Understanding Compound Interest in Mathematics
This detailed content explains the concept of compound interest in mathematics, covering key terms like moneylender, borrower, principal, rate, and amount. It also delves into simple interest, types of interest, and provides formulas for calculating compound interest based on different scenarios. Prepared by Ms. Bhanu Sachdeva, Assistant Professor at I.B. College, Panipat, this resource is beneficial for students studying finance and commerce.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ClassB.B.A-II semester Subject Mathematics Topic Compound Interest Prepared By Ms. Bhanu Sachdeva (Assistant Professor) Department of Commerce and Management I.B.(PG) College,Panipat (Affiliated to Kurukshetra University,Kurukshetra)
COMPOUND INTEREST COMPOUND INTEREST KEYWORDS: Moneylender Borrower Principal Rate Interest Amount
Explanation Explanation of keywords Moneylender: A moneylender is a person who lends money which has to be paid back at a high rate of interest. Borrower: A borrower is a person who gets money from someone with intension of giving it back after a period of time. Principal:The money borrowed by a borrower from a moneylender is called a principal.
EXPLANATION OF KEYWORDS EXPLANATION OF KEYWORDS Rate : The interest paid for the use of Rs. 100 is called rate percent. Interest: The extra amount paid by the borrower to the lender is called interest. Amount: The total money returned after a fixed time is a amount. Amount= Amount=Principal+Interest Principal+Interest. .
INTEREST Types of Interest Simple Interest Compound Interest
SIMPLE INTEREST Simple interest: When interest is calculated on the original principal for any length of time, it is called simple interest. FORMULA OF SIMPLE INTEREST Simple interest = Principal Time Rate/100 i.e. S.I. = (P R T)/100
COMPOUND INTEREST COMPOUND INTEREST Compound interest: The difference between original sum and final amount is called compound interest. FORMULA OF COMPOUND INTEREST C.I. = A-P
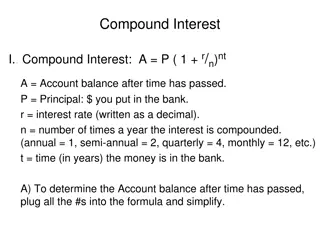
FORMULAS FORMULAS FOR FINDING AMOUNT Amount(A) = P(1+r/100)nWhere n is number of time period. Applicable when time is complete i.e 2years or 3years Amount (A)=P(1+r/100)i(1+fr/100)where i is an integer and f is a fraction. Applicable-when time is not complete i.e 2.5years or 3.5years Amount = P(1+r1/100)(1+r2/100)(1+r3/100) Applicable -when rate of interest is different for different years
Example based on first formula Example1. Find the compound interest on Rs.8000 for 4 years at 10% per annum. Solution: Here principal(p)=Rs.8000,Rate(r)=10%per annum, Time(t)=4 years Using the formula, A=P(1+r/100)nwe have A=8000(1+10/100) =8000(110/100) =Rs. 8000(11/10) =Rs. 8000x11/10x11/10x11/10x11/10 =Rs.11712.8 therefore compound interest (C.I)=A-P=Rs.(11712.8-8000) =Rs.3712.80
EXAMPLE BASED ON SECOND FORMULA EXAMPLE BASED ON SECOND FORMULA Example : A man deposits Rs.3200 in a finance company for 2.5 years at 10% per annum.Find the amount he received Solution: Here P=Rs.3200,r=10% per annum t=2.5years A=P(1+r/100)n(1+fr/100) =3200(1+10/100)2(1+1/2*10/100) =3200(110/100)2(1+5/100) =3200(11/10)2(105/100) =3200*11/10*11/10*21/20 =Rs.4065.6
Examle Examle based on third formula based on third formula Example-A man deposited Rs.5000 in a bank for three years. If he got compound interest at 4% for Istyear.3% for second year and 2% for third year. Find the amount he got at end of 3years. Solution:Here P = Rs.5000 r1 =4%,r2=3%,r3=3% Using A=P(1+r1/100)(1+r2/100)(1+r3/100) A=5000(1+4/100)(1+3/100)(1+2/100) A=5000x104/100*103/100*102/100 A=104*103*51/100=5463.12
THANK YOU THANK YOU