Understanding the Role of Glucose in Photosynthesis
Exploring how plants use glucose produced during photosynthesis, including its various uses such as providing energy, being stored as starch, and contributing to the formation of plant cell walls and other essential chemicals. The process of photosynthesis, the fate of glucose, and the conversion of glucose into structural and storage carbohydrates are discussed in detail.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
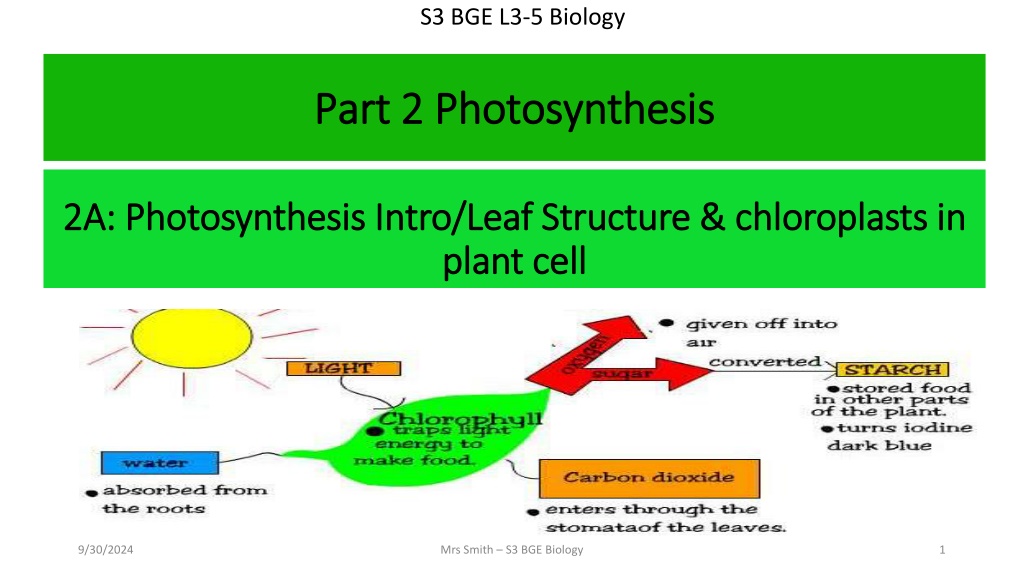
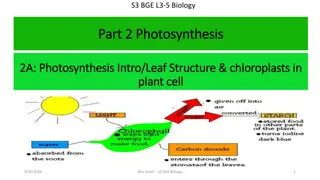
S3 BGE L3-5 Biology Part 2 Photosynthesis Part 2 Photosynthesis 2A: Photosynthesis Intro/Leaf Structure & chloroplasts in 2A: Photosynthesis Intro/Leaf Structure & chloroplasts in plant cell plant cell 9/30/2024 Mrs Smith S3 BGE Biology 1
National 5 Biology Learning Intentions Learning Intentions Level 3 Planet Earth: Biodiversity & interdependence SCN 3-02a; Topical Science SCN 3-20b National 3: Unit 1: Key Area 1.4 The process of photosynthesis The uses of sugar made during photosynthesis Level 5 Planet Earth: Biodiversity and interdependence SCN 5-02a; Topical Science SCN 5-20a National 5: Unit 3: Key Area 3.3b. Photosynthesis, Fate of glucose. The chemical energy in sugar is available for respiration or the sugar can be converted into other substances such as starch (storage) and cellulose (structural) L3 Learning Outcomes: You should be able to o Describe the uses of sugar made during photosynthesis. o Define starch and cellulose and the role of each in the plant. L5 Learning Outcomes: as well as L3 outcomes: you should be able to o Describe that sugar can be broken down by respiration to supply the plant with energy for vital processes such as cell division and reproduction. o Describe the conversion of glucose into plant products. Specifically describe how glucose is converted into structural and storage carbohydrates. 9/30/2024 Mrs Smith S3 BGE Biology 2
STARTERLESSON: Unscramble the lesson keywords SHIOTTPYSHONS Photosynthesis LOSGEUC Glucose TEWAR Water DCIAORXBIODNE Carbon Dioxide PTCRDOUS Products LTHPCOOLYRH Chlorophyll ASAMOTT Stomata Extension Write the role of each word in photosynthesis
S3 BGE L3-5 Biology What do plants use glucose for? Discuss What do plants use glucose for? Discuss 9/30/2024 Mrs Smith S3 BGE Biology 4
S3 BGE L3-5 Biology L3 L3 The uses of Glucose The uses of Glucose The glucose made during photosynthesis can be Released immediately to give energy for all the plant s activities. Stored as STARCH Made into CELLULOSE, which is needed to make plant cell walls. Helps to make other important chemicals, including proteins and oils. 9/30/2024 Mrs Smith S3 BGE Biology 5
(L5) THE USES OF SUGAR MADE DURING PHOTOSYNTHESIS The sugar made in the process of photosynthesis is a source of chemical energy. This energy is available for respiration or can be converted into plant products such as STARCH and CELLULOSE.
GLUCOSE: STORED AS CARBOHYDRATES Unlike humans, plants cannot source different food types. The only food available to plants as they grow is the carbohydrate (glucose) made during photosynthesis. Some of this sugar is broken down again by respiration to supply the plant with energy for vital processes such as cell division and reproduction.
GLUCOSE: STORAGE & STRUCTURAL CARBOHYDRATES STORAGE CARBOHYDRATES Some of the remaining glucose molecules become linked into long chains and packed together into starch grains found in the cell s cytoplasm. This plant product is the plant s store of food and can be converted back to sugar when energy is required. Starch is therefore called a storage carbohydrate. STRUCTURAL CARBOHYDRATE Other glucose molecules are built into long chains of cellulose. These are gathered to form the fibres needed to build cell walls. Cellulose is therefore called a structural carbohydrate.
GLUCOSE: STORAGE & STRUCTURAL CARBOHYDRATES
PLENARY TASK: COMPLETE THE WORKSHEET: Uses of glucose
National 5 Biology Have you achieved the Learning Intentions? Have you achieved the Learning Intentions? CAN YOU L3 Learning Outcomes: o Describe the uses of sugar made during photosynthesis o Define starch and cellulose and the role of each in the plant L5 Learning Outcomes: o Describe that sugar can be broken down by respiration to supply the plant with energy for vital processes such as cell division and reproduction. o Describe the conversion of glucose into plant products. Specifically describe how glucose is converted into structural and storage carbohydrates. 9/30/2024 Mrs Smith S3 BGE Biology 11