Business to Business Marketing
Market segmentation in business-to-business marketing helps marketers efficiently target specific customer groups based on factors like firmographics, industry sectors, organization size, and location. By identifying homogeneous groups, marketers can tailor solutions to address customer needs effect
1 views • 17 slides
Advantages of Having Money: Why Financial Stability Matters
Having sufficient money provides various advantages, including easier life management, ability to afford conveniences and luxuries, and financial stability during uncertain times. Money enables economic freedom, convenience in purchases, homogeneous experiences like vacations, and elasticity in payi
1 views • 5 slides
Understanding Perfect Competition in Markets
Perfect competition in markets involves a large number of buyers and sellers dealing with identical products, leading to firms being price takers. This form of market structure allows for freedom of entry and exit, perfect knowledge of prices and technology, and homogeneous products. Sellers cannot
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Second-Order Recurrence Relations: A Detailed Guide
Explore the concept of second-order linear homogeneous recurrence relations with constant coefficients through definitions, examples, and the Distinct Roots Lemma. Learn about characteristic equations and how to find solutions to recurrence problems. Delve into the Single Root Case and understand ho
0 views • 11 slides
Organometallic Chemistry III: Transition Metal Complexes and Homogeneous Catalysis
Explore the reactivity of transition metal complexes, including bond metatheses and various reactions. Learn about orbital considerations, synthesis, and spectroscopic properties of organometallic complexes. The course covers basics from AC1, focusing on ligands, electron counting, and MO diagrams.
5 views • 8 slides
Understanding Magmatic Differentiation and Magma Mixing
Magmatic differentiation is the process through which a single homogeneous magma can produce diverse rock types by generating fractions of different compositions. This variation in igneous rocks results from mechanisms like fractional crystallization, liquid immiscibility, vapor transport, and diffu
1 views • 29 slides
Understanding Solidification Process in Metal Casting
Solidification in metal casting involves nucleation and growth processes, impacting the final product's quality. Factors such as type of metal, thermal properties, and mold shape influence solidification. Homogeneous nucleation occurs below the equilibrium freezing point, while heterogeneous nucleat
1 views • 8 slides
Crystallization Principles in Chemical Engineering: Understanding Crystal Formation and Purification Methods
Crystallization is a key process in chemical engineering, involving the formation of solid particles within a homogeneous phase to obtain pure chemical substances. This article discusses the principles of crystallization, the importance of crystal size control, equilibria in the process, and the con
1 views • 40 slides
Understanding Solubility of Organic Compounds
A solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of a solute dissolved in a solvent. Solubility refers to the ability of one compound to dissolve in another. The solubility of organic compounds can be categorized based on chemical reactions like acid-base interactions. Different methods such as gravity
0 views • 6 slides
Overview of T.H. Rogers Vanguard Program & Magnet School
T.H. Rogers is a Vanguard Magnet School in Houston, Texas that specializes in gifted and talented education. This program offers accelerated instruction for identified students with a focus on academics and character development. Students must apply, qualify as GT, and be selected via the HISD Magne
0 views • 52 slides
Understanding Fluid Mixing in Chemical Reactions
The problems associated with fluid mixing during reactions are crucial for fast reactions in both homogeneous and heterogeneous systems. These issues involve the degree of segregation of the fluid and the timing of mixing. Concepts like RTD are intertwined with fluid mixing, affecting the behavior o
1 views • 46 slides
Understanding Equilibrium in Perfect Competition Markets
Perfect competition in economics refers to a situation where numerous buyers and sellers are involved in trading identical goods freely, with full market knowledge and no government restrictions. Key characteristics include a large number of buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, free entry and e
1 views • 14 slides
Understanding Homogeneous Systems of Linear Equations
Homogeneous linear equations are systems in which the constant term in each equation is zero. They can have one or infinitely many solutions but always have at least one solution. Learn how to solve homogeneous systems, distinguish between trivial and nontrivial solutions, and understand null space
1 views • 12 slides
2D Geometric Transformations for Computer Graphics
In this lecture on 2D Geometric Transformations, Assistant Professor Dr. Samsun M. BA ARICI covers topics such as translation, rotation, scaling, homogeneous representations, and coordinates. The lecture delves into basic transformations like reflection and shearing, as well as practical application
2 views • 81 slides
Travel Demand Modeling in Transportation Engineering
Travel demand modeling (TDM) is crucial for estimating future travel demand based on assumptions like traffic volume. It helps evaluate roadway improvements, bus services, manage congestion, and estimate pollution emissions. Factors influencing travel demand include land use, population characterist
4 views • 19 slides
Understanding Market Segmentation and Consumer Behavior in Marketing Management
Market segmentation is crucial for companies to effectively target different customer segments with tailored products and marketing strategies. By dividing the market based on characteristics and preferences, businesses can maximize customer satisfaction, improve marketing strategies, and increase p
0 views • 10 slides
Introduction to Chemical Thermodynamics: Systems and Properties
Chemical thermodynamics explores energy changes in chemical reactions. It includes terms like system, surroundings, and boundaries. Systems can be isolated, closed, or open, each with distinct characteristics. Homogeneous and heterogeneous systems have different compositions. Properties in a system
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding 2D Viewing Transformations and Windowing Concepts
Exploring two-dimensional transformations, homogeneous coordinate systems, matrix formulation, and concatenation of transformations. Concepts like windowing, window-to-viewport transformation, viewing transformation, and the 2D viewing pipeline are discussed with relevant images and explanations.
6 views • 38 slides
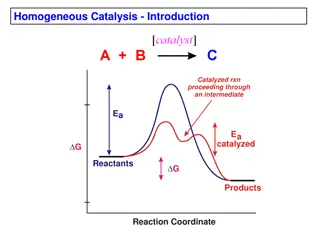
Understanding Homogeneous Catalysis and Its Advantages
Homogeneous catalysis involves catalyzed reactions proceeding through an intermediate with lower activation energy. This method offers advantages such as selectivity, activity, ease of study, and modification but can be sensitive to deactivation. Comparing with heterogeneous catalysts prevalent in i
1 views • 14 slides
Understanding Liquid Mixtures in Nursing Chemistry
A comprehensive overview of liquid mixtures in nursing chemistry, including types of mixtures, properties of solutions and suspensions, and the distinction between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. Explore the concepts of solutions, suspensions, colloids, and emulsions with clear explanations
7 views • 18 slides
Fundamentals of Food Sampling and Analysis
Discover the key methods and procedures for sampling, transportation, and storage of environmental parameters, focusing on food sampling and analysis. Explore the importance of representative samples, quality analysis results, and risks associated with sampling. Learn about homogeneous vs. heterogen
5 views • 36 slides
Quantitative Estimation of Metal Ions in a Mixture
Dr. Saadia Rashid Tariq explains the quantitative estimation of copper(II), calcium(II), and chloride in a mixture. The process involves iodometric titration for copper(II), complexometric titration for calcium(II), and gravimetric estimation for chloride. Detailed procedures, reactions, requirement
1 views • 8 slides
Understanding Homogeneous Systems of Linear Equations
Homogeneous linear equations consist of a system where the constant terms in every equation are 0. They can have one or infinitely many solutions, with at least one solution always present. Learn how to solve these systems, distinguish trivial and nontrivial solutions, and explore the concepts of nu
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Complex Wavevectors in Homogeneous Media
Exploring the concept of complex wavevectors in a homogeneous medium, this content delves into monochromatic waves, Maxwell equations, wave propagation, and the relationship between material properties and wave behavior. It discusses how the complex nature of wavevectors impacts fields, damping, and
0 views • 17 slides
Lab Procedure for Standard/Control Sample Preparation
Here is a detailed lab procedure for standard/control sample preparation, including preheating the hot plate, labeling petri dishes, preparing the mixture, adding phosphorescent powder, heating the mixture, and stirring continuously. Images are provided for each step to assist in the process.
1 views • 15 slides
Mixture Separation Lab Procedure & Analysis
In this practical lab activity, students are tasked with separating a mixture containing Sand, Salt, Poppy Seeds, and Iron Filings. The procedure involves a step-by-step approach including identifying three separation strategies, executing the chosen method, recording observations, and calculating p
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Linear Systems
Gaussian Elimination is a powerful method used to solve systems of linear equations. It involves transforming augmented matrices through row operations to simplify and find solutions. Homogeneous linear systems have consistent solutions, including the trivial solution. This method is essential in li
0 views • 16 slides
Pure Substances vs. Mixtures: Characteristics and Differences
Pure substances have a fixed composition and distinct properties, while mixtures vary in composition and properties. Pure substances cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical methods, whereas mixtures can be. This article explores the characteristics, distinctions, and examples of pure
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Chromatography: A Practical Experiment
Chromatography is a process used to separate components of a mixture by employing a mobile phase that carries the mixture through a stationary phase. This experiment by Mariam Nimri explores the effects of different solvents on chromatography results, with a hypothesis that vinegar can impact pigmen
1 views • 10 slides
Practical Guide to Pharmaceutics Experiments by Mr. Nilesh A. Shinde
This practical guide covers Experiment No. 9 on preparing Magnesium Hydroxide Mixture, including ingredients, procedure, and the definition of pharmaceutical mixtures in pharmaceutics. It provides detailed steps for creating the mixture, along with the characteristics and storage instructions for Ca
0 views • 8 slides
Safety and Interest in Pure CH4 vs. Ne/CH4 Mixture at Queen's University Meeting
Explore the safety implications and scientific interest in comparing pure CH4 with a Ne/CH4 mixture at the 6th NEWS-G Collaboration Meeting held at Queen's University. The study delves into background rates, interactions between gases, mass ratios, event rates, signal-to-background ratios, and overa
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Linear Algebra Concepts: Systems of Equations, Orthogonal Matrix, and Quadratic Forms
Explore the concepts of simultaneous linear equations, homogeneous and non-homogeneous systems, orthogonal matrices, and various types of quadratic forms in linear algebra. Learn about the characteristics of positive definite, semi-positive definite, and negative definite quadratic forms represented
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Label Switching in Bayesian Mixture Models
In the interactive talk "Reversing Label Switching" by Earl Duncan, the concept of label switching in Bayesian mixture models is explored. Label switching poses challenges in making accurate inferences due to symmetric modes in posterior distributions. Duncan discusses conditions for observing label
0 views • 13 slides
Solving Mixture Problems Using the Bucket Method
Mixture problems occur in various scenarios like blending goods for sale or obtaining desired solutions. The bucket method involves setting up buckets with starting values, additive values, and the desired mixture to solve equations efficiently. An example problem is demonstrated step-by-step for cl
0 views • 12 slides
GCSE Separation Challenge: Iron, Sulfur, Sand, and Food Dyes Mixture
Students are tasked with separating a mixture containing iron, sulfur, sand, and food dyes using various techniques. They work in pairs, following provided instructions and using specific equipment. Marks are awarded based on successful separation and organization. The challenge involves planning, e
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Mixtures: Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous and Separation Techniques
Explore the differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, with examples like Cheerios and trail mix. Learn about mixtures like apple juice and orange juice with pulp. Discover how to separate mixtures based on their composition, whether they are homogeneous or heterogeneous, using tech
0 views • 16 slides
Continuous Asphalt Mixture Compaction Assessment Using Density Profiling System
Development of a comprehensive work plan for the assessment of asphalt mixture compaction using the Density Profiling System (DPS). The project aims to create a master database of field and lab measurements, refine protocols for dielectric value-density relationships, propose changes for sensor bias
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Magnetic Field of a Steady Current
Exploring the behavior of magnetic fields in the presence of conduction currents, discussing differential equations for B and H, considering boundary conditions and vector potential A. The content emphasizes solving equations to find H and B, with special cases for homogeneous and piecewise homogene
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Mixtures: Types and Examples
A mixture is a combination of different ingredients that can be separated. There are various types of mixtures such as liquid solutions, solid solutions, and gas solutions. Liquid solutions involve solid substances dissolved in a liquid, like sugar in water, while solid solutions include metal alloy
0 views • 15 slides
Reservoir Modeling Using Gaussian Mixture Models
In the field of reservoir modeling, Gaussian mixture models offer a powerful approach to estimating rock properties such as porosity, sand/clay content, and saturations using seismic data. This analytical solution of the Bayesian linear inverse problem provides insights into modeling reservoir prope
0 views • 10 slides