Models of the Atom: Nucleus, Protons, Electrons
Dive into the fundamental concepts of atoms, exploring their structure with a focus on the nucleus, protons, electrons, and neutrons. Discover how the periodic table reveals crucial information about elements, such as atomic number and mass number. Explore the evolution of atom models and the necess
3 views • 20 slides
Evolution of Mathematical Theories and Proof Systems
Development of mathematical theories such as model theory, proof theory, set theory, recursion theory, and computational complexity is discussed, starting from historical perspectives with Dedekind and Peano to Godel's theorems, recursion theory's golden age in the 1930s, and advancements in proof t
3 views • 29 slides
Green Chemistry Principles and Efficiency in Chemical Processes
Green chemistry focuses on designing sustainable chemical products and processes to minimize hazardous substances. It advocates for waste prevention, efficient reactions, and use of raw materials. Chemical engineers play a key role in optimizing percentage yield and atom economy for efficient produc
0 views • 49 slides
Quantum Theory and the Atom: Electrons in Atoms and the Periodic Table
Delve into the fascinating world of quantum theory and the atom in Chapter 9, where we compare Bohr's model with the quantum mechanical model. Understand de Broglie's wave-particle duality and Heisenberg's uncertainty principle's impact on our current electron view. Discover the relationships among
0 views • 31 slides
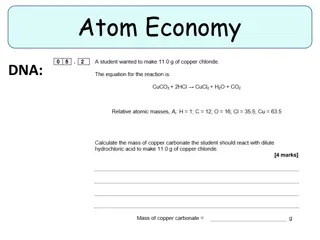
Atom Economy in Chemical Reactions
Explore the concept of atom economy in chemistry, learn how to calculate atom economy of a reaction, and understand why it is important for industrial processes. Watch a video, answer questions, and practice with worked examples and self-assessment tasks to grasp the significance of efficient indust
1 views • 21 slides
Parts of the Atom: A Visual Journey
Delve into the discovery of the constituents of an atom, from the negatively charged particles in the electron cloud to the positively charged particles in the nucleus. Learn about protons, neutrons, and the particle with no charge as they form the building blocks of matter. Engage with visually sti
5 views • 17 slides
Basic Electrical Concepts
Delve into the fundamentals of electricity, covering atom structure, electrical materials, direct and alternating currents, and more. Gain insights into key terms and definitions essential for basic circuit analysis. Explore the significance of atom charges, materials conductivity, and the role of p
0 views • 21 slides
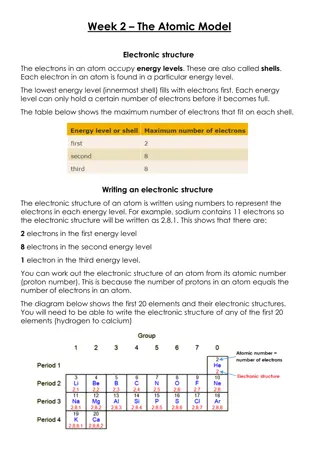
Atomic Structure: Electrons, Energy Levels, and Historical Models
The atomic model describes how electrons occupy energy levels or shells in an atom. These energy levels have specific capacities for electrons. The electronic structure of an atom is represented by numbers indicating electron distribution. Over time, scientists have developed atomic models based on
1 views • 5 slides
Exploring the Vector Atom Model in Quantum Physics
Delve into the Vector Atom Model as presented by Dr. R. R. Mistry, discussing the quantum numbers, coupling, exclusion principles, and effects like Zeeman and Stark. Learn how this model explains complex atomic spectra and spatial quantization, offering a deeper understanding of atomic structures.
1 views • 11 slides
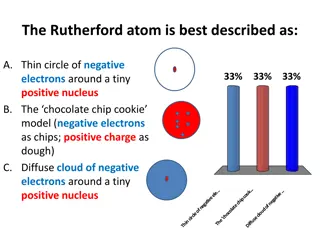
The Rutherford Atom and Its Structure
The Rutherford atom is characterized by a thin circle of negative electrons surrounding a tiny positive nucleus. In this model, the electrons are in a diffuse cloud around the nucleus, forming the majority of the atomic volume but only a small fraction of the mass. Protons define an element's atomic
0 views • 17 slides
Evolution of Atomic Models: From Thomson to Bohr
Scientists from J.J. Thomson to Niels Bohr made groundbreaking discoveries in understanding the structure of the atom. Thomson's plum-pudding model was followed by Rutherford's nuclear model, revealing the nucleus. Bohr introduced the concept of discrete energy levels and orbits for electrons. These
5 views • 22 slides
Atom Structure and Properties Questions
This series of questions delves into the intriguing world of atoms, covering topics such as atom size comparison, proton count identification, location of metals on the Periodic Table, nucleus charge explanation, atomic number significance, various arrangements of the Periodic Table, subatomic parti
0 views • 12 slides
Degenerate Perturbation Theory in Quantum Mechanics
Exploring time-independent perturbation theory, specifically focusing on non-degenerate and degenerate spectra. The lecture covers approximation schemes, treatment of multi-electron atom term values, and the effects of spin-orbit interaction. Concepts include evaluating expectation values, wavefunct
0 views • 13 slides
Limits on Dark Energy Using Atom Interferometry - UC Berkeley Study
Research conducted by Paul Hamilton Müller's group at the University of California, Berkeley, focuses on using atom interferometry to explore dark energy. The study delves into screened scalar fields as dark energy, future reach with atom interferometry, known unknowns related to dark energy densit
1 views • 39 slides
Atom Probe Sample Request Details and Instructions
This detailed guide provides instructions and recommendations for submitting a sample request for atom probe analysis. It includes information on how to describe the sample, provide images, and outline the goals of the analysis. By following these guidelines, customers can facilitate discussions wit
1 views • 5 slides
Theories of Interest in Microeconomics II
Explore various theories of interest in economics, including the Classical Theory, Liquidity Preference Theory by Keynes, Productivity Theory, Abstinence Theory, Time-Preference Theory, Fisher's Time Preference Theory, and the Loanable Fund Theory. These theories offer different perspectives on the
2 views • 6 slides
Deciphering Heavy Atom Coordinates from Difference Patterson Map: An Overview
Understanding how to determine heavy atom coordinates from a difference Patterson map involves recognizing the relationship between Patterson peak coordinates (u,v,w) and space group symmetry operators in crystallography. By solving equations that relate these coordinates, the absolute positions of
1 views • 5 slides
Evolution of Atomic Theory: From Democritus to Thomson
Examine the evolution of atomic theory through the contributions of key scientists such as Democritus, Dalton, and Thomson. Explore the concept of subatomic particles, different models of the atom, and the impact of experiments on our understanding of the atom over time. From the solid sphere model
0 views • 33 slides
Evolution of Atomic Models: From Rutherford to Quantum Mechanics
Various atomic models have been proposed throughout history, starting with John Dalton's idea of atoms as tiny particles to J.J. Thomson's Plum Pudding model. Ernest Rutherford's discovery of the nucleus and Niels Bohr's quantum model of the atom revolutionized our understanding. Bohr's proposal of
0 views • 38 slides
Quantum Chemistry Learning Goals and Concepts
This content covers the learning goals and concepts of quantum chemistry leading up to the Schrodinger equation and potential energy wells, excluding the material on the hydrogen atom introduced later. It explores models of the atom, including observations of atomic spectra, the Bohr model, de Brogl
0 views • 22 slides
Quantum Theory and Key Figures in Physics
Explore the evolution of quantum theory through the perspectives of renowned physicists such as Albert Einstein, Niels Bohr, Werner Heisenberg, Erwin Schrödinger, Prince Louis de Broglie, and Max Planck. Learn about atomic line spectra, fundamental equations, and models used to represent the atom.
0 views • 23 slides
Factors Affecting Acid Strength: Atoms, Size, Hybridization, and Electronegativity
The strength of acids is influenced by various factors such as the atom on which the negative charge of the acid's conjugate base rests, atom size, hybridization, and electronegativity. The stability of negative charges on atoms, atom size allowing charge delocalization, preferred orbital types for
0 views • 23 slides
The Basics of Atom Structure in Electronics
Learn about the fundamental concepts of atom structure in electronics, including the components of atoms, the Bohr model, electron orbits, energy levels, valence electrons, and more. Understanding these principles is essential for grasping the underlying mechanisms of electronic devices.
0 views • 18 slides
Properties of Light and Models of the Atom in Chemistry
Delve into the fascinating world of light properties and atom models in chemistry. Unravel the scientific process, from successes to flaws, and master concepts like wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. Explore key experiments and models such as the Rutherford, Bohr, and DeBroglie models, as well as
0 views • 24 slides
Basic Biochemistry: Matter, Elements, and Atom Structure
Basic Biochemistry explores the science of matter, chemical reactions, elements, and atom structure. It covers the properties and transformations of matter, the significance of essential elements for life, and the structure of atoms including protons, neutrons, and electrons. This foundational knowl
0 views • 50 slides
Atomic Structure and the Elements Overview
The atom, composed of a nucleus and electrons, forms the basis of all matter. Elements, grouped in families on the Periodic Table, exhibit similarities and differences based on their atomic structures. The arrangement of electrons in orbits determines an atom's chemical properties and reactivity. By
0 views • 11 slides
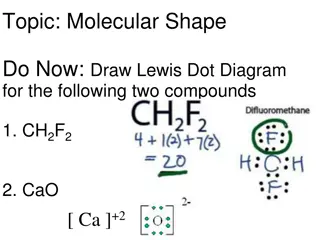
Topic: Molecular Shape
Explore the relationship between Lewis structures and molecular shapes, with a focus on factors influencing molecular geometry such as electron pairs and atoms around the central atom. Utilize VSEPR theory to predict shapes based on electron-pair repulsion. Understand how different atom arrangements
0 views • 22 slides
Introduction to Alcohols: Structure and Properties
Alcohols are essential molecules in organic chemistry, characterized by the hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom. They are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the carbon atom's alkyl group attachments. Alcohols vary in solubility, vapor pressure, and physical properties
0 views • 24 slides
Bohr's Model of Atom and U.Nithya - M.Sc., M.Phil.
In this educational presentation about Bohr's model of the atom, U.Nithya, an experienced instructor with M.Sc. and M.Phil. qualifications, provides comprehensive insights through a series of informative slides. Delve into the world of atomic structure, electrons, and energy levels with detailed exp
0 views • 40 slides
The Model of the Atom: Discovery and Development
Explore the evolution of atomic theory from the old plumb pudding model to the groundbreaking discoveries by Ernest Rutherford and Hantaro Nagaoka. Discover how theories and experiments shaped our understanding of the atom and learn about the collaborative nature of scientific advancement. Delve int
0 views • 8 slides
Intermediate 2 Physics: Exploring Ionising Radiations and Atom Structure
In the study of Intermediate 2 Physics, delve into the intricacies of ionising radiations and the components of an atom. Understand the phenomena of ionisation, electron gain or loss, and the concept of ions. Explore the nature of nuclear radiation types - alpha, beta, and gamma particles. Gain insi
0 views • 47 slides
Atom Economy and Percentage Yield in Science
Making scientific processes economical and efficient is key in the synthesis of chemical compounds. Atom economy and percentage yield play crucial roles in optimizing production methods to ensure cost-effectiveness and minimal waste generation. Learn how these concepts influence the efficiency of ch
0 views • 11 slides
Exploring the Evolution of Atomic Theory and the Structure of the Atom
Uncover the journey of atomic theory development from early Greek beliefs to modern models. Discover key scientists, experiments, and models that have shaped our understanding of the atom's structure and radioactivity over time.
0 views • 43 slides
Quantum Numbers and Spherical Harmonics in Hydrogen Atom
Understand the significance of quantum numbers (n, l, m) and their impact on the 3D behavior of wavefunctions in hydrogen atoms. Explore the interplay of orbital and magnetic numbers, nodal surfaces, and spherical harmonics in polar plots. Dive into the radial and angular parts of the hydrogen atom
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Electrotechnics: Atom Structure and Current Flow Fundamentals
Explore the foundational concepts of Electrotechnics, delving into the atom's structure, electron movement, EMF, resistance, power calculations, and more. Gain insights into how the atom's components influence electron behavior and current flow, essential for grasping Kirchhoff's laws and practical
0 views • 14 slides
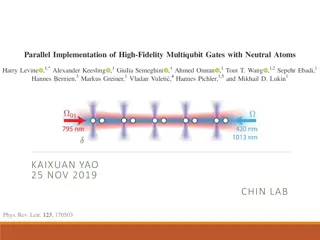
Cutting-edge Developments in Neutral Atom Quantum Computing
Explore the cutting-edge developments in neutral atom quantum computing, including qubit configurations, experimental setups, single qubit manipulation techniques, state preparation methods, and advanced quantum gates such as CZ, CNOT, and Toffoli gates.
0 views • 15 slides
Exploring Quantum Theory and Atomic Spectra through Key Figures
Delve into the world of quantum theory and atomic line spectra by learning about the key figures involved such as Albert Einstein, Niels Bohr, Werner Heisenberg, Erwin Schrödinger, Prince Louis de Broglie, and Max Planck. Discover the experiments, models, equations, and successes that have shaped o
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Bohr's Model of an Atom in Inorganic Chemistry
Learn about Bohr's model of the atom, proposed by Neil Bohr in 1915 as a modification of Rutherford's model. Discover the postulates, stationary states, and Bohr's theory of the atomic spectrum of hydrogen. Understand how electrons revolve around the nucleus in specific orbits, each with fixed energ
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Atom-Photon Interactions: Methods and Results
Dive into the world of atom-photon interactions with Gilad Laredo's presentation from Spring 2017. Explore the transition probabilities, time-independent Hamiltonians, and the Floquet theorem. Learn how to solve complex equations and generalize problems in this fascinating field of study.
0 views • 18 slides
Development of Atomic Theory: From Greek Concepts to John Dalton's Model
Explore the historical journey of the atomic model, tracing back to the Greeks' ideas of matter as discontinuous grains to John Dalton's Atomic Theory in the 19th century. Contrasting the Greek BB model with Dalton's evidence-supported theory, this evolution sheds light on the scientific advancement
0 views • 48 slides