The Intricate Pathways of Choline Synthesis and Oxidation in Molecular Biology
Delve into the complex processes of choline synthesis and oxidation pathways, involving the integration of hydride ions and various molecules, essential for the production of phosphatidylcholine and other crucial compounds in biological systems. Learn about the enzymes and mechanisms that drive the de novo synthesis of choline, ethanolamine phosphate, and phosphatidylcholine, as well as the oxidation of choline through intricate pathways in molecular biology, highlighting the significance of these processes in cellular function and energy production.
Uploaded on Sep 14, 2024 | 4 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
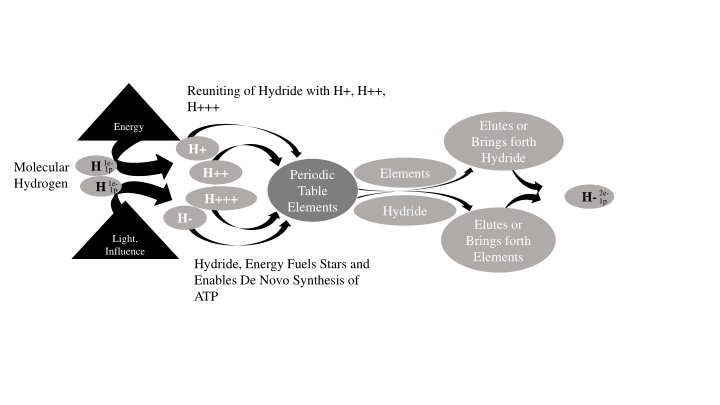
Reuniting of Hydride with H+, H++, H+++ Elutes or Brings forth Hydride Energy H+ H 1e- 1p Molecular Hydrogen H++ Elements Periodic Table Elements H 1e- 1p H-2e- H+++ 1p Hydride H- Elutes or Brings forth Elements Light, Influence Hydride, Energy Fuels Stars and Enables De Novo Synthesis of ATP
Hydride integrated as the most negatively polarized Hydrogen in CH3, and CH3 integrated into the Choline Molecule and its paired balancing atom, along with exhibition of Choline in Phosphatidylcholine. CH3 H 1e- 1p CH3 N+ X- H-2e- C 1p CH3 H 1e- 1p H-2e- 1p
De Novo Synthesis of PMME to PDME to Choline as Phosphatidylcholine from Phosphatidylethanolamine Also, De Novo Synthesis of Ethanolamine Phosphate by S1P Lyase Phosphatidyl Serine (PS) Synthase to PS Decarboxylase Pathway CH3 CH3 N+ X- CDP-Ethanolamine Pathway CH3 N+ CH3 PC Newly Synthesized phosphatidyl ethanolamine CH3 N+ S1P Lyase/Hexadecenal De Novo Ethanolamine Phosphate Synthesis, prevents Signaling (Inflammatory G Protein, inflammatory Survival, Detrimental Eicosanoids) CH3 PDME N+ PMME CH3 Phosphatidylethanolamine Methyltransferase Enzymes 1, 2, 3 Methyl Carrier or Thetin CH3 Methyl Carrier or Thetin CH3 Methyl Carrier or Thetin
De Novo Synthesis of Choline and Oxidation of Choline with the Choline Oxidation Pathway Choline Oxidation Pathway CH3 Betaine, N,N,N-Glycine Betaine, Trimethylglycine CH3 N+ X- CH3 Betaine Aldehyde
De Novo Synthesis of Choline and Oxidation of Choline with the Choline Oxidation Pathway Free Fatty Acid Noninflammatory/Inflammatory Phospholipase, Diesterase and TATA Boxless Calcium Independent iPLA2 Arachidonate Free Phosphatides Membrane phospholipids Lysophosphatidylcholine DHA/EPA/Omeg-3, Palmitoylate (first fatty acid in Fatty Acid beta oxidation), Oleoyl, and Ether Linked Fatty Acid Shuffling Reintegration of Free Fatty Acid, Phosphatides MBOAT/ LPCAT Reintegration of Free Fatty Acid, Arachidonate, Phosphatides Phosphatidylcholine Synthesis form Lyusophosphatidylcholine
Choline Deficiency = Choline Dysbiosis, not necessarily a Deficiency Inhibition or Impairment of Phosphatidyl Ethanolamine Methyltransferase Inducible Nitric Oxide Expression Expression P53 inhibition of Sugar Absorption GLUT 1/3/4, Insulin Receptor, Phosphofrucktokinase Upregulation of P53 Upregulation of Homocysteine P53 inhibition of Glycolysis and Pentose Phosphate Pathway, impairing DNA/RNA/NADPH, Sugar Depletion, Reactive Oxygen Species Depletion Inhibited Glycolysis deprives Choline Acetyltransferase of Acetyl-CoA, impairing Acetylcholine Synthesis, increases Free Choline, decreases Acetylcholine Synthesis, inverts polarity of Neuron Action Potential, causes NKCC1 to KCC2 Switch Primary Choline Transporters are Sodium Coupled, and all transporters can be occupied by particulate factors or competing molecules or inflammation Eating uses digestive juices, depleting many grams of Phosphatidylcholine, such that without 800 mg a day minimum of choline ingestion/Synthesis, Eating causes net depletion of Choline Free Choline becomes metabolized by Choline Kinase, upregulating CDP- Choline Pathway, produces Phosphocholine feed forward pathogen, pathology and inflammatory signaling factor Phospholipases and Diesterases Catabolize Cellular Membranes free Choline and Fatty Acids, mimicking Choline Availability Trimethylamine-N- Oxide and less than optimal digestive pathway microflora, as well as inflammation by TNF Alpha, impair absorption of Choline
Coronavirus, Covid 50 or More Factors 20 or More Factors S-Adenosyl Homocysteine and Homocysteine increased by almost every drug/therapeutic, toxin, atmospheric particulate, environmental particulate, Choline Deficiency, iNOS, diseases generally, age, detrimental behavioral potential, and any of 50, 20 or 12 factors Conscious Function, Prevention of Disease, alleviation of disease, pioneering development, regenerative development 12 or more factors Potentially inhibit PEMT Inadequate Choline, Hydride, CH3, PEMT Function, Enriched Phosphatidylcholine, and Lands Cycle Fatty Acid Shuffling, S1P Lyase. Upregulated S-Adenosyl Homocysteine, Homocysteine, iNOS, uNOS, Trimethylamine-N-Oxide, AP1, SP1, C Reactive Protein, MCP1, Choline Kinase, S1P, IDO, Nitrosamine, Methylglyoxal, Oxalate, D/L Lactate/Lactic Acid iNOS upregulated by Electromagnetic/Electricity Infrastructure/Influence, Wifi Networks, Wireless Communications and Protocols, Mobile devices, Electronics, , Email, Atmospheric/Environment Particulate, Choline Inadequacy, Some Therapeutics, Chlorine/Flourine Water, Every Virus, Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide, restraint, Enriched PC CH3 Pathway Pervasively Included in abated vital being, disease, detrimental behavior 50 or More Factors 20 or More Factors CH3 N+ X- PDME CH3 12 or more factors Potentially inhibit PEMT Inadequate Choline, Hydride, CH3, PEMT Function, Enriched Phosphatidylcholine, and Lands Cycle Fatty Acid Shuffling, S1P Lyase. Upregulated S-Adenosyl Homocysteine, Homocysteine, iNOS, uNOS, Trimethylamine-N-Oxide, AP1, SP1, C Reactive Protein, MCP1, Choline Kinase, S1P, IDO, Nitrosamine, Methylglyoxal, Oxalate, D/L Lactate/Lactic Acid NAD+ NADH S-Adenosyl Homocysteine Homocysteine Homocysteic Acid CH3 CH3 N+ PMME CH3 CH3 Hydride H-2e- H 1e- 1p PEMT Inhibition CH3 1p N+ H-2e- C CH3 PEMT 1p Phosphatidylethanolamine Methyltransferase Enzymes 1, 2, and 3 CH3 1e- 1p H
Primary inhibitors of Phosphatidylethanolamine Methyl transferase are the Primary ways that any disease, persistent impairment, behavioral health statuses, detrimental aspects of aging and Detrimental Human Behavior, all uses to emerge, persist, progress, impart detriment and elude physiological prevention/repair capabilities. PEMT impairing Factor Decrease in Disease, impairment, adverse health events and adverse behavior Natural management Pharmacological Management S-Adenosyl Homocysteine at 0.0012 Micromoles per liter or Higher. Homocysteine Aggregate at 7 Micromoles Per Liter or Higher. 99.99 percent or decrease from 500 per 10,000 study participants per decade to 1 per 10,000 study participants per decade Choline 800 mg/day minimum, 4/7 mg per kg of mass each day. Dimethylacetothetin, Red Sage/Danshen/Salvia M all with B6, Choline, Phosphatidylcholine, Methylsulfonyl Methane with Molybdenum, S - Methylmethionine Sulfonium with Zinc and 6s 5678 Tetrahydrofolate, Trimethylglycine with Zinc and 6s 5678 Tetrahydrofolate, Folic Acid with B12, Vitamin B6, Dimethyl Sulfide, Trimethylsulfonium, NAD+ to assist S- Adenosyl Homocysteine Hydrolase activity, and diatomic metal cations which are utilized in PEMT and other enzyme catalysis, Alpha GPC, Lysophsophatidylcholine, Glutathione, Cystathionine, Phosphatidylcholine. Depleters of Homocysteine Choline Deficiency, Nutritional 33 percent decrease in adverse outcomes unless correlated with elevated Homocysteine, then being a 99.98+ decrease in adverse outcomes Choline dense or enriched foods. Nutritional Choline at 800 mg/day or 4/7 mg per kg of mass. Management of Homocysteine and other inhibitors of PEMT. Supplemental Choline, Managing inhibitors of PEMT and enhancing Choline Pathway.. CRISPR GENE Repair Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase 67 percent decrease in detrimental outcomes Curcumin, Irinotecan, other, EMF protection for Homes, communications, phones, electrical infrastructure, wireless Networks, Devices, Wireless Devices, etc. Filtered water without Chlorine/Fluorine/Particulates, Atmospheric cleansing devoid of toxic particulates iNOS inhibitors that inhibit iNOS at the transcription level.
Primary inhibitors of Phosphatidylethanolamine Methyl transferase are the Primary ways that any disease, persistent impairment, behavioral health statuses, detrimental aspects of aging and Detrimental Human Behavior, all use to emerge, persist, progress, impart detriment and elude physiological prevention/repair capabilities. PEMT impairing Factor Decrease in Disease, impairment, adverse health events and adverse behavior Natural management Pharmacological Management SP1 33 percent decrease in adverse outcomes Curcumin SP1 inhibitors AP1 33 percent decrease in detrimental outcomes Berberine AP1 inhibitors C-Reactive Protein 88 percent decrease in adverse outcomes Curcumin C-Reactive Protein Inhibitors Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 33 Percent Decrease in Adverse Outcomes Grapeseed Extract 33 DMB Nitrosamine 33 Percent Decrease in Adverse Outcomes Garcinia Kola Seed extract Kolaviron
Primary inhibitors of Phosphatidylethanolamine Methyl transferase are the Primary ways that any disease, persistent impairment, behavioral health statuses, detrimental aspects of aging and Detrimental Human Behavior, all use to emerge, persist, progress, impart detriment and elude physiological prevention/repair capabilities. PEMT impairing Factor Decrease in Disease, impairment, adverse health events and adverse behavior Natural management Pharmacological Management Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase. 33 Percent Decrease in Adverse Outcomes with Curcumin, Irinotecan, or other iNOS inhibitors. Using EMF protection stickers, blankets, clothing, coverings, material, curtains, etc. Covering electrical power outlets. Turning of wireless networks, communications and other devices. Removing personal information, locations, telemetry services, names, communication information, addresses, etc from internet connected systems and from systems not connected to internet. Avoiding Restraint. Using Filtered water without Chlorine, Fluorine, Nitrosamine, or toxic factors. Avoid extreme low frequency sound and magnetic fields. Obtain 800 mg+ or Between 7 and 4 mg of Choline each day. Coat communcations and electrical infrastructure in environment and dwellings. Improve atmospheric population or particulate factors. iNOS inhibitors Uncoupled Nitric Oxide Synthase 33 percent decrease in adverse outcomes Uncoupled NOS is managed with L-Arginine, Ca2+(sometimes atypically), Tetrahydrobiopterin, Superoxide Dismutase, Catalase, N-Acetyl L Cysteine, Vitamin. Sapropterin, Calcium, Iron. 33 percent decrease in adverse outcomes Grapeseed Extract, Olive Oil, 33DMB, Pro/Pre/Post Biotic, Broad Spectrum Antibiotic, all manage Trimethylamine-N-Oxide while management of Trimethylamine-N-Oxide is the only way known to improve Carotid Intima Media Thickness other than mechanical intervention. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide
Primary inhibitors of Phosphatidylethanolamine Methyl transferase are the Primary ways that any disease, persistent impairment, behavioral health statuses, detrimental aspects of aging and Detrimental Human Behavior, all use to emerge, persist, progress, impart detriment and elude physiological prevention/repair capabilities. PEMT impairing Factor Decrease in Disease, impairment, adverse health events and adverse behavior Natural management Pharmacological Management Red Sage or Danshen, while other natural inhibitors abound. IDO Inhibitors IDO or Indoleamine 2,3 Dioxygenase Water, N Acetyl L Cysteine, L-Arginine, and Magnesium as well as Potassium, typically as Chloride version of the Metals, can be utilized to manage. Kidney Stuff by Golden Standards. Improvement Renal Function and Hepatic Function Methylglyoxal and Oxalate manage Methylglyoxal, Homocysteine, Oxalate, S-Adenosyl Homocysteine, Trimethylamine-N-Oxide, Uncoupled NOS, and iNOS, including managing Choline availability to prevent these from becoming factors. Ringer's Solution and Methylene Blue, D Lactate/Lactic Acid and L Lactate/Lactic Acid