Understanding Matter: Properties and Changes
Matter is anything that has mass and volume. This includes the concepts of mass, volume, chemical changes, temperature effects, particle model, kinetic molecular theory, and describing matter based on physical properties. Learn about different states of matter, such as solids, liquids, and gases, and their respective characteristics and behaviors.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Minji Han Matter -Section 1.2-
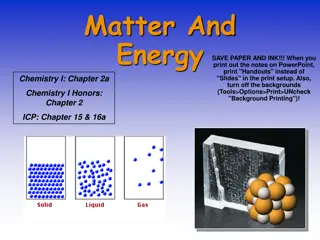
What is a matter? Matter: Anything that has mass and volume Mass is the amount of matter in a substance or object (often measured in grams) Volume is the amount of space a substance or an object occupies (often measured in liters)
Chemical Change Chemical Change : A change in matter that occurs when substances combine to form new substances. Examples : Cooking eggs Baking cakes
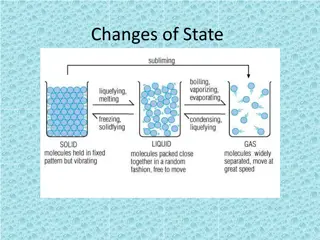
Temperature and Changes of State Changes of State depends on temperature Melting : the change of state from a solid to a liquid Boiling : the change of state from a liquid to a gas Condensation : the change of state from a gas to a liquid Solidification : the change of state from a liquid to a solid Sublimation : changing from a solid to a gas Deposition : changing from a gas to a solid
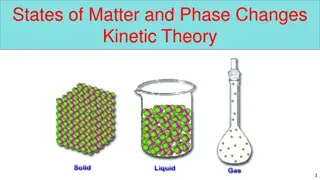
The Particle Model of Matter Matter is made of small particles There are spaces between the particles Particles are always moving Particles are attracted to each other. The strength of attraction depends on the type of particle
Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic energy : the energy of motion All particles in every solid, liquid, and gas are always moving, so they have kinetic energy. Solid : vibrates Liquid : move by sliding past each other Gas : move around quickly Energy makes particles move. The more energy the particles have, the father apart they can get.
Describing Matter(Physical Property) Qualitative properties : can be described but not measured Quantitative properties : can be measured with numbers State Solubility : ability to dissolve in water Color Conductivity : ability to conduct electricity or heat Malleability : ability to be beaten into sheets Viscosity : resistance to flow Ductility : ability to be drawn into wires Density: ratio of a material s mass to its volume Crystallinity : shape or appearance of crystals Melting Magnetism : tendency to be attracted to a magnet Boiling
Pure Substances Pure Substance: made up of only one kind of matter. Ex) gold, water, oxygen Element -can t be broken down or separated into simpler substances. -gold and oxygen Pure Substance Compound -composed of at least two elements combined in a specific way -hydrogen and oxygen
Citations Science 9 textbook section 1.2