Understanding Photosynthesis: A Comprehensive Overview
Photosynthesis is the fundamental process through which plants produce food in the form of glucose. This intricate process involves the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose using sunlight as the energy source. The key player in photosynthesis is chlorophyll, a green compound found in chloroplasts. This summary provides insights into the reactants, energy sources, and compounds involved in photosynthesis, along with a description of the leaf structures essential for this process.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process which produces "food" in plants. The product is a sugar, known as "glucose" and is used by plants in various ways, such as to produce cell walls and protein.
Photosynthesis Any glucose that the plant does not use is converted into either lipids or starch, and is stored for later use.
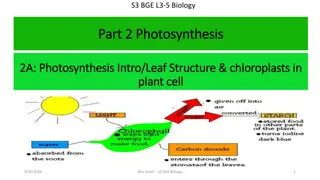
Photosynthesis Plants use a substance called chlorophyll, which is green and found in structures in a plant leaf called chloroplasts. There are four raw materials to consider: Chlorophyll Carbon dioxide Water Sunlight
Photosynthesis You will need to MEMORISE the WORD version at the top because in your Biology studies it will come up many times and is a favourite for tests and exams. You don t necessarily need to memorise the symbolic version but it s a bonus if you can recite it if asked.
Photosynthesis Q. What are the two REACTANTS involved in photosynthesis ? Carbon Dioxide Water Q. Name the energy source involved in photosynthesis Sunlight Q. Name the green compound involved in photosynthesis Chlorophyll
Photosynthesis This CROSS SECTION of a leaf shows the structures involved in keeping the leaf healthy and which get involved in this process. We will take a brief look at each part starting on the next slide.
Photosynthesis EPIDERMIS - The skin of the leaf. The epidermis serves several functions: it protects against water loss, regulate gas exchange, secretes metabolic compounds, and (especially in roots) absorbs water and mineral nutrients. The epidermis is covered in a waxy substance (waxy cuticle) to help prevent excess moisture loss.
Photosynthesis PALISADE MESOPHYLL LAYER - Palisade cells contain the largest number of chloroplasts per cell, which makes them the primary site of photosynthesis in the leaves of those plants that contain them, converting the energy in light to the chemical energy of carbohydrates. Beneath the palisade mesophyll are the spongy mesophyll cells, which also perform photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis STOMATA AIR SPACES Both are adaptations of the structure of the leaf to allow gases to move freely around, in and out, of the leaf. GUARD CELLS control the opening and closing of the stomata so that excessive moisture and gas loss is avoided.
Photosynthesis Q. Would you expect to find chloroplasts in the roots of a plant?