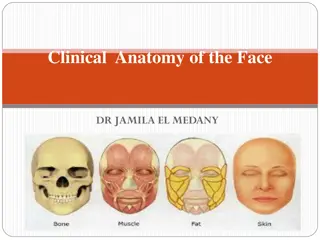
Overview of Muscles of Mastication in Anatomy
This presentation by Dr. Sushma Tomar provides detailed information on the principal and accessory muscles of mastication, focusing on the Masseter and Temporalis muscles. It covers their origins, insertions, nerve supplies, actions, and applied aspects like trismus. The content is accompanied by images for better understanding.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Presented by :- Dr. Sushma Tomar Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
MUSCLES OF MASTICATION PRINCIPAL MUSCLES OF MASTICATION- o Four paired muscles:- o Masseter o Temporalis o Medial Pterygoid (internal pterygoid) o Lateral Pterygoid (external pterygoid) ACCESSORY MUSCLES OF MASTICATION- 1) Buccinator 2) Digastric 3) Mylohyoid. 4) Geniohyoid.
MASSETER MASSETER oQuadrilateral muscle. oConsists of 3 layers of fibers. ORIGIN: Superficial layer (largest):- Lower border of anterior 2/3rd of zygomatic arch. Adjoining maxillary process of zygomatic bone. Middle layer:- Lower border of posterior 1/3rd of zygomatic arch. Deep layer:- Deep surface of zygomatic arch.
MASSETER MASSETER contd INSERTION: Lateral surface of the ramus of the mandible. contd NERVE SUPPLY: Masseteric branch of anterior division of mandibular nerve.
MASSETER MASSETER contd contd ACTIONS: o Elevation of the mandible. o Protraction of mandible (by superficial fibers). o Retraction of mandible (by deep fibers).
APPLIED ASPECTS OF MASSETERS TRISMUS Tonic spasm of both masseters in tetanus.
TEMPORALIS TEMPORALIS A fan-shaped muscle. Bipennate muscle. ORIGIN: o Floor of temporal fossa below the inferior temporal line. o From overlying temporal fascia. It covers the majority of the temporal bone and lesser portions of the frontal and parietal bones. INSERTION: o On the coronoid process of the mandible. o Anterior border of ramus of mandible.
TEMPORALIS TEMPORALIS contd contd NERVE SUPPLY: o Deep temporal branches of mandibular nerve. ACTIONS: o Elevation of mandible. o Retraction [Retrusion (pull back) ] ofthemandible (by posterior fibers).
MEDIALPTERYGOID MEDIALPTERYGOID (INTERNAL PTERYGOID) (INTERNAL PTERYGOID) o Quadrilateral muscle. ORIGIN: o Arises by 2 heads - Superficial head. - Deep head. SUPERFICIAL HEAD (small):- o From tuberosity of maxilla. o Lateral surface of pyramidal process of palatine bone. DEEP HEAD (large):- o Medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate. INSERTION: Medial surface of the ramus of the mandible below and behind the mandibular foramen and mylohyoid groove.
MEDIALPTERYGOID MEDIALPTERYGOID contd NERVE SUPPLY: contd o Branch from trunkof mandibular nerve. ACTION: o Elevation of mandible (closing of mouth). o Protrusion of mandible (along with lateral pterygoid). o Side to side movements of mandible (chewing) (lateral and medial pterygoid muscles of two sides contract alternately).
LATERAL PTERYGOID LATERAL PTERYGOID (EXTERNAL PTERYGOID) (EXTERNAL PTERYGOID) o Key muscle of infratemporal region. ORIGIN: o Arises by 2 heads- Upper head. - Lower head. UPPER HEAD:- Infratemporal surface and infratemporal crest of greater wing of the sphenoid. LOWER HEAD:- Lateral surface of lateral pterygoid plate.
LATERAL PTERYGOID LATERAL PTERYGOID contd INSERTION: contd o Pterygoid fovea at anterior surface of Neck of mandible. o Capsule and articular disc of temporo-mandibular joint. NERVE SUPPLY: o Branch from anterior division of mandibular nerve.
LATERAL PTERYGOID LATERAL PTERYGOID contd ACTIONS: contd o Depression of mandible (opening of mouth). o Protrusion of mandible (along with medial pterygoid) o Side to side movements of mandible (chewing) (lateral and medial pterygoid muscles of two sides contract alternately).