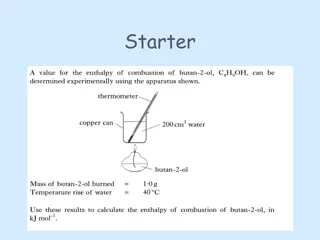
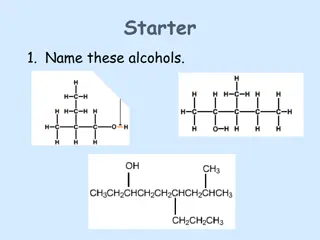
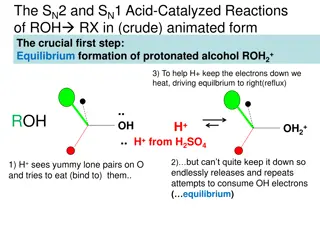
Introduction to Alcohols: Structure and Properties
Alcohols are essential molecules in organic chemistry, characterized by the hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom. They are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the carbon atom's alkyl group attachments. Alcohols vary in solubility, vapor pressure, and physical properties based on their molecular weight. This versatile class of compounds finds applications in beverages, antifreeze formulas, antiseptics, fuels, and medical preservatives.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Alcohols are some of the most important molecules in organic chemistry. They contain the hydroxyl functional group (- OH), bonded to a carbon atom of an alkyl, or substituted alkyl group(R).
Table (1): Alcohol Classification. Types of Alcohol. Primary Alcohol Secondary Alcohol Tertiary Alcohol
Most of the alcohols are known to be colourless liquids or even are said to behave as solid at room temperatures. Alcohols with less molecular weight are said to be highly soluble in water; and with their increase in molecular weight, they tend to become less soluble and their vapour pressures, boiling points, densities, and the viscosities to increase.
Examples of alcohols 1. Primary Alcohols Primary alcohols are those alcohols where the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group (OH) is attached to only one single alkyl group. .
2. Secondary Alcohols Secondary alcohols are those where the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group is attached to two alkyl groups on either side. The two alkyl groups present may be either structurally identical or even different. Some examples of secondary alcohols are given below
3. Tertiary Alcohols Tertiary alcohols are those which feature a hydroxyl group attached to the carbon atom which is connected to 3- alkyl groups. The physical properties of these alcohols mainly depend on their structure.
Uses of Alcohols There are several uses of alcohols. Some are listed below. Alcohols are consumed as beverages where the alcohols specifically consist of 30 40 per cent of ethanol by volume. These are used as an anti-freezing agent with a mixture of a solution containing ethylene glycol dissolved in water. Alcohol ethanol is used as an antiseptic agent. Some alcohols are used as fuels in internal combustion engines like the methanol. In the field of medicine, a few of them are used as preservatives for the specimens in laboratories
Ethanol (CH3CH2OH): -Ethanol is a solvent: it s a widely safe solvent, so used to dissolve many organic compounds that are insoluble in water especially for medicine, to extract active constituents from inert parts of crude drugs. - Ethanol is an effective in killing organisms like bacteria, fungi, and viruses, so it is commonly used as hand sanitizer gels & medical wipes at clinics and hospitals. - Ethanol spirits consist of a mixture of Ethanol with a small quantity of methanol, and possibly some color added. Because methanol is poisonous, industrial Ethanol spirits are unfit to drink. - Ethanol can be used as a fuel. it burns to produce carbon dioxide and water, as shown in the equation below: CH3CH2OH + 3 O2 2 CO2+ 3 H2O.
Type of Cell Reactions for Respiration: Alcohol is a sours of energy for cell metabolism, some cell reactions have been done by two types depending on the presence of oxygen they are: 1-Aerobic respiration Reactions. 2-Anaerobic respiration Reactions.
Fermentation Alcohols can be formed using fermentation. Fermentation is usually done by using yeast to act on carbohydrates to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide. Rice, malt, fruits and etc, which are sources of carbohydrates, are used to react with yeast. E.g. converting glucose to ethanol: C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 Conditions for fermentation are as follow: - yeast as a biological catalyst - in the absence of oxygen - temperature at 37 C
Antibiotics: are chemical compounds can fight bacterial infections either by killing bacteria or slowing and suspending its growth. They do this by: attacking the wall or coating surrounding bacteria, interfering with bacteria reproduction. It s important to avoid drinking alcohol when taking medication (Antibiotics) or feeling unwell. Alcohol Consumption while taking Antibiotics cause: 1.An upset of stomach and stomach pain. 2. diarrhea. 3. Ulcers. 4- Digestive problems
But the signs of Alcohol with Antibiotics reaction cause following side effects: 1-A rapid heart rate. 2-Sever headache. 3-Reddening and warming of skin (Flushing When to avoid drinking alcohol completely Completely avoid drinking alcohol when taking drugs. Antibiotics can cause dangerous reaction with alcohols, Also causing symptoms of being sick. Alcoholism should avoid alcohol, while taking these medications. Other medicines sometimes contain alcohol, so avoid using these while taking metronidazole or tinidazole.
The Antibiotic which can react with Alcohol cause dangerous reaction include: 1- Metronidazole. 2- Tinidazole. 3- Doxycycline.
Alcohol's Effects on the Body: Alcohol swallowed by mouth to the stomach then a small amount pass by stomach wall to the blood stream. About 20 percent of the alcohol from a single drink moves directly to the blood vessels, while most alcohol through intestine and to blood circulation (to reach all over the body). Numerous factors can affect Blood alcohol concentration BAC and how body react to alcohol, including: Age. Weight. Drinking alcohol on an empty stomach. Consuming medications. Liver disease. Drinking many drinks in a short period of time.
1-The effect of alcohol on brain: Alcohol reach's the brain in a short time. interferes with the brain s communication pathways, and can affect brain function, and who looks resulting in change mood and behavior, also reduce the brains ability for controlling body activates (speech, vision and harder to think clearly). 2-The effect of alcohol on nervous system (CNS) : Alcohol slows down & can disrupt the sympathetic nervous system which is made up of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. That affects how signals flow through the body, controls the constriction and dilation of blood vessels. Heavy drinking cause rising of blood pressure & damage nervous cells. High blood pressure can lead to many other health problems, including kidney & heart disease.
3-The effect of alcohol on heart : Alcohol elevate the heart rate, and expanding of blood vessels. Heavy drinking, makes platelets more likely to clump together into blood clots, which lead to heart attack & doubled the risk of death. 4-The effect of alcohol on liver: Normal liver function lead to cleans the blood, and helps digest food. It is a bodily superhero, it has the power to regenerate when it has been damaged, replacing old tissue with new cells. Anything that keeps your liver from doing its job or from growing back after injury may put your life in danger . Alcohol interferes with the liver s function, so the liver unable to break down fats creating fatty acids. Damaged liver result in Cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is a condition in which liver tissue is destroyed and then replaced with scarred tissue. (scarred that it is unable to function, no blood flow in scared area.) Most peoples die due to Cirrhosis are heavy drinkers.
Liver Cirrhosis : There are four stages for liver cirrhosis the last stage indicate the complete destruction of the liver causing death. Signs & Symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis : -High blood pressure, and abdominal swelling. -Jaundice yellowing skins and eyes. -Destruction of the liver. -IRREVERSIBLE.
5-The effect of alcohol on gastro intestinal tract(GIT): The gastrointestinal system is damaged by alcohol. Thus it is less able to absorb nutrients, which can lead to malnutrition. Because alcohol supplies calories, alcoholic drinks can be very obese. Alcohol is absorbed so quickly that its energy is available almost immediately. This energy is burned first, so the body fuel that would normally be used for energy is stored as fat. 6-The effect of alcohol on immune system: Drinking too much can weaken immune system, making body a much easier target for disease.
Alcoholism:A disease in which person has a physical or psychological dependence on drinks alcohol, characterized as an impaired ability to work or socialize normally Blood Alcohol Concentration(BAC): Is the amount of alcohol in a person s body is measured by the weight of the alcohol in a certain volume of blood. 8% is the legal driving limit.
The breathalyzer: To test the amount of alcohol consumed, a sample of the patient s breath releases it into an concentration of alcohol. The alcohol vapor in a person's breath reacts with an orange solution known as potassium dichromate. When alcohol is present, this solution turns green. This color change creates an electrical current, which the breathalyzer can convert into a value to determine the BAC. Generally, the BAC limit in the U.S. is 0.08%. The legal alcohol limit in England, Wales and Northern Ireland for driving is 80 milligrams of alcohol per 100 millilitres of blood or 35 micrograms of alcohol per 100 millilitres of breath