Atoms and Molecules: Basics and Models
Explore the world of atoms and molecules with a focus on distinguishing between them, understanding atomic structures through historic models like Bohr and Rutherford, and the modern atomic model. Discover how atoms form the basis of all matter and how they are organized within molecules.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Atoms and Molecules S8P1.a. Distinguish between atoms and molecules.
Matter Matter is anything that occupies space. All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are the building blocks of matter.
Atoms, Molecules and Elements
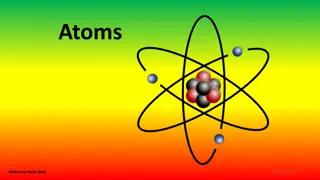
Atomic Models This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels.
Atomic Models A model uses familiar ideas to explain unfamiliar facts observed in nature. A model can be changed as new information is collected.
Ernest Rutherford In 1908, the English physicist Ernest Rutherford began to unravel the mysteries of the atomic structure. Through his experiments he discovered that atoms were mostly open space.
Ernest Rutherford Rutherford concluded that an atom had a small, dense, positively charged center. He called the center of the atom the nucleus The nucleus is tiny compared to the atom as a whole.
Bohr Model In 1913, the Danish scientist Niels Bohr proposed an improvement. In his model, he placed each electron in a specific energy level.
Bohr Model According to Bohr s atomic model, electrons move in definite orbits around the nucleus, much like planets circle the sun. These orbits, or energy levels, are located at certain distances from the nucleus.
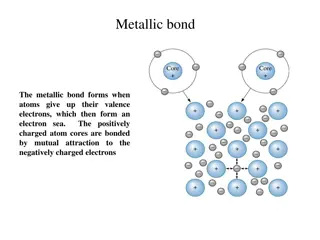
Todays Atomic Model According to the modern atomic model, an atom has a small positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which there are enough electrons to make an atom neutral.
Electron Cloud A space in which electrons are likely to be found. Electrons whirl about the nucleus billions of times in one second They are not moving around in random patterns. Location of electrons depends upon how much energy the electron has.
Electron Cloud Depending on their energy they are locked into a certain area in the cloud. Electrons with the lowest energy are found in the energy level closest to the nucleus Electrons with the highest energy are found in the outermost energy levels, farther from the nucleus.
Atomic - Molecular Theory of Matter The Atomic - Molecular Theory of Matter states that all matter is composed of small, fast moving particles called atoms. These atoms can join together to form molecules.
Atomic Structure Nucleus - the central portion of the atom. Contains the protons and neutrons.
Electron Cloud - area around the nucleus where electrons are found. Electrons are arranged within the electron cloud in energy levels. (Energy levels are sometimes called shells or orbits). Atomic Structure
Subatomic Particles Proton - positive charged particle found in the nucleus. Neutron - particle with no charge. Found in the nucleus. Electron - negative charged particle found within the electron cloud
Valence Electrons In an atom, valance electrons can be found in the outermost electron shell. They are the main point of interaction between one atom and another, and are very important for the formation of molecules.
Molecules A molecule is the smallest particle of a pure chemical substance that still retains its composition and properties. Molecules are made of two or more atoms.
Making molecules with atoms