Understanding Toxicity: Mole-Mass Conversions in Chemistry
Explore the toxic nature of arsenic compounds and learn how to convert between moles and mass in this chemistry lesson. Understand the relationships between mass, moles, and the number of particles in a substance, and practice converting moles to mass and vice versa. Work in pairs to delve into the concept of stoichiometry and solution chemistry, focusing on toxic compounds such as arsenic oxides and sulfides.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Living By Chemistry SECOND EDITION Unit 4: TOXINS Stoichiometry, Solution Chemistry, and Acids and Bases
Lesson 78: Mountains into Molehills Mass-Mole Conversions
ChemCatalyst Arsenic, As, arsenic (III) oxide, As2O3, and arsenic (III) sulfide, As2S3, are all toxic because they contain arsenic. a. Which is more toxic, 1 mol of As or 1 mol of As2O3? Explain your thinking. b. Which is more toxic, 1 g of As2O3or 1 g of As2S3? Explain.
Key Question How are moles related to mass?
You will be able to: convert the number of moles of a compound or an element to mass in grams convert the mass of a sample in grams to moles
Prepare for the Classwork Work in pairs.
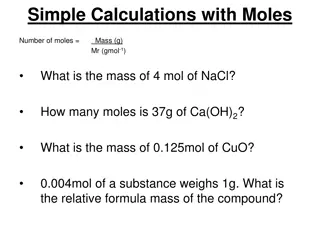
Discussion Notes The relationship between mass (g) of a substance and number of moles is proportional. Mass (g) = k moles The proportionality constant, k, is equal to the molar mass of the substance.
Discussion Notes (cont.) The relationship between the number of particles of a substance and the number of moles is also proportional. Number of particles = k number of moles In this case, the proportionality constant, k, is equal to Avogadro s number, 6.02 X 1023.
Wrap Up How are moles related to mass? In order to convert moles to mass, multiply the number of moles by the molar mass. In order to convert mass to moles, divide the number of grams by the molar mass.
Check-In A sample of chlorine gas, Cl2, has a mass of 11 g. How many moles of Cl2(g) is this?