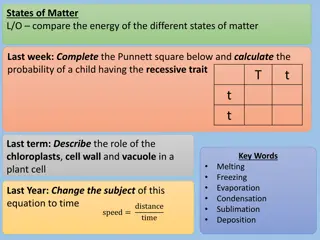
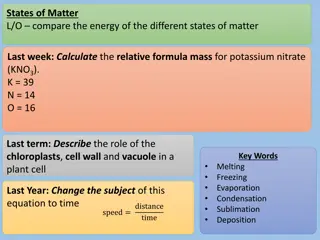
States of Matter, Properties, and Changes Study Guide Answers
This study guide provides answers to questions related to states of matter, properties, and changes. It covers topics such as physical and chemical changes, measuring liquid volume, defining matter, particle arrangements in solids, liquids, and gases, mass, sublimation, phase changes, and more.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
States of Matter, Properties, and Changes Study Guide Answers
1. Are these examples of physical or Chemical Change? a. burning paper. Chemical b. baking cookies. Chemical c. heating table sugar. Depends d. dissolving salt in water. Physical e. filtering. Physical f. burning wood. Chemical g. boiling water. Physical h. crushing a can. Physical
i. gas burning on a stove. Chemical j. rust forming on an iron fence. Chemical k. salt dissolving in a glass of water. Physical l. using electricity to break down water into hydrogen and oxygen. Chemical 2. In the laboratory, how is the volume of a liquid usually measured? Name the instrument. Displacement, graduated cylinder 3. Anything that has mass and takes up space is called ___________________. Matter 4. How do liquid water, ice, and water vapor differ from each other? Different states or phases of matter
5. Define Matter. Anything that has matter and takes up space 6. How are the particles arranged in a solid, liquid, gas? Explain and draw an example. Solid = definite shape and volume, vibrates in place. Liquid = No definite shape, definite volume, slips and slides past, flows. Gas = No definite shape or volume. Moves freely.
7. __________________ is the amount of matter contained in an object. Mass 8. When an inflated balloon is exposed to cold air, what happens? a. the temperature inside the balloon rises. b. the pressure inside the balloon rises. c. the volume of the balloon decreases. d. the volume of the balloon increases.
9. What happens during sublimation? Substance changes from a solid to a gas. 10. The change from liquid to solid, or the reverse of melting, is called _______________. Freezing Point 11. According to the phase change diagram, the freezing point of water is the same as its _____________. Melting Point 12. How would you describe the process of vaporization? A Change from liquid to gas.
13. An uncovered pot of soup is simmering on a stove, and there are water droplets on the wall above the back of the stove. What sequence can you conclude has occurred? a. melting, then boiling b. freezing, then thawing c. vaporization, then condensation d. condensation, then vaporization 14. Stars and lightning are both examples of which state of matter? Plasma 15. The amount of space that a gas takes up is its _______________. Volume
16. If Density = Mass/Volume, what is the density of a fishing sinker with a mass of 75g and a volume of 3cm3? 25 g/cm3 17. The tarnishing of metal is an example of a ____________________ change. Chemical 18.Dissolving a spoonful of sugar in tea or coffee is an example of a ____________ change. Physical 19. Vapors coming off of dry ice at room temperature is an example of_____________. Sublimation
20. Be able to label the phase change diagram. A. Freezing Point B. Melting Point C. Condensation D. Boiling Point/ Vaporization 21.The standard unit of measure for mass in the metric system is _____________. Grams
22. Be able to answer each choice below in complete sentences and in a minimum of 1 paragraph. a. Is the melting of an ice cube considered a physical change or a chemical change? Explain your reasoning. Physical, change of state, nothing new is made, easily reversable. b. Compare solids, liquids, and gases in terms of shape and volume. Solid = definite shape and volume. Liquid = No definite shape, definite volume. Gas = No definite shape or volume. c. Suppose you buy some inflated party balloons that are at room temperature (about 20 C). What will happen to those balloons if you take them outside on a cold day? Explain. Pressure in balloon will decrease as temperature decreases. Gas particles will lose energy and move closer together. Volume of balloon will decrease. d. Explain what happens to the water molecules in an ice cube when it is removed from a freezer. Molecules absorb heat, gain energy, flow past each other and become disorganized, Change from solid to liquid.
e. Is making ice cream the old fashioned way a chemical or physical change? Explain your reasoning. Physical, change of state, nothing new is made, dissolving and freezing are physical changes. 22. What does the Law of Conservation of Matter/Mass state? Give an example that proves the law. Matter cannot be created or destroyed; it only changes forms. Melting ice POE, frozen ice cubes and melted ice cubes has the same mass before and after the physical change. Alka-Seltzer Tablet and Water POE, mass of the closed system was the same before and after the chemical change.