The Role of Inorganic Nitrate in Preventing Contrast-Induced Nephropathy
Contrast-Induced Nephropathy (CIN) poses risks to patients undergoing angiography. This study evaluates the potential benefits of dietary inorganic nitrate in preventing CIN and its mechanisms. Results show promising renoprotective effects, highlighting a potential preventive approach for at-risk pa
1 views • 25 slides
Understanding Physiological Acid-Base Balance in Pharmaceutical Inorganic Chemistry
This lecture delves into the fundamental concepts of pharmaceutical inorganic chemistry, focusing on the mechanisms and uses of various pharmaceutical products that correct body disorders. Topics covered include acids and bases, intra and extracellular electrolytes, and the role of buffers in mainta
10 views • 14 slides
Overview of Herbicides Classification and Groups
Herbicides are classified based on their chemical nature into inorganic and organic types. Inorganic herbicides, such as arsenic acid and copper sulfate, do not contain carbon atoms, while organic herbicides, like glyphosate and 2,4-D, contain carbon atoms. The classification includes various groups
4 views • 15 slides
Microplastic Occurrence in South Korean Groundwater by Well Depth and Hydrogeology
The study conducted by Kangwon National University in South Korea analyzed microplastic occurrence in groundwater from wells of varying depths and hydrogeological settings. Samples were collected from the National Groundwater Monitoring Network pipes in Gapyeong and Chuncheon. Water type analysis re
7 views • 6 slides
What is TDS
TDS stands for Total Dissolved Solids, a crucial parameter in water quality assessment. It refers to the combined content of all inorganic and organic substances dissolved in water. These substances can include minerals, salts, metals, ions, and other organic compounds.
0 views • 7 slides
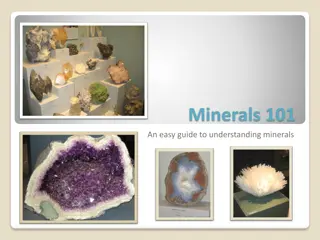
Understanding Minerals: A Comprehensive Guide
Earth's crust is composed of rocks made up of different minerals, which are naturally occurring, inorganic solids with distinct atomic structures and chemical compositions. Minerals exhibit properties like solidity, natural occurrence, inorganic nature, fixed composition, and crystal form. Identifyi
2 views • 20 slides
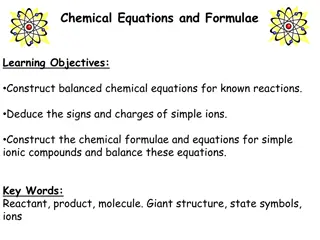
Understanding Chemical Equations and Formulae
Learn to construct balanced chemical equations for known reactions, deduce signs and charges of simple ions, and create chemical formulae for ionic compounds. Understand the concepts of reactants, products, molecules, giant structures, state symbols, and chemical formulas for various substances. Gai
3 views • 7 slides
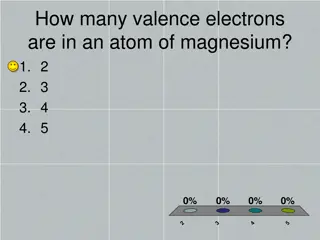
Chemistry Concepts: Valence Electrons, Ion Charges, and Ionic Compounds
Explore various key concepts in chemistry such as valence electrons in magnesium, Lewis Dot structure for silicon, charges on ions like strontium, formation of ions to achieve noble-gas electron configuration, elements forming ions with specific charges, and the octet rule. Learn about the character
1 views • 48 slides
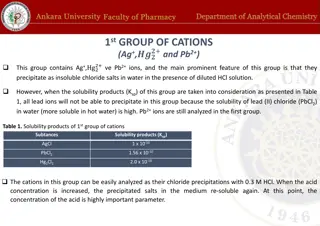
Analysis of 1st Group of Cations: Ag+ and Pb2+ Ions
The analysis of cations in the 1st group involving Ag+ and Pb2+ ions is carried out by precipitating insoluble chloride salts in the presence of diluted HCl solution. The solubility products of AgCl, PbCl2, and Hg2Cl2 play a crucial role in the precipitation reactions. Various reagents such as HCl,
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding the Gibbs-Donnan Effect in Biological Systems
The Gibbs-Donnan Effect, named after physicists Gibbs and Donnan, explains the selective permeability of membranes to ions, leading to the establishment of Donnan potential. This phenomenon affects the distribution of ions and proteins across cell membranes, influencing processes like osmosis and io
0 views • 27 slides
Plant Mineral Nutrition: Absorption and Circulation of Ions in Roots
Plant mineral nutrition involves the absorption and translocation of ions across roots. Salts are absorbed passively and actively, with ions moving into the root's apoplasm via free diffusion. The Casparian strip in endodermal cells acts as a barrier, allowing ions to pass only through the protoplas
0 views • 27 slides
Impact of Land-Use Consolidation Program on Farm Inputs in Rwanda
The study evaluates the effects of Rwanda's land-use consolidation program on farm input uptakes, specifically focusing on hybrid seeds, inorganic fertilizers, and pesticides. Results show significant increases in the adoption of hybrid seeds and inorganic fertilizers among participating households
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Ionization of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids, as proton donors, can undergo ionization to form ions in chemical reactions based on the Brønsted-Lowry theory. Ionization involves the complete loss or gain of electrons, leading to the formation of cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions). Through e
1 views • 13 slides
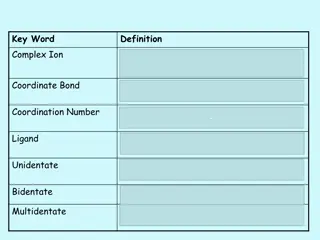
Understanding Complex Ions and Coordinate Bonds in Chemistry
Complex ions in chemistry are formed when transition metals or their ions bond with ligands through coordinate bonds. Ligands utilize their lone pairs of electrons to form dative covalent bonds with transition metals, determining the coordination number of the cation. Complex ions play a crucial rol
1 views • 29 slides
Understanding Valence Electrons and Ionic Charges in Elemental Bonding
Valence electrons play a crucial role in the formation of ions as elements combine. Nonmetals gain electrons to become negatively charged ions, while metals lose electrons to become positively charged ions. This process leads to the creation of electrically attractive elements open for bonding. The
0 views • 17 slides
Innovative Use of Sea Water in Drilling Fluid Development
This work focuses on leveraging sea water as an alternative to inorganic salts in drilling fluid formulations, reducing logistical costs and enhancing offshore operations. The development process involved scaling down additives to nano-size, aiming to create a product that not only replaces Lime in
1 views • 10 slides
Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry: Applications and Importance
Inorganic pharmaceutical chemistry explores the study of elements and compounds excluding carbon, with diverse applications in pharmacy. It encompasses the synthesis and use of inorganic compounds in drug development, catalysis, pigments, and agriculture. The field also delves into the medicinal val
1 views • 6 slides
Understanding Fertilizers and Their Types
Fertilizers are essential for plant growth, providing nutrients necessary for healthy development. They are classified into organic and inorganic types, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Organic fertilizers, sourced from natural materials like plants and animals, enrich the soil with o
2 views • 7 slides
Understanding Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes in Chemistry
Atoms are neutral with equal protons and electrons. Ions are charged atoms resulting from gaining or losing electrons, while isotopes are atoms with varying numbers of neutrons. The atomic number always signifies the number of protons in an atom, unaffected by electron or neutron changes. Explore th
2 views • 5 slides
Overview of Herbicides Classification and Chemical Nature
Herbicides are classified based on their chemical nature into inorganic and organic herbicides. Inorganic herbicides do not contain carbon atoms, while organic herbicides contain carbon atoms. They are further categorized into 31 classes, each with distinct properties and modes of action. This class
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Angular Overlap Method in Advanced Inorganic Chemistry
Exploring the Angular Overlap Method (AOM) in advanced inorganic chemistry provides a qualitative discussion on the physical rationale behind the theory of complexes. By considering the interaction of atomic orbitals and the degree of overlap, AOM offers insights into energy quantification in coordi
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Rodenticides: Types, Effects, and Treatment
Rodenticides are chemical preparations used for rodent control, primarily targeting mice and rats. They play a crucial role in managing rodent populations to prevent associated losses. The chapter covers an introduction to rodenticides, their classification into organic and inorganic types, mechanis
0 views • 19 slides
Exploring Bioinorganic Chemistry: Connecting Inorganic and Biochemistry
Bioinorganic Chemistry bridges the gap between inorganic chemistry and biochemistry, understanding the vital role of inorganic elements in living systems. This interdisciplinary field delves into the structure, function, and exploitation of metal ions in biological processes, emphasizing their inter
0 views • 47 slides
Overview of Wastewater Treatment Units and Processes
Screening units with screens and racks remove coarse solids, comminutors reduce the size of suspended solids, and grit chambers remove sand and metal fragments from wastewater to protect downstream equipment and processes. The floatation tank removes grease, while different designs of grit chambers
5 views • 15 slides
Coordination Numbers in Inorganic Compounds: Geometries and Structures
In inorganic coordination complexes, the coordination number refers to the number of atoms bonded to the central atom. Common geometries include octahedral, tetrahedral, and square planar, depending on the type and number of ligands. Transition metal complexes exhibit different coordination numbers
2 views • 8 slides
Isomerism in Inorganic Complexes: A Comprehensive Overview
Isomerism in inorganic complexes is a fascinating phenomenon arising from the specific spatial arrangements of atoms within molecules. This article delves into the types of isomerism found in coordination compounds, such as structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. The importance of studying isomers
0 views • 67 slides
Understanding Mineral Nutrition in Plants
Mineral nutrition in plants involves the acquisition of essential elements in the form of inorganic ions from soil, followed by their absorption and utilization in various plant processes. Around 60 different elements have been reported in plants, with 30 being essential for plant growth. These esse
0 views • 39 slides
Impact of Replacing Inorganic Zinc with Organic Zinc on Buffalo Calves
The study explores the effects of replacing inorganic zinc with a lower level of organic zinc (zinc propionate) on performance, biochemical constituents, and mineral status in buffalo calves. Zinc deficiency is a critical issue affecting growth, immunity, and reproduction in livestock. Inorganic min
0 views • 27 slides
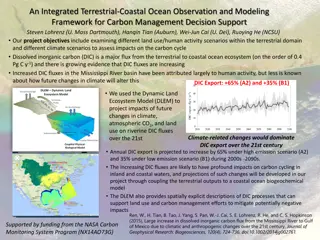
Integrated Terrestrial-Coastal Ocean Framework for Carbon Management
An advanced framework integrating terrestrial and coastal ocean observations and modeling is developed to support carbon management decisions. The study focuses on assessing the impacts of land use, human activities, and climate scenarios on the carbon cycle, particularly dissolved inorganic carbon
0 views • 5 slides
Methods of Business Expansion and Key Terms Explained
Methods of business expansion can be organic or inorganic, with inorganic methods including strategic alliances, mergers, and takeovers. Key terms such as inorganic growth, joint ventures, acquisitions, and subsidiaries are crucial for understanding business expansion strategies.
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding the Biochemistry of Insect Hemolymph
Insect hemolymph, also known as blood, plays a crucial role in maintaining the tissues throughout the body. It consists of plasma containing hemocytes suspended in a fluid rich in various chemicals. The pH of the hemolymph ranges between 6.4 and 6.8, with variations in volume across different insect
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Organic Chemistry and Macromolecules
Organic chemistry focuses on compounds with carbon bonds, while inorganic chemistry deals with other compounds. Carbon is unique due to its ability to form multiple bonds, creating diverse structures like chains and rings. Organic compounds, produced by living organisms, range from simple to complex
0 views • 32 slides
Understanding Electrolyte Activity Coefficients and Equilibrium Constants
This article delves into the practical aspects of dealing with individual ions in aqueous solutions, particularly focusing on partitioning thermodynamic parameters between ions in salts. It explores the Debye-Hückel theory, which explains the electrostatic interactions between ions in solution and
0 views • 20 slides
Mechanism of Mineral Absorption in Plants: Active vs Passive Methods
Plants absorb minerals from the soil in the form of inorganic ions through both passive and active methods. Active mineral absorption requires metabolic energy, whereas passive absorption occurs along the concentration gradient by simple diffusion. The roots play a vital role in mineral absorption d
0 views • 14 slides
Detecting Cobalt(II) Ion Reactions in Solutions
This experiment outlines various methods for detecting Cobalt(II) ions (Co2+) in solution using reagents like sodium hydroxide, ammonia, sodium or potassium carbonate, and more. Observations and changes in color are noted throughout the process to identify the presence of the Cobalt ions. The reacti
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Heterotrophic Nutrition in Organisms
Heterotrophic nutrition refers to the process where organisms, such as animals, rely on preformed organic molecules from their environment or other organisms for nutrients and energy. These organisms are unable to produce organic compounds from inorganic sources and must obtain nourishment from exte
0 views • 55 slides
Analysis of Inorganic Fertilizer Supply Chain in Uganda
Examining the accessibility and quality of inorganic fertilizers in Uganda, the study focuses on key regions, targeted fertilizers, methodology, findings on moisture content and weight compliance, and implications for farmers. The research sheds light on challenges and opportunities in the country's
0 views • 17 slides
Essential Nutrients for Plant Tissue Cultures: A Comprehensive Guide
The composition of culture media for plant tissue cultures includes inorganic and organic nutrients, sources of energy like sucrose and amino acids, and essential macro and micronutrients. Providing gas exchange, waste removal, and growth regulators, the medium supports plant growth by offering acce
0 views • 22 slides
Optical Sideband Cooling of Ions in a Penning Trap - Research Summary
Researchers at Imperial College London, led by Richard Thompson, have made significant contributions in the field of optical sideband cooling of ions in a Penning trap. This technique involves laser cooling in the trap, large Lamb-Dicke parameters, sideband cooling of ions, coherent manipulation of
1 views • 34 slides
Understanding Acids and Bases in Chemistry
Acids, derived from the Latin word "acidus" meaning sour, produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water. Bases, defined as compounds dissociating into metal ions and hydroxide ions in water, have common characteristics like a bitter taste. The Brønsted-Lowry theory expanded the definitions of acids
1 views • 50 slides