Understanding Photosynthesis: Energy Conversion in Living Organisms
Explore the process of photosynthesis and how energy is harnessed by living organisms through the conversion of sunlight into high-energy sugars. Discover the essential role of ATP in cellular processes and learn about key scientists who contributed to our understanding of photosynthesis. Delve into the photosynthesis equation, detailing how plants utilize sunlight to produce oxygen and sugars essential for their survival.
Uploaded on Sep 30, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Photosynthesis Chapter 8
Energy and Life Section 8-1
Energy and Life Energy is the ability to do work. All living things use energy stored in chemical compounds to survive. (FOOD) Heterotrophs eat food to get energy Autotrophs make their own food from sunlight and inorganic molecules to get energy. When are you not using energy?
Chemical Energy and ATP Energy from food is changed into another form cells can use. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) energy molecule of the cell (made by what organelle?) Must break down the foods to generate the ATP. Breaking the bonds between the phosphate atoms will release the energy from ATP. Used ATP is now ADP. (what is ADP?) Energy stored in foods (glucose) will change ADP back into ATP.
ATP The ATP molecule! (Know this structure) Section 8-1 Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups
Figure 8-3 Comparison of ADP and ATP to a Battery Section 8-1 ATP being made from ADP! ADP ATP Energy Energy Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) + Phosphate Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Partially charged battery Fully charged battery This energy that will be stored into the ATP molecule which comes from food!
Photosynthesis: An Overview Section 8-2
Who Were the Scientists? Jan Van Helmont 1643 1. What do plants take from the soil? 2. Trees gain mass from water not soil. Joseph Priestley 1771 1. Something in the air kept candle burning. 2. Plants released oxygen. Jan Ingenhouz 1779 1. Oxygen was only produced by plants in the presence of light.
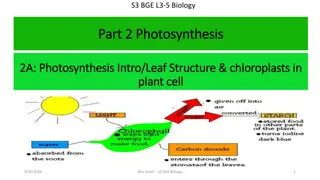
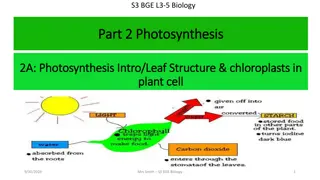
Photosynthesis Equation Light 6CO2 + 6H2O ------- C6 H12O6 + 6O2 Light Carbon dioxide + water ------ sugar + oxygen Photosynthesis uses the sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy sugars (glucose)! What will the plant do with the sugar it has made? Generate ATP for cellular processes!
Light and Pigments Photosynthesis uses pigments in the leaf to obtain sunlight. Pigments absorb and reflect light. Chlorophyll is the green pigment in chloroplasts. Why is it green? Two main types of chlorophyll: Chlorophylla and Chlorophyll b Other pigments (red, orange, yellow) are found in Plastids which will absorb energy and transfer to chlorophyll.
Figure 8-5 Chlorophyll Light Absorption Section 8-2 Absorption of Light by Chlorophyll a and Chlorophyll b What wavelengths does chlorophyll work the best in? Chlorophyll b What wavelengths does chlorophyll not work well in? Chlorophyll a Which color light would a plant grow best under: Green, red, yellow? V B G Y O R
Photosynthesis: Reactants and Products Section 8-2
The Reactions of Photosynthesis Section 8-3
The Chloroplast Structure of Chloroplast: 1. Thylakoids saclike photosynthetic membrane (they look like pancakes!) a. Contains light absorbing pigments b. Light Dependent reaction occurs here 2. Grana(um) stacks of thylakoids 3. Stroma space surrounding the thylakoids a. Calvin cycle occurs here.
The Reactions Two reactions run the photosynthesis process: 1. Light-Dependent reaction - sunlight required to run; it is a reactant 2. Calvin Cycle (aka Light-Independent reaction) - no sunlight required to run - however, needs products of light reaction to run.
Light Dependent Reaction Takes place in the thylakoids Sunlight excites electrons in chlorophyll Electron energy passed to carrier molecule NADP+ to make NADPH. H2O is broken down to use H+ ions to convert ADP to ATP by ATP synthase protein. Oxygen atoms released as waste.
Figure 8-7 Photosynthesis: An Overview Section 8-3 H2O CO2 NADP+ ADP + P Calvin Cycle Light- Dependent Reactions ATP NADPH Sugars O2
Light Independent Reaction or Calvin Cycle Takes place in the stroma. CO2 combines a 5 carbon sugar to produce two 3-carbon molecules. Catalyzed by the enzyme RUBISCO. ATP and NADPH from light phase convert the 3-carbon molecules into glucose!
Figure 8-7 Photosynthesis: An Overview Section 8-3 H2O CO2 NADP+ ADP + P Calvin Cycle Light- Dependent Reactions ATP NADPH Sugars O2
How is the Rate of Photosynthesis Controlled? Availability of water lack of water slows process down plants in warm climates have waxy coating to reduce water loss Temperature best rate occurs between 0 and 35 degrees Celsius Intensity of light increasing light intensity increases rate