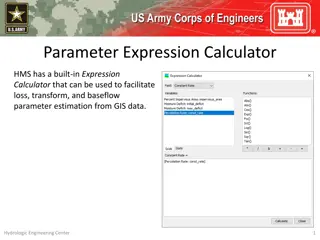
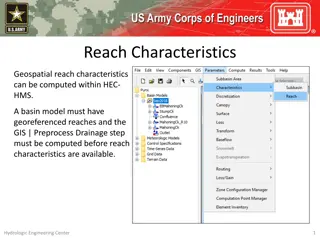
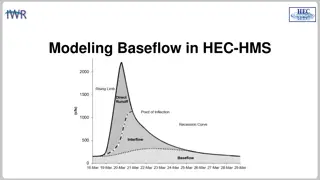
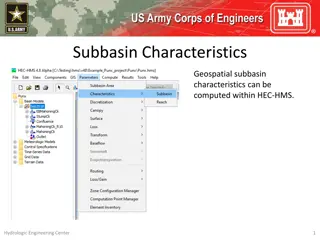
Understanding Canopy and Surface Methods in HEC-HMS
Explore the various canopy and surface methods utilized in HEC-HMS for managing water resources. Learn about canopy interception, evapotranspiration, common parameter values, and factors affecting losses. Delve into available methods, canopy storage values, and surface depression storage. Enhance your knowledge of dynamic canopy techniques and surface storage depths for different terrains.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Canopy and Surface Methods within HEC-HMS Hydrologic Engineering Center 1
Losses within HEC-HMS Interception / Canopy Storage Evapotranspiration Surface / Losses Depression Storage Excess Precipitation Infiltration / Soil Storage Hydrologic Engineering Center 2
Objectives Provide an overview of the available canopy and surface methods within HEC-HMS Supply commonly used parameter values Discuss factors that affect canopy and surface losses Hydrologic Engineering Center 3
Canopy Interception Vegetation can intercept precipitation and reduce the amount of that arrives at the ground surface Vegetation can also extract water from the soil in a process called transpiration Evaporation and transpiration are often combined and referred to as evapotranspiration Hydrologic Engineering Center 4
Available Canopy Methods Dynamic Canopy Gridded Simple Canopy Simple Canopy Hydrologic Engineering Center 5
Common Canopy Storage Values Zinke (1967) gives the following canopy interception depths: Canopy Description Storage (in) General Vegetation 0.05 These values must be calibrated and validated! Grasses and Deciduous Trees 0.08 Coniferous Trees 0.1 Hydrologic Engineering Center 6
Surface / Depression Storage Surficial depressions can temporarily store water Puddles Rough areas Captured precipitation empties over time due to infiltration and/or evapotranspiration Hydrologic Engineering Center 7
Available Surface Methods Gridded Simple Surface Simple Surface Hydrologic Engineering Center 8
Common Depression Storage Values Bennet (1998) gives the following surface depression depths: Surface Description Storage (in) Steep, smooth slopes 0.04 These values must be calibrated and validated! Most areas with impervious surface 0.125 0.250 Most areas with pervious surface 0.25 0.50 Flat agricultural land with conservation tillage 2.0 Hydrologic Engineering Center 9
Factors that Affect Canopy Interception and Surface / Depression Storage Storm character Duration Intensity Precipitation form Time of year Vegetation Type Density Catchment slope Drought Wildfire Blue River Lake, Sep 2020 Hydrologic Engineering Center 11
Review Three canopy and two surface methods are available within HEC-HMS In general, canopy and surface losses are small Multiple phenomena can affect the amount of canopy and surface losses Next lecture will focus on infiltration methods within HEC-HMS Hydrologic Engineering Center 12