal force. This motion is characterized by angular speed, centripetal acceleration, and the necessary centripetal force. The concept of uniform circular motion and angular displaceme
3 views • 38 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Motion
Exploring the foundational concepts of motion and forces, this content delves into Isaac Newton's First Law of Motion. Describing how objects behave when the net force acting on them is zero, the law highlights the significance of inertia and balanced forces in determining an object's state of rest
0 views • 9 slides
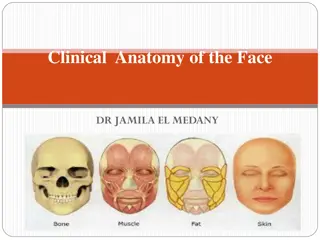
Clinical Anatomy and Muscles of the Face Explained
Detailed information on the clinical anatomy of the face, covering the skin's criteria, skin tension lines, muscles of facial expression, muscles acting on the forehead, muscles of the eyelids, and muscles of the mouth. Understand the structure, function, and importance of each component in facial a
0 views • 34 slides
Understanding Vertical Motion and Gravity in Kinematics
Explore the principles of vertical motion and gravity in kinematics through scenarios involving throwing objects, free-fall motion, and calculating heights. Learn how to model vertical motion with acceleration due to gravity, find maximum heights of thrown objects, solve extended problems, and under
2 views • 12 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Explore the fundamental concepts of Newton's Laws of Motion, including net forces, combining forces, balanced versus unbalanced forces, and the concept of inertia. Learn how these principles explain the behavior of objects in motion and at rest, and discover the impact of mass on an object's resista
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Joint Motion: Osteokinematic and Arthrokinematic Movements
Joint motion involves osteokinematic movements, which are under voluntary control and include flexion, extension, and more. End-feel sensations like bony, capsular, and springy block indicate different joint conditions. Arthrokinematic motion refers to how joint surfaces move during osteokinematic m
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion explain the relationship between forces and motion. The first law states that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a net force, while the second law describes how force is related to an object's mass and acceleration. The third law states that for every ac
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding the Muscular System and Its Anatomy
The muscular system is vital for movement, posture maintenance, and organ protection. It consists of skeletal muscles that contract to create movement, circular muscles called sphincters for controlling openings, and muscle fibers arranged in fascicles with collagen layers like epimysium and endomys
0 views • 59 slides
Understanding Textual Entailment in Natural Language Processing
This collection of images showcases various aspects of textual entailment, where one text can entail another. It explores the relationship between statements like "muscles move bones" and "muscles generate movement". Different levels of entailment are depicted, culminating in complete textual entail
0 views • 72 slides
Trap Tox in Dubai.pptx
Trap Tox refers to a cosmetic procedure where Botox (botulinum toxin) is injected into the trapezius muscles, which are the muscles located between the shoulders and neck. This treatment is designed to relax these muscles.
4 views • 5 slides
Understanding Upper Extremity Injuries and Shoulder Physiology
Upper extremities are prone to various injuries in sports, including sprains, strains, dislocations, fractures, and repetitive motion injuries like arthritis and tendonitis. The shoulder complex involves bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and articulations. Joints like the sternoclavicular, acromio
0 views • 63 slides
Understanding the Triangles of the Neck
The neck is divided into various triangular areas by muscles such as the sternomastoid muscle. These triangles play important roles in anatomy, with the investing layer of deep fascia roofing them. Moreover, muscles like the omohyoid and sternomastoid have specific origins and actions in the neck re
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion describe how objects behave in response to external forces. The first law states that objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by a force, while objects at rest stay at rest. The second law relates force, mass, and acceleration, showing how they are interconnected
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Motion and Newton's Laws
Explore the concepts of motion, distance, speed, and velocity as they relate to Newton's Laws of Motion. Learn about measuring motion, calculating speed, graphing motion on distance-time graphs, and understanding velocity. Discover how motion is constant and how relative motion is used. Practice cal
0 views • 36 slides
Understanding Motion and Newton's Laws
Motion is the constant change in position of objects, measured by distance and displacement. Speed is the rate of motion, while velocity includes direction. Graphing motion helps visualize speed changes over time. Newton's Laws explain the behavior of objects in motion.
0 views • 38 slides
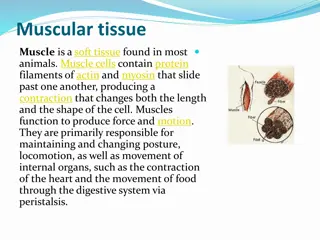
Understanding Muscle Tissue: Structure and Function
Muscle tissue is a vital component in most animals, facilitating movement and maintaining posture. Derived from embryonic cells, muscles come in three types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth, each serving specific functions in the body. While skeletal muscles are under voluntary control, cardiac and sm
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Dependent and Relative Motion in Dynamics
Dependent Motion and Relative Motion are fundamental concepts in Dynamics, providing the foundation for future analysis. Dependent Motion involves constraints like ropes or cables, while Relative Motion considers observers in motion. Dynamics involves applying a limited set of equations in diverse w
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Motion: Types and Physics
Motion refers to a body changing position with respect to its surroundings. Different types of motion include linear, rotatory, and oscillatory motion. The physics relating to motion is called Mechanics, which comprises Dynamics and Kinematics. Scalars and vectors play a crucial role in describing t
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Motion Perception in Computational Vision
In computational vision, the concept of motion opponency plays a crucial role in how the brain processes left and right motion inputs. By examining psychophysical results and the construction of motion opponent energy filters, we explore how the brain handles motion information. Additionally, the Ve
0 views • 23 slides
Muscles of the Anterior and Medial Thigh Anatomy Overview
Explore the anatomy of the muscles in the anterior and medial compartments of the thigh, covering origins, insertions, nerve supplies, and actions. Learn about the divisions, compartments, and common muscles responsible for knee extension and hip flexion. Discover the structures of the femoral trian
0 views • 18 slides
Muscular System Jeopardy - Learn About Muscle Functions and Facts
Explore the Muscular System Jeopardy game to understand how muscles work, muscle group names, exercises to build muscles, and the importance of healthy muscles. Discover interesting facts about muscle function, including how messages from the brain trigger muscle contractions, the role of tendons in
0 views • 52 slides
Understanding Motion in Physics: Definitions and Examples
An object is said to be in motion if it changes position with time, while rest implies no change. Learn about types of motion such as linear and circular, as well as vibratory motion and reference points. Explore how objects can be in motion relative to one reference point while at rest relative to
0 views • 4 slides
Evolution of Motion Theories: Aristotle to Einstein
Explore the progression of motion theories from Aristotle's belief in a force for motion to Galileo's discoveries on gravity, Newton's laws of motion, and Einstein's theories of relativity and quantum mechanics. Discover how our understanding of motion has evolved over the centuries, shaping the way
0 views • 20 slides