Topic: Molecular Shape
Explore the relationship between Lewis structures and molecular shapes, with a focus on factors influencing molecular geometry such as electron pairs and atoms around the central atom. Utilize VSEPR theory to predict shapes based on electron-pair repulsion. Understand how different atom arrangements result in linear, bent, trigonal planar, pyramidal, and tetrahedral molecular shapes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
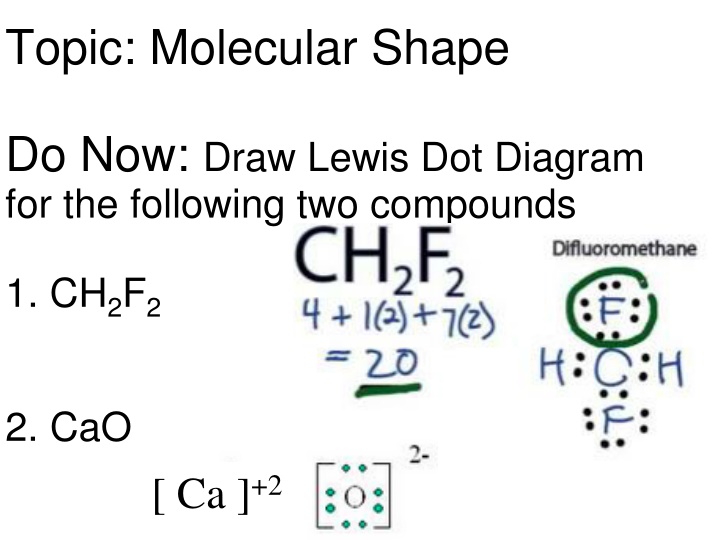
Topic: Molecular Shape Do Now: Draw Lewis Dot Diagram for the following two compounds 1. CH2F2 2. CaO [ Ca ]+2
Use the Lewis Structure Lewis structure is 2-D, but can help figure out 3-D shape H O H
REMINDER:Bonding Capacity Atom Lewis Structure # Unpaired Electrons Bonding Capacity . H H .. 1 1 F, Cl, Br, I F: .. . 1 1 C, Si C ... 4 4 N, P N ... 3 3 O, S O: 2 2 Ne, Ar, Kr :Ne: 0 0
Molecular Shape Determined by overlap of orbitals Shape determined by two factors: 1. # e- groups (pairs) around the central atom pay close attention to the free electron pairs 2. total # atoms bonded to central atom Free electron pairs Central Atom
VSEPR (A model used to predict the shape of individual molecules based on the extent of electron-pair electrostatic repulsion) VSEPR= Valence shell electron pair repulsion: Basically free electrons will repel one another causing the molecule to bend
2 atoms (no central atom) Always linear Examples H2 O2 N2 HCl
3 atoms Can be linear or bent Must look at central atom If free electrons, then will be bent Central atom Free electrons so bent Central atom No free electrons so linear
4 atoms that form triangles Look at central atom No free electrons = trigonal planar - Free electrons = trigonal pyramidal
4-Atom Molecules: Planar = no real central atom, no free electrons either
5 atom molecules Always tetrahedral Examples CCl4 CH4 CH2I2
Summary of Molecular Shapes Start with Lewis Structure! Look at total number of atoms Look at # of atoms bonded to central atom Look at free pair(s) of electrons around central atom
Asymmetric Molecules Polar Bent & trigonal pyramidal are always polar
Lets try a few Name the SHAPE and POLARITY
BENT POLAR
Trigonal Planar POLAR
Tetrahedral POLAR
Trigonal Pyramidal POLAR
linear POLAR
linear POLAR
bent POLAR
tetrahedral NONPOLAR