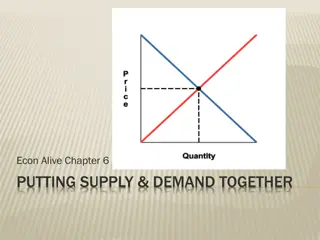
Demand and Supply in Economics
Demand and supply are core concepts in economics, driving the market economy. Demand reflects the desire for a product at different prices, with an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. Supply, on the other hand, represents what producers are willing to offer at various prices, with a positive correlation between price and quantity supplied. The laws of demand and supply govern these relationships, shaping the demand and supply curves that illustrate market dynamics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Demand Demand and Supply are most fundamental concepts of economics and it is the backbone of a market economy Demand refers to how much (quantity) of a product or service is desired by buyers. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product people are willing to buy at a certain price; The relationship between price and quantity demanded is known as the demand relationship
The Law of Demand The law of demand states that, if all other factors remain equal, the higher the price of a good, the less peoplewill demand thatgood Higher the price, the lowerthe quantitydemanded The slopeof Demand curve is downward
Supply Supplyrepresents how much the market can offer. The quantity supplied refers to the amount of a certain good producers are willing to supply when receiving a certain price. The correlation between price and how much of a good or service is supplied to the market is known as the supply relationship
The Law of Supply Like demonstrates the quantities that will be sold at a certain price The supplyrelationship showsan upward slope. This means that the higher the price, the higher the quantitysupplied. Producers supply more at a higher price because selling a higher quantity at a higher price increases revenue. the law of demand, the law of supply