Understanding Eye Tracking: Techniques and Applications
Eye tracking is a process that involves measuring gaze points and eye movements, providing insights into conscious and unconscious information processing. Techniques such as contact lenses and remote trackers have evolved over the years, enabling real-time video-based systems. Different eye tracking devices like Electro-oculography (EOG) and Video-Oculography (VOG) serve specific purposes in measuring eye positions and movements. This technology plays a crucial role in various fields, including Human-Computer Interaction (HCI).
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Eye Tracking Refs. content:V. NavalpakkamandEChurchill, slide design: W. Zhu
Overview What Eye Trackingis What Eye Trackersmeasure UseofEyeTrackingMethodsinVariousFields Some HCI Examples
What is Eye Tracking Eyetrackingistheprocessof: Measuringthepointof gaze( where we arelooking ) Measuringthemovementof theeyerelativeto thehead. Eyetrackeristhedevicefor measuringeyepositionsandeyemovement. Development of Eyetracker Eyetrackinghasbeenamethodfor understandingconsciousandunconscious informationprocessingusingcornealreflectionreportedin1901 Techniquesusingcontactlensesto improveaccuracydevelopedin 1950s (invasive) Remote(non-invasive)trackersrely onvisiblefeaturesof theeye(e.g.,pupil) Fastimageprocessingtechniqueshavefacilitatedreal-timevideo-basedsystems
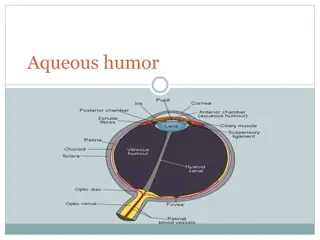
The Anatomy of the Eye Therearetwo lightreceptorcellsin the retina: conecellsand rodcells. Thevisualfieldisacombination of the two primary types of vision: Foveal vision : create high resolution and colorful image,which isform by tightly packed conecellswhich accountfor 6%of total retinal light receptors. Peripheralvision:create blurry andlesscolorful image, which is form by rod cells which account for the other 94%of total retinal light receptors.
Eye Tracking Devices Surfaceelectrodes,electrooculogram,Electro-oculography(EOG) Scleralcontactlens/searchcoil Photo-Oculography (POG)or Video-Oculography(VOG) Video-BasedCombinedpupil/corneal reflection
EOG EOGmethod relies on measurement of skin s potential differences, using electrodes placed around theeye EOGtechniquesarehelpful inmeasuringsaccade latency, but not goodat measuringlocation(unless head isalso tracked) Usedmore for diagnosis
Scleral contact lens/search coil Scleralcoil embedded in contact lensand electromagnetic fieldframes While scleral coils offer high spatial resolution (0.01 )andhightemporal resolution (1,000Hz), they are invasive and uncomfortable for participants, hence less preferred, except in clinicalsettings.
Video-Based Combined pupil/corneal reflection Based on real-time image processing to recognizeand localize pupil and corneal reflection The Red-Eye effect when we take photo Headmounted vsremote
Calibration Eye tracker measures characteristics of the user s eyes and uses them together with an internal, anatomical 3D eye model to calculate the gaze data. The model includes information about shapes, light refraction and reflection properties of the different parts of the eyes (e.g. cornea, placement of the fovea, etc.) During the calibration the user is asked to look at calibration dots.During this period several imagesof the eyes are collected and analyzed.
Ideal Eye Tracking Methods Should Have: 1.Accuracy 6.Noprior calibration 2.Reliability 7. Real-timeresponse 3.Robustness 8.Work for dynamicdisplays 4.Non-intrusiveness 9.Allow for study participants mobility 5.Thepossibilityfor free headmovements 10. Bescalable
What is measured with Eye Tracking?
Types of Eye Movements Our pupilsarealways moving View staticscene Saccades Fixation View dynamicscene Vergence,Smoothpursuit, Drift, Rotation etc. A strong hypothesis is the eye-mind hypothesis (Just & Carpenter, 1976), according to which it provides a dynamictrace of where aperson s attention isbeingdirected in relation toa visual scene. Eyefixations areknown to bedriven by perceptual salienceandrelevance asdetermined from prior experience to beimportant or informative (Loftus & Mackworth, 1978)
Saccades Saccadesarethe type of eyemovement usedto move the fovea rapidly from onepoint of interest toanother Can be furthercategorized Duration: 30 120 msec Amplitude :400 - 600 /sec Latency :100 30 msec Refractory period :100 300 msec
Fixation Fixationisthe period of time where the eyeiskept alignedwith the target for acertain duration, allowing for the imagedetails to beprocessed. Relatively stableeye-in-head position: Spatialdispersion:<2 Minimal duration :100 200 msec Thresholdvelocity : <15 100 /msec
Interpret eye gazedata Area Of Interest(AOI or ROI): Certain parts of a display or interface under evaluation,andanalyzingthe eyemovements that fall within suchareas Fixationduration:How longdo usersnoticeasmeasured by dwell-time onapart of the visual scene Numberoffixations:How often do usersnotice apart of the visual scene Sequenceoffixations:Theorder in which usersnotice different parts of the visual scene Transitionsbetweenpairsofareasofinterest:How frequently usersvisit onearea of interest from another
Gaze Plot(single user) vs Heat Map(aggregated)
Use of Eye Tracking in various fields Vision Science(Neuroscience/Psychology): visual search, memory, sceneperception Computer Vision:PerceptualModels of EyeGaze,predict eyegazefor images/videos Psychology: Examinationof cognitive processin ReadingBehavior Neuroscience:Detect medicalconditions; Detect disorders Market Research/usabilityTests HCI Understandingthe perceptual aspectsof userattention ondisplays Cognitive aspectsof attention Social aspects ofattention Asaninput method,usinggazeasanalternative to the keyboardandmouse
Benefits &Limitations Benefits Limitations Eyemovements arefaster than other input methods No prior training or knowledgeisrequired for normal people Candetermine where the user sinterests are Eyetrackers areexpensive Somepeople might have to be excluded Only oneparticipant at the same time(slower than other researchmethodslike Mturk surveys)