Supply and Demand Dynamics in Economics
Explore the relationship between supply and demand in economics, focusing on concepts such as equilibrium price, changes in demand or supply, shifts in equilibrium price, and the impact on equilibrium quantity. Learn about shortages, surpluses, and how the market self-corrects to restore balance.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
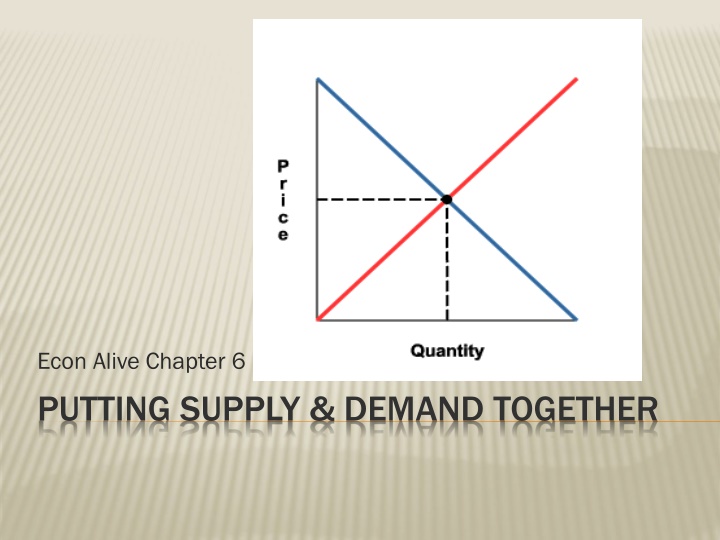
Econ Alive Chapter 6 PUTTING SUPPLY & DEMAND TOGETHER
EQUILIBRIUM PRICE Price at which Quantity Demanded and Quantity Supplied are equal In the real world, Demand and Supply work together
CHANGES IN DEMAND OR SUPPLY DEMAND AND SUPPLY CAN STILL CHANGE! CHANGES IN DEMAND CHANGES IN SUPPLY Key Words: Buyers/Consumers Determinants: Population Income of Consumers Change in Consumer Tastes Price of Substitutes Price of Complementary Goods Consumer Expectations Key Words: Sellers/Suppliers/ Producers/Manufacturers Determinants: Price of Inputs # of Firms in the Industry Business Taxes/Government Policy Technology Producer Expectations Natural Disaster/Major Event
SHIFTS IN EQUILIBRIUM PRICE When Demand or Supply changes, Equilibrium price changes
Increases Equilibrium Price & Quantity INCREASE IN DEMAND INCREASE IN DEMAND
Decrease in Equilibrium Price and Quantity DECREASE IN DEMAND DECREASE IN DEMAND
Increases Equilibrium Price Decreases Equilibrium Quantity WHEN SUPPLY DECREASES WHEN SUPPLY DECREASES
Equilibrium Price Decreases Equilibrium Quantity Increases WHEN SUPPLY INCREASES WHEN SUPPLY INCREASES
SHORTAGE Situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied
SURPLUS Situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
USE THE FORCE! (OF THE MARKET) We don t like shortages or surpluses! The market wants to correct itself and adjust the price to get back to equilibrium!
PRICE CONTROLS Government gets involved To help consumers? Protect interest groups? Creates: Price Ceilings Price Floors
PRICE CEILING Legal maximum price that may be charged for a good or services Often creates shortages
PRICE FLOOR Legal Minimum price that may be charged for a good or service Often creates surpluses