Understanding Polymers and Their Properties
Polymers are long chains of repeating monomers, with both natural and synthetic varieties. Natural polymers include silk, cellulose, and DNA, while synthetic ones encompass plastics, fibers, and elastomers. The properties of polymers, such as molar mass and monomer structure, determine their functio
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Composition of Soil Organic Matter in Soil Microbiology
Soil organic matter is vital for soil properties and plant nutrition. It consists of plant residues, animal remains, and microbial tissues, comprising complex compounds like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and more. The composition varies with plant type, age, and nature. Leguminous plants are rich i
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Carbohydrates in Living Organisms
Carbohydrates, along with proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, are essential macromolecules in living organisms. They are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. Carbohydrates provide the main energy source for living things, with examples including glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
0 views • 58 slides
Understanding Easy-Care and Durable Press Finishes for Textiles
Easy-care and durable press finishes play a vital role in enhancing the quality and longevity of textiles, particularly those made of cellulose fibers. These finishes reduce shrinkage, improve wrinkle recovery, and maintain fabric appearance. While beneficial, they may impact fiber flexibility and s
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Stabilizers in Dairy Technology by B.K. Singh
Stabilizers are key ingredients used in ice cream and related products to enhance viscosity, stability, texture, and shelf life. They help in preventing wheying off, controlling crystal growth, and maintaining product quality during storage. Various types of stabilizers, including proteins, plant ex
0 views • 15 slides
Properties and Utilization of Common Polysaccharides in Food Chemistry
Polysaccharides are carbohydrates with more than 10 monosaccharide units, commonly found in foods like starch, cellulose, glycogen, hemicellulose, and pectic substances. Starch, a natural polymer of D-glucose, is a major energy source in the human diet, present in cereals, roots, and tubers. It cons
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding the Digestive System of Ruminant Animals
Ruminant animals have a unique digestive system that allows them to efficiently digest cellulose. Their stomach consists of four chambers, each serving a specific function in the digestion process. The breakdown of cellulose by microbes in the rumen produces glucose, which provides energy for the an
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding the Structural Roles of Biomolecules in Living Organisms
Explore the essential roles of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in cell structure and function. Learn how cellulose, keratin, myosin, phospholipids, and more contribute to the structural integrity and metabolic activities within living organisms. Discover the significance of these biomolecules in
4 views • 23 slides
Characteristics of Phaeophyta - Brown Algae (Seaweeds)
Phaeophyta, also known as brown algae or seaweeds, exhibit unique characteristics including cellulose fibers with Alginic acid, food reserves like laminarin and mannitol, and a life cycle consisting of both haploid and diploid stages. They possess photosynthetic pigments giving them their brown colo
1 views • 26 slides
Affinity Chromatography: A Breakthrough in Biochemical Research
Affinity chromatography, developed in the 1930s by A. Wilhelm Tiselius, is a vital technique for studying enzymes and proteins. It relies on the specific affinity between biochemical compounds and utilizes matrices like agarose for binding sites. Ligands such as amino and hydroxyl groups play crucia
1 views • 27 slides
Sawdust as a Low-Cost Adsorbent for Water Treatment
Sawdust, a renewable natural resource, has been studied for its effectiveness as an adsorbent for removing contaminants from water. It contains cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, and other components that aid in adsorption. Research indicates its suitability for removing dyes, toxic salts, and heavy
0 views • 22 slides
Topical Hemostats, Glues, and Lasers in Neurosurgery at AIIMS
Hemostasis is crucial in neurosurgery for controlling bleeding without ligatures. Various topical hemostats like chemical, mechanical, collagen, thrombin, and fibrin glues are used. Surgicel and Oxycel, oxidized cellulose polymers, act as physical matrices aiding in clot formation. Gelatin sponges l
0 views • 22 slides
Classification and Characteristics of Phylum Protozoa
Phylum Protozoa comprises unicellular, microscopic, eukaryotic organisms found mostly in aquatic habitats. They exhibit diverse locomotory structures such as cilia, flagella, or pseudopodia. These protists may possess a cellulose cell wall and various membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria and
0 views • 21 slides
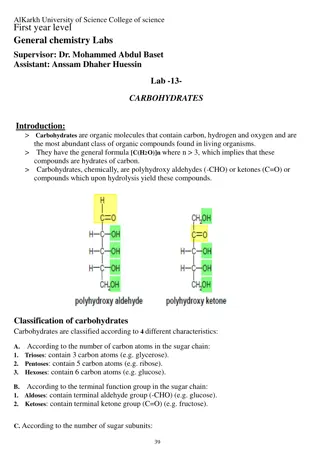
Understanding Carbohydrates: Composition, Structure, and Function
Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a specific ratio. Monosaccharides such as glucose, fructose, and galactose are carbohydrate monomers, while polysaccharides like lactose, sucrose, starch, cellulose, and glycogen are carbohydrate polymers. The chemical formula for glucose
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Starches, Cellulose, Gums, and Pectins in Food
Explore the roles of starches, cellulose, gums, and pectins in the diet. Learn about their structures, functions, and how they affect food texture and properties. Discover how these components bind, thicken, and provide structure in various food preparations.
1 views • 29 slides
Exploring CMF Twist in Cellulose Nanocrystals: Simulations, Experiments, and Implications
Explore the twist phenomenon in cellulose nanocrystals known as CMF through simulations and experimental evidence. Discover how isolated cellulose chains twist, the challenges in visualizing CMF twist, proposed alterations upon drying, and the implications of CMF twist in forming a liquid crystal ph
1 views • 7 slides
Understanding Carbohydrates: A Comprehensive Overview
Carbohydrates are essential organic compounds found abundantly in living organisms, containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. This summary delves into the classification of carbohydrates based on characteristics like the number of carbon atoms, terminal function groups, and the number of sugar subuni
0 views • 5 slides
Advanced Moisture Renewal Mask for Oncology Spa Services
Bel Mondo Beauty introduces a breakthrough Moisture Renewal Mask made from bio cellulose, a fabric with incredible skin affinity and efficient ingredient transfer. This professional series mask targets oncology spa services, developed in collaboration with Oncology Spa Solutions to care for clients
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Carbohydrates in Science: Structure, Types, and Applications
Explore the comprehensive study of carbohydrates, including their types such as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Learn about the molecular structure and functions of cellulose, starch, and other key carbohydrates. Delve into the chemistry of sugars, nucleic acids, and protein syn
0 views • 32 slides
Revolutionizing Plastics: Making Cellulose-Based Plastic from Hemp in New Mexico
New Mexico State University could lead the way in establishing a plastics industry using cellulose plant fibers, such as hemp, to create eco-friendly and sustainable plastic products. Zeoform, a material made from cellulose fibers and water, offers a patented process to form industrial-strength plas
0 views • 14 slides
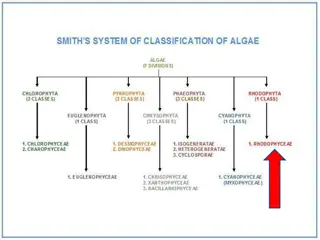
Main Characteristics of Rhodophyta: The Red Algae Division
Rhodophyta, or red algae, are mostly marine algae with distinct photosynthetic pigments giving them a red color. Their main characteristics include the presence of phycoerythrin pigment, floridean starch as food reserve, thalloid plant body structure, oogamous sexual reproduction, and cell walls con
0 views • 27 slides
Overview of Fiber Chemical Composition and Types
Fibers consist of polymers made from simple molecules, with natural fibers like wool, silk, cotton, and linen having specific compositions including proteins, cellulose, and glucose. Man-made fibers like rayon and acetate are chemically altered cellulose, while synthetic fibers like nylon and polyes
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Cellulosic Fibres in Textile Raw Materials
Fiber concept includes the flexibility and characteristics of fibers as textile raw materials, with a focus on cellulose, the most abundant polymer in nature. Cellulose fibers, such as cotton, exhibit unique structural properties and molecular formations that contribute to their properties in fabric
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Plant Cell Walls: Structure and Function
Plant cell walls play a crucial role in providing structure and protection to plant cells. This article delves into the composition of primary and secondary cell walls, highlighting the presence of cellulose, pectins, and glycans. The secondary cell wall, rich in lignin, offers mechanical support, e
0 views • 38 slides
Understanding Polysaccharides: Structure and Function in Chemistry
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates made up of multiple monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic linkages. Examples include starch, cellulose, and glycogen. Starch, a major plant carbohydrate, consists of amylose and amylopectin. Amylose forms a linear structure, while amylopectin is highly b
0 views • 13 slides
Obtention of Cellulose Nanofiber from Almond Shell Using Different Chemical Treatments
This study conducted in Trabzon, Turkey, focused on obtaining cellulose nanofibers from almond shells through various chemical treatments. Different procedures involving alkaline solutions, bleaching, hydrolysis, and acetylation were used to remove lignin content and achieve optimal crystallinity. A
0 views • 7 slides
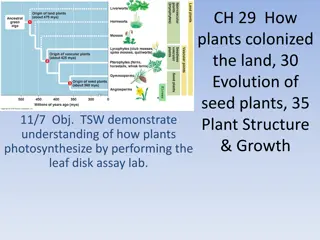
Understanding Plant Evolution and Characteristics
Plants colonized land through various adaptations such as multicellularity and photosynthesis. They exhibit characteristics like chlorophyll, cellulose cell walls, and apical meristems. Plant evolution includes alternation of generations, with gametophytes and sporophytes undergoing meiosis and mito
0 views • 15 slides
Polymer Reactivity and Modification: Synthesis and Reactions
Reactions of polymers involve the synthesis of new polymers through modification, such as esterification of cellulose, crosslinking of polyisoprene, hydrolysis of poly(vinyl acetate), and chlorination of polyethylene. Polymer reactions utilize chemical processes to create new materials, carriers, or
0 views • 48 slides
Fish Packaging Technology Overview
Explore the use of nonethylenic thermoplastics like polyamides or nylons in fish packaging technology, citing examples such as Nylon 6, Nylon 6:6, and Nylon 6:10. Learn about their important properties, applications in gas/vacuum packaging and boil-in-bag pouches, as well as the benefits of combinin
0 views • 21 slides