Understanding Simple Interest: Calculations and Examples
Explore the concept of simple interest, including its definition, types, terminology, and calculations. Learn how to calculate interest based on principal, rate, and time with practical examples. Discover how to determine interest earned, balance, and interest rates in various scenarios involving deposits and loans.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Simple Interest Essential Skill: Explicitly Assess Information and Draw Conclusions
Simple Interest What is interest and why does it exist? When you deposit money into a savings account, the bank invests your money and pays you interest based on an interest rate When you take out a loan, you will have to pay interest on the money you borrow
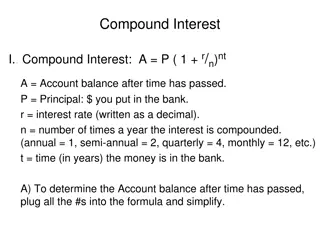
There are two types of interest: Simple Interest: When interest is earned or paid only on the principal. Compound Interest: When interest is earned or paid on both the principal and any interest that has been earned or accrued previously.
Simple Interest Terminology Principal- the original amount of money you deposit Interest- the amount of money you earn from the bank Rate- the percent of interest Time- the amount of time (in years) you invest for Balance- the principal plus the interest
Here is how to calculate simple interest Interest = (principal)(rate)(time) I= Prt 1.) Suppose you deposit $400 in a savings account. The interest rate is 5% per year. A.) What is the amount of interest in six years? B.) What is the balance in six years?
I= Prt 2.) Johnny deposited $575 in a savings account for 3 years at an interest rate of 8%. How much interest will he earn? What is his new Balance? 3.) I = ____ , P = $225, r = 3% , t = 2 years
4.) I = ____ , P = $1000, r = 6% , t = 3 months 5.) I = $300 , P = $1000, r = ___ , t = 5 years 6.) Sammie earned $204 in interest when she deposited $1,700 in a bank account for six years. What is her rate of interest?
7.)Emily deposits $7000 in an account that earns 7% simple interest. About how long will it take for her account balance to reach $8,000? 8.) Sarah deposits $4500 in an account. Four years later there is $5250 in the account. What was the simple interest rate she earned on the account?
9.) You get a summer job at a bakery. Suppose you save $1,400 of your pay and deposit it into an account that earns simple annual interest. After 9 months, the balance is $1,421. Find the annual interest rate.