Understanding Photosynthesis: Process and Importance in Plants
Photosynthesis is a vital process in green plants where they use carbon dioxide and water to produce sugar and oxygen, facilitated by chloroplasts. Limiting factors such as light, water, and temperature can impact photosynthesis rate. Green plants are producers that make their own food through photosynthesis, while humans and animals are consumers who obtain energy from the food they eat.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
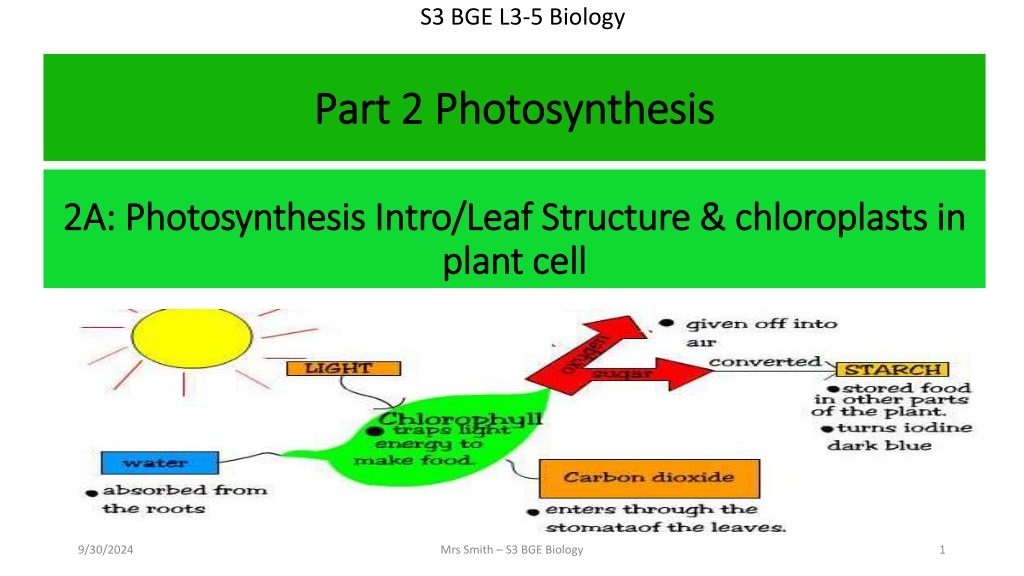
S3 BGE L3-5 Biology Part 2 Photosynthesis Part 2 Photosynthesis 2A: Photosynthesis Intro/Leaf Structure & chloroplasts in 2A: Photosynthesis Intro/Leaf Structure & chloroplasts in plant cell plant cell 9/30/2024 Mrs Smith S3 BGE Biology 1
National 5 Biology Learning Intentions Learning Intentions Level 3 Planet Earth: Biodiversity & interdependence SCN 3-02a; Topical Science SCN 3-20b. National 3: Unit 1: Key Area 1.4 The process of photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process in which green plants use carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil to produce sugar and oxygen. Level 4 Planet Earth: Biodiversity and interdependence SCN 4-02a; Topical Science SCN 4-20a National 4: Unit 1: Key Area 1.6 The effect of limiting factors on photosynthesis. 1.6. If any of the requirements are low or missing, the photosynthesis rate is limited L3 Learning Outcomes: You should be able to Describe the process of photosynthesis. Give the word equation for photosynthesis. State the conditions needed for photosynthesis. Understand the role of chloroplasts in photosynthesis. L4 Learning Outcomes: as well as L3 outcomes: you should be able to Understand that if any of the requirements are low or missing (light, water, carbon dioxide or a suitable temperature), the photosynthesis rate is limited. 9/30/2024 Mrs Smith S3 BGE Biology 2
S3 BGE L3-5 Biology Needs of living things: Discuss Needs of living things: Discuss 9/30/2024 Mrs Smith S3 BGE Biology 3
S3 BGE L3-5 Biology Needs of living things: Discuss Needs of living things: Discuss Remember plants are living things too! 9/30/2024 Mrs Smith S3 BGE Biology 4
How do humans (consumers) get energy. How do humans (consumers) get energy. Humans and animals are consumers organisms that need to get their energy from the foods they eat. Traditionally humans were hunters and gathers of food. Later we also learned to grow and farm the food we eat. Now as consumers we can buy our food from restaurants and supermarkets.
How do plants (producers) get energy. How do plants (producers) get energy. Plants need energy too They get nutrients in two ways 1. Water and minerals are taken up from the soil through their roots. 2. All green plants produce their own food. (This is why they are called producers). Although there are species of carnivorous plants (which are both producers and consumers)
So how do green plants make their own food? So how do green plants make their own food? Photosynthesis! Photosynthesis! PHOTOSYNTHESIS is a very important chemical reaction carried out by all green plants to make food. Green plants contain chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are the site pf photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, plants use carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil to produce a sugar called GLUCOSE, and oxygen.
Can we feed plants? Can we feed plants? Gardeners/ sometimes say that they feed their plants This isn t true food. It wont give the plant any energy but fertilisers do contain minerals that help the plant grow and keep it healthy. It s the same with carnivorous plants such as Venus fly traps, pitcher plants, and sundews which all consume insects, but that s not how they get their energy. They still get their energy from the sun and transform it into food (glucose) using photosynthesis. They use the dead insects to get essential minerals. This is because carnivorous plants are found in environments where there are very low levels of nutrients in the soil.
Photosynthesis Word Equation Photosynthesis Word Equation The Raw materials (ingredients) The Raw materials (ingredients) The raw materials are the ingredients required for photosynthesis to take place. We always find the raw materials on the left- hand side of the word equation (shown in red). Without water, which is carried from the soil and carbon dioxide, which is take from the air, photosynthesis cannot occur.
Photosynthesis Word Equation Photosynthesis Word Equation The Products (new substances) The Products (new substances) The products are the new substances which are made during the chemical reaction (photosynthesis). We always find the products on the right-hand side of the word equation (shown in blue). The glucose made by photosynthesis provides energy for the plant to grow and to carry out all living processes. Oxygen is also produced during photosynthesis. Some of the oxygen is used inside the plant for a process called respiration, which releases the energy needed by the plant to carry out its activities. However, most of the oxygen is not needed and is released as a by-product into the air.
Conditions needed: Conditions needed: CHLOROPLASTS + LIGHT CHLOROPLASTS + LIGHT The chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis (where photosynthesis happens). The energy needed for photosynthesis to take place comes from the sun. CHLOROPLASTS contain a green pigment called CHLOROPHYLL that absorbs the LIGHT ENERGY from sunlight. The light energy is converted to chemical energy in glucose using the chlorophyll
Where CHLOROPLASTS are found: Where CHLOROPLASTS are found: REVISION CELL STRUCTURE REVISION CELL STRUCTURE In S1 you learned that the cell is the most basic unit of all living things. All organisms including plants are made of cells. Only green plant cells have chloroplasts (Remember this is where photosynthesis happens!) The more chloroplasts a leaf has, the more light it can absorb to carry out photosynthesis. Why do onion cells not have chloroplasts? Chloroplasts in plant cells seen using a microscope.
TASK: CARD SORT TASK: CARD SORT WORD EQUATION CARD SORT WORD EQUATION CARD SORT Carbon dioxide Water. You must learn this equation. Each person in each group should arrange the cards into a word equation. Who s the quickest group Light Energy Chlorophyll Reacts to produce. Glucose which is converted into starch. EXTENSION TASK: CARD SORT EXTENSION TASK: CARD SORT Can Can you repeat as a chemical you repeat as a chemical equation? equation? Oxygen Raw materials. Products
EXTENSION WORK EXTENSION WORK In biology the structure of living things is related to their function (the job they do). Leaf s are especially adapted to carry out photosynthesis so that the plant can make its own food (glucose).
EXTENSION Continued EXTENSION Continued TASK LABEL THE DIAGRAM TASK LABEL THE DIAGRAM
EXTENSION Continued EXTENSION Continued Understanding structure related to function Understanding structure related to function At level 3 and 4 you do not need to learn the table in the next slide. However, in biology it is useful to understand how the structure of an organism (or its parts) helps it carry out it s job. In addition, L5 looks at the structure of the leaf again when looking at Transport systems in plants (KA2.5a). So later on you can MAKE THE LINK
EXTENSION Continued EXTENSION Continued Understanding structure related to function Understanding structure related to function Structure in the leaf which helps photosynthesis Waxy cuticle Thin and made of wax, this stops the plant form losing the water which is needed for photosynthesis. Epidermis This is a thin transparent protective layer. It protects the leaf without stopping light reaching the chloroplasts in the next layer Mesophyll cells These are packed with chloroplasts to increase the absorption of sunlight. The upper layer of mesophyll cells are long and thin to allow light has to pass through as many chloroplasts as possible. Air spaces Air spaces between the photosynthesising cells and the stomata increase the surface area inside the cell to increase gas exchange (Diffusion of Carbon dioxide into the cell and oxygen out of the cell). Stomata These are pores on the underside of the leaf which allow gases (Carbon dioxide and Oxygen) to diffuse in and out of the leaf. Guard Cells Control the opening and closing of the stomata so that the leaf does not lose too much water Network of Xylem Carries water from the roots up the stem, into the veins of the leaf to deliver water and dissolved mineral salts to the mesophyll cells (containing the chloroplasts) Phloem Carries away the sugars made during photosynthesis to all parts of the plant. Function (How the structure helps photosynthesis)