Introduction to Fluid Mechanics Course (CHE-S202): Branches, Nature, Scope, and Important Topics
This course provides an introduction to Fluid Mechanics (CHE-S202) covering the branches, nature, scope, important topics like basic equations, pressure measurement, mass balance, energy balance, and transport processes for momentum, heat, and mass. It explores mathematical and physical principles, with a focus on design and operation of storage vessels and equipment for various transfer processes and reactions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
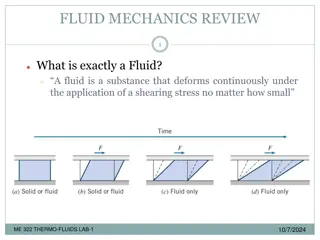
FLUID MECHANICS (CHE-S202) INTRODUCTION TO THE COURSE
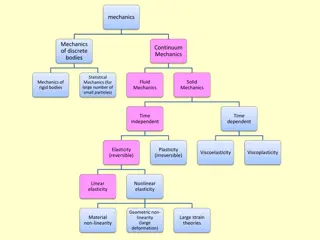
Branches of Fluid Mechanics Fluid Mechanics Fluid Dynamics Fluid Statics (Motion) (Static) (Hydrostatics/Hydraulics) (Fluid kinematics)
Nature and Scope Nature: Mathematical (vectors, vector calculus) Physical principles (law of conservation of- mass/ energy/angular momentum) Scope: Foundational Design and operation of storage vessels Design and operation of equipments for: (1) Momentum transfer (fluid moving machinery -pipes, pumps, blowers, nozzles, turbine, compressors, valves etc.) (2) Heat transfer (heat exchangers-heaters/coolers/condesers etc.) (3) Mass transfer(separators/purifiers -distillation columns, absorbers, adsorbers, extractors etc.) (4) Reactions (reactors-plug flow, mixed flow etc)
Important Topics Basic Equation of Fluid Statics Pressure Measurement Mass Balance Energy Balance (First Law of Thermodynamics) Bernoulli s Equation Laminar Flow Fluid Friction Drag Forces Flow Through Porous Media Boundary Layer Turbulent Flow Surface Tension
Transport Processes S. No. Transported quantity Driving Force Basic Law Defined property 1 Momentum Velocity gradient Newton s law of Viscosity Viscosity 2 Heat Temperature gradient Fourier s law of conduction Thermal conductivity 3 Mass Concentration gradient Fick s law of diffusion Diffusivity