Effective Production Planning and Workflow for High-Performance Manufacturing
Production planning is crucial for organizing and structuring work efficiently to meet customer demand and ensure profitability. Key elements include scheduling resources, concurrent engineering, and using planning tools like flow charts and Gantt charts in lean manufacturing processes. Understanding plant capacity, design capacity, and bottlenecks helps optimize workflow and increase overall productivity.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
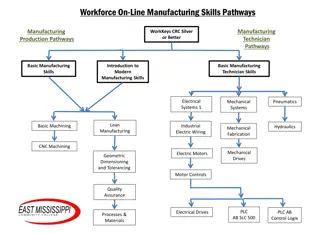
Unit 48.1 Production Planning and Workflow High-Performance Manufacturing Production Technician
PRODUCTION PLANNING Purpose of Planning Organize and structure work for effective performance and goal attainment. Set and balance priorities, anticipate obstacles, and formulate plans consistent with available human, financial, and physical resources. Production planning The process of analyzing and scheduling resources to best meet the needs of the customer and ensure profitability Meeting Customer Demand Identifying the customer s needs. Forecast, a projection of future demand for a product
PRODUCTION PLANNING Scheduling Resources Material Availability Tool and Equipment Availability Scheduling Labor Ensuring Safety Production plan includes operator training and safety training Key Elements Production Environments Materials Input Process Output Feedback
PRODUCTION PLANNING Concurrent Engineering A process that brings together people from different departments to develop the design and the process at the same time. It directly affects the production worker s job: Determine whether or not a job can be done Equipment needs are identified, reducing set-up times Identify potential problems Reduces the times needed to introduce a new product Encourages teamwork and communication
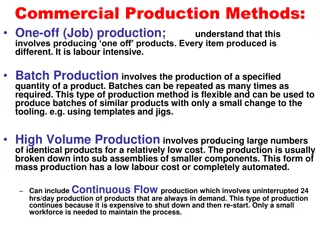
PRODUCTION PLANNING Product Life Cycle The change in demand for a particular product over time Planning Tools Flow Charts Visual representation of a process in a step-by-step format Gantt Charts Used to schedule and organize resources within a time frame Computerized Planning System Applying model systems to company s specific resources. Performs calculations designed to organize material, equipment, and personnel resources
Lean Manufacturing Four Principles Lean Management https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wfsRAZUnonI
WORK FLOW Moving Material Work flow is the movement of materials through the production process Plant Capacity Capacity of a process is the maximum rate at which inputs can be transformed to create outputs Design Capacity The target rate at which the facility is designed to operate Effective Capacity The rate of output under normal working conditions Actual Output The amount of production in a given period Bottlenecks Point at which the production rate restricts the flow of materials
WORK FLOW Arranging Facilities Facility Layout Arrangement of work areas, equipment, and departments Production Layout Moves large volumes of material in a sequence to produce standardized goods Process Layout Groups similar functions into work stations Fixed-Position Layout Used to produce very large, low-volume products
WORK FLOW Cellular Manufacturing A combination of process and product layouts. More flexible because machines can be moved into and out of cell. Team is responsible for all aspects of the product. They lend themselves to customization of standard products to meet specific customer needs Line Balancing Process of deciding how to assign groups of tasks to workstations Cycle Time Maximum time allowed for each workstation to complete its task Cycle Time Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WmAwcMNxGqM
WORK FLOW Production Scheduling The advantages: Shorter lead times for production Shorter production cycles Efficient use of equipment and labor Substantial cost savings Less lost time Reduced inventory costs
LEGO Exercise Round 1 - Assemble 3 Vehicles Total Quiet (No talking!) No Team Involvement Only Bin of Parts Assemble and measure time
LEGO Exercise Round 1 - Assemble 3 Vehicles Total Quiet (No talking!) No Team Involvement Only Bin of Parts Assemble and measure time Round 2 - Assemble 3 Vehicles Continuous Improvement Process (CIP) Job Rotation (optional) Team Involvement (anyone can build, subassembly OK) Visual and Standardized Work Set Goal on Time Assemble and measure time, compare to goal!
LEGO Exercise Round 3 - Assemble 3 Vehicles Continuous Improvement Process (CIP) Job Rotation (optional) Team Discussion, draw Layout including Part Introduction Create Job Instructions for each person Team Involvement (anyone can build, subassembly OK) Visual and Standardized Work Set Goal on Time Assemble and measure time, compare to goal!
Category: Manufacturing Process and Production Production Planning and Workflow Individual Work: Time: 1:00 Task: Logon and complete the assigned LAB
This course is 100% funded by the MoSTEMWINs $19.7 million grant from the U.S. Department of Labor, Employment and Training Administration (TAACCCT). The product was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This MoWINs product was created by North Central Missouri College and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License