Biological Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Coenzymes
Explore the fascinating world of biological oxidation-reduction reactions catalyzed by oxidoreductases. Coenzymes play a crucial role in these processes, facilitating the transfer of hydrogen atoms. NAD+ is a well-known coenzyme involved in accepting and donating hydrogen. Witness the oxidation of ethanol and learn about key compounds like Coenzyme A, garlic, and resveratrol. Dive into the mechanism of oxidation in living systems, converting C6H12O6 and O2 into CO2, H2O, and energy. Delve into the significance of dihydroxyacetone in biochemical pathways.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
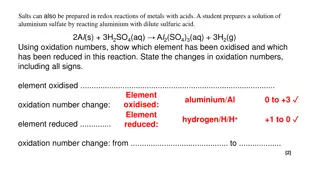
Biological Oxidation-Reduction Oxidoreductases catalyze biological redox reactions Coenzymes (organic molecules) are required to donate or accept hydrogen NAD+is a common coenzyme COO- H CH2 COO- + NAD+ 12.6 Oxidation and Reduction in Living Systems COO- H O C Malate dehydrogenase C CH2 COO- O + NADH + H+
Oxidation C6H12O6 + O2 ? CO2 + ?H2O + energy